Forex Trading for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Currency Market Success
The forex trading market stands as the largest financial marketplace worldwide, with an impressive daily trading volume of approximately $7.5 trillion—outpacing all other financial markets combined. The United States alone holds a commanding 40 percent share of global forex activity, with North America generating over $323 billion in forex market revenue each year. This dominance reflects the U.S. dollar’s unrivaled status as the world’s primary reserve currency, involved in approximately 88 percent of all currency transactions.
The domestic forex trading community has undergone remarkable expansion, with 335,000 active traders now participating in currency markets nationwide. Recent data show trading volumes surging 17.2 percent year-over-year and retail trader participation rebounding 11 percent after three consecutive years of decline. This resurgence signals a profound shift in financial consciousness, particularly among millennials and Generation Z, who increasingly view currency trading as a pathway to long-term independence.
Technological innovation has democratized market access through commission-free forex trading platforms, intuitive mobile applications, and AI-driven market insights. Where banks once imposed opaque pricing and substantial minimum deposits, fintech firms now offer transparent spreads, fractional lot sizing, and demo accounts funded with virtual capital. This level of sophistication aligns perfectly with younger traders’ preference for flexibility, real-time data, and on-the-go decision making.
Educational accessibility further empowers new entrants via free online courses, interactive forex trading simulators, and university-certified programs that allow participants to master complex concepts at their own pace. The trader demographic skews 91.5 percent male, with 61 percent holding bachelor’s degrees, and spans age groups from early-career professionals to seasoned experts—demonstrating the market’s broad appeal across different life stages.
All participants benefit from world-class regulatory protections enforced by the CFTC and NFA, tier-1 regulators that uphold stringent capital requirements and robust client-fund safeguards under the Dodd-Frank Act. The convergence of advanced technology, rigorous oversight, accessible education, and diverse trader profiles positions U.S. currency markets uniquely for sustained growth, offering prepared traders ample opportunity to build meaningful wealth through disciplined forex expertise.
Understanding the Forex Market Landscape
What Makes Forex Trading Unique
Foreign exchange trading represents the ultimate expression of global commerce, where participants simultaneously purchase one currency while selling another, creating the currency pairs that serve as the fundamental building blocks of all forex transactions. This elegant mechanism enables traders to profit from the perpetual fluctuations in relative currency values, driven by the complex interplay of economic fundamentals, monetary policy decisions, and geopolitical developments across the globe.
Unlike traditional stock markets that operate through centralized exchanges with physical locations, forex functions as a sophisticated decentralized over-the-counter network spanning the globe, operating continuously 24 hours daily across five trading days. This revolutionary structure eliminates the constraints of centralized trading floors, instead connecting participants through advanced electronic communication networks that facilitate instantaneous price discovery and trade execution across multiple time zones.
The market’s extraordinary liquidity—exceeding $7.5 trillion in average daily volume—stems from an intricate ecosystem of diverse participants, each bringing distinct motivations, resources, and forex trading capabilities. Institutional traders, including central banks, commercial banks, hedge funds, and multinational corporations, command substantial market influence through their massive transaction volumes and sophisticated analytical capabilities. These institutional players often execute trades worth hundreds of millions of dollars, utilizing advanced algorithmic systems and privileged access to market data that enables them to move currency prices significantly.
Retail traders—individual investors like yourself—contribute essential market liquidity and bring unique perspectives that can sometimes challenge institutional dominance. While retail traders typically operate with smaller position sizes, their collective actions can create meaningful market movements, particularly during periods of coordinated buying or selling pressure. Recent technological advances have democratized market access, providing retail traders with institutional-grade tools, real-time data feeds, and sophisticated analytical platforms that were previously exclusive to professional forex trading desks.
This dynamic ecosystem creates continuous opportunities for profit through currency price fluctuations driven by economic indicators, central bank policy announcements, geopolitical events, and evolving market sentiment. The constant flow of global news, economic releases, and political developments ensures that currency values remain in perpetual motion, providing astute traders with regular opportunities to capitalize on correctly anticipated price movements.
Market Sessions and Timing for Traders in the USA
Forex trading operates across four major sessions, each offering distinct characteristics for traders:
New York Session (8:00 AM – 5:00 PM EST): Peak activity for USD pairs with highest volatility during market opens and economic releases.
London Session (3:00 AM – 12:00 PM EST): Overlaps with New York session from 8:00 AM – 12:00 PM EST, creating maximum liquidity and forex trading opportunities.
Tokyo Session (7:00 PM – 4:00 AM EST): Lower volatility but important for Asian currency pairs, especially USD/JPY.
Sydney Session (3:00 PM – 12:00 AM EST): Quieter session but relevant for commodity currencies like AUD/USD.
The Power of Session Overlaps
Traders achieve maximum advantage during the London-New York overlap (8:00 AM – 12:00 PM EST), when both major financial centers operate simultaneously. This four-hour window accounts for only 19% of the trading day yet captures an astounding 37% of total daily forex volume. The overlap period delivers unparalleled liquidity and volatility, with some currency pairs experiencing even higher concentration:
- USD/CAD: 45% of daily volume
- EUR/USD: 41% of daily volume
- GBP/USD: 38% of daily volume
- AUD/USD: 34% of daily volume
Peak forex trading intensity occurs between 8:30 AM – 9:00 AM EST, when 7 percent of the entire daily volume enters the market within just 30 minutes. This extraordinary concentration stems from simultaneous European and U.S. trader activity, combined with critical economic releases that often occur during the early overlap hours.
The overlap period delivers several strategic advantages: tightest bid-ask spreads, maximum price-movement potential, highest execution quality, and greatest depth of liquidity. Professional traders typically structure their schedules around these peak hours, recognizing that the confluence of European and North American market participation creates optimal conditions for significant profit opportunities while minimizing execution risk through enhanced liquidity.
Understanding these session dynamics enables traders to align strategies with market rhythms, concentrating intensive efforts during high-opportunity periods and adopting more conservative approaches during quieter Asian sessions. This strategic timing approach helps maximize profit potential while optimizing the time investment required for forex trading activities.
Major Currency Pairs Every Trader Should Know
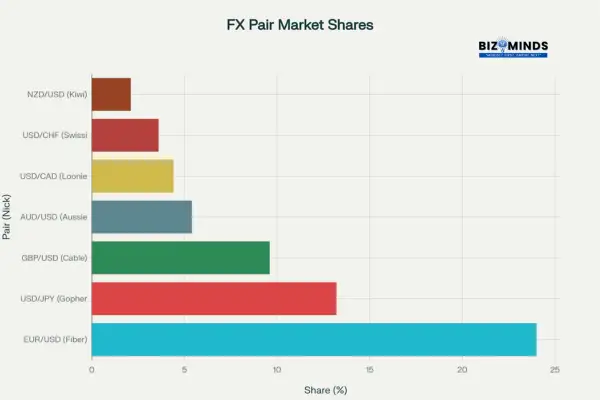
Major Currency Pairs Market Share in Global Forex Trading
The seven major currency pairs dominate global forex trading, all featuring the US dollar paired with other major economies’ currencies. These pairs offer optimal conditions for beginners due to high liquidity, tight spreads, and predictable price movements.
The EUR/USD (Fiber) is the most actively traded currency pair in the forex market, making up about 24% of the total global forex trading volume. This pair reflects economic dynamics between the European Union and United States, making it ideal for fundamental analysis based on Federal Reserve and European Central Bank policies.
USD/JPY (Gopher) holds a 13.2% share of the forex market and acts as a key indicator for gauging risk sentiment among traders. The Japanese yen’s safe-haven status creates predictable patterns during economic uncertainty, while Bank of Japan interventions provide clear technical signals.
GBP/USD (Cable) exhibits higher volatility than other majors, offering greater profit potential alongside increased risk. Brexit-related developments and Bank of England decisions significantly impact this pair’s movements.
Traders often prefer USD/CAD (Loonie) because of the close geographic ties between the US and Canada, as well as the pair’s strong correlation with oil prices. Recent data shows USD/CAD experiencing substantial volume increases of $26.0 billion in recent surveys, highlighting growing interest.
Essential Forex Trading Concepts and Terminology
Understanding Pips, Spreads, and Position Sizing
PIPS
A pip, short for “percentage in point,” is the smallest standardized unit of price movement in a forex quote, usually found at the fourth decimal place (0.0001). For example, if the EUR/USD pair moves from 1.2000 to 1.2001, that one-pip change on a standard lot (100,000 units) corresponds to a $10 gain or loss. In forex trading, a mini lot equals 10,000 units where each pip movement typically equals $1, while a micro lot represents 1,000 units with each pip worth $0.10. Understanding pip values helps traders convert market fluctuations into precise dollar amounts, enabling effective risk management in forex trading.
SPREADS
The spread is the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) prices quoted by your broker. Regulated U.S. brokers often offer razor-thin spreads of 1–3 pips on major pairs such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY, whereas exotic pairs (e.g., USD/TRY or USD/SEK) can widen to 10–50 pips. If EUR/USD has a bid of 1.2000 and an ask of 1.2003, you pay a 3-pip cost immediately upon entering a trade—meaning the pair must move at least 3 pips in your favor just to break even.
POSITION SIZING
Position sizing defines the amount of capital you allocate to a single trade, playing a crucial role in managing risk and optimizing your trading outcomes. To protect your account from large swings, beginners should start with micro lots and risk only 1–2% of their forex trading capital per position. For instance, with a $5,000 account, risking 1% means a maximum $50 loss per trade. If your stop-loss is set 25 pips away, you would trade 0.2 mini lots (2 micro lots), because 25 pips × $1 per pip × 2 mini-lot units = $50 risk.
Leverage and Margin Considerations
In the U.S., retail forex leverage is capped at 50:1 for major currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD) and 20:1 for minors (e.g., EUR/GBP) under CFTC/NFA regulations. Leverage magnifies both potential profits and losses; for instance, a 50:1 leverage ratio allows you to control $50,000 in currency with only $1,000 of your own capital. However, if the market moves 2% against you, that same $1,000 deposit could be wiped out completely.
Margin refers to the collateral you must maintain to keep positions open. If you open a standard-lot EUR/USD position at 50:1 leverage, you need $2,000 in margin (100,000 ÷ 50). The amount of usable (free) margin is what remains after subtracting the required margin from the account balance. If your trades move adversely and your free margin falls too low, you may receive a margin call—a broker’s demand to deposit more funds or close positions to limit risk.
Conservative forex traders focus on risk per trade rather than maximum leverage. By risking only 1–2% of account equity on any single trade—and using appropriate lot sizes and stop-loss orders—you can endure periods of drawdown while preserving capital for the long term
Choosing the Right Broker for Forex Trading
Regulatory Requirements and Safety
In the United States, every retail forex broker must be registered with both the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA). These regulatory bodies enforce rigorous oversight, including mandatory $20 million minimum net capital for Forex Dealer Members (FDMs) and regular financial audits. This framework ensures brokers maintain sufficient reserves to honor client withdrawals and protects you from counterparty default. Additionally, segregated client fund requirements and membership in the NFA’s Customer Protection Fund further bolster safety, offering up to $500,000 in coverage per account for qualifying losses.
Top-Rated Forex Brokers
A review of market reputation, regulatory standing, platform quality, and client feedback highlights the following top-rated brokers:
- OANDA: Honored as “Broker of the Year” by TradingView, OANDA offers access to 68 currency pairs, tight spreads starting at 0.1 pip on majors, and an award-winning educational suite—including live webinars and proprietary research.
- FOREX.com: A household name, FOREX.com provides robust forex trading tools such as Advanced Charting, Market Insights, and customizable API integrations, along with 24/5 research from in-house analysts.
- tastyfx (formerly IG): Ideal for novices, tastyfx features an intuitive web and mobile interface, real-time educational videos, and a demo account preloaded with $100,000 in virtual funds for risk-free practice.
- Interactive Brokers: Catering to seasoned traders, IBKR delivers institutional-grade platforms, ultra-low tiered commissions starting at 0.2 basis points, and advanced order types like Guaranteed Stop Loss Orders for precise risk management.
- Charles Schwab: Combining comprehensive banking services with a dedicated forex desk, Schwab supports multi-asset portfolio integration, 24/5 customer support, and zero-commission forex trading on certain account tiers.
Key Selection Criteria
When evaluating brokers, forex traders should prioritize:
- Regulatory compliance: Verify active CFTC and NFA registrations
- Spreads and commissions: Compare total trading costs across preferred pairs
- Platform quality: Ensure compatibility with analytical tools and order types
- Educational resources include access to market analysis, informative webinars, and comprehensive learning materials to support your forex trading journey
- Customer support: 24/5 availability during market hours
- Funding options: Convenient deposit/withdrawal methods with reasonable processing times
Risk Management: The Foundation of Successful Forex Trading
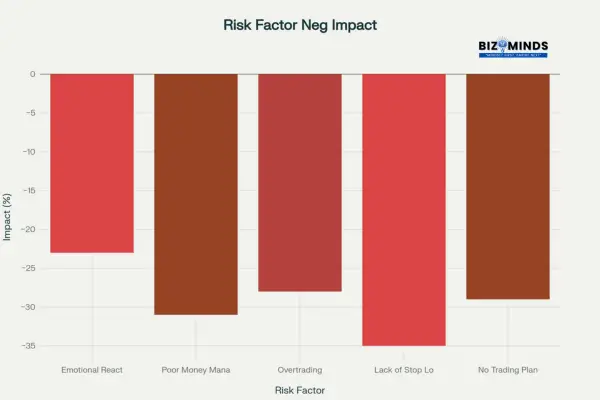
Common Risk Factors and Their Impact on Forex Trading Performance
Effective risk management distinguishes successful traders from those who lose capital quickly. Academic research consistently demonstrates that emotional reactivity and poor risk management create the most significant performance drains.
Position Sizing and the 1% Rule
Never risk more than 1-2% of total account capital on any single trade. For a $10,000 account, maximum risk per trade should not exceed $100-200. This approach allows for extended losing streaks without account devastation.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss orders automatically close positions when prices move against you, limiting maximum loss per trade. Set stops based on technical levels, not arbitrary percentages, typically 20-50 pips for major pairs depending on timeframe and volatility.
Take-profit orders automatically secure your gains by closing a trade once your set price target is achieved. Maintain minimum 1:2 risk-reward ratios, meaning if you risk $100, target at least $200 profit.
Money Management Rules for American Traders
Implement systematic approaches to capital preservation:
- Maximum daily loss limits: Stop forex trading if daily losses exceed 2-3% of account value
- Position correlation: Avoid multiple positions in highly correlated pairs (EUR/USD and GBP/USD often move together)
- Leverage discipline: Use minimal leverage until consistently profitable
- Emergency fund: Maintain separate savings for living expenses, never trade money you cannot afford to lose
Fundamental Analysis for Currency Markets
Economic Indicators Impact on USD Pairs
American traders possess advantages when analyzing USD-based pairs due to familiarity with domestic economic indicators. Key reports affecting dollar strength include:
Federal Reserve Policy: Interest rate decisions and FOMC statements significantly influence USD value across all major pairs. Rising US rates typically strengthen the dollar as international investors seek higher yields.
Employment Data: Monthly Non-Farm Payrolls and unemployment reports directly impact Federal Reserve policy expectations. Strong employment data often leads to dollar appreciation.
Inflation Metrics: Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) influence Fed policy direction. Higher inflation may prompt rate increases, strengthening the dollar.
GDP Growth: Quarterly gross domestic product figures reflect overall economic health, influencing long-term currency trends.
Economic Calendar Usage
Successful traders monitor economic calendars showing scheduled releases with expected market impact ratings. High-impact events often create volatility spikes, offering opportunities for prepared traders while creating risks for the unprepared.
Technical Analysis Fundamentals
Chart Types and Timeframes
The candlestick charts offer detailed price data by displaying the open, high, low, and close values for each time period, helping traders analyze market trends effectively. Traders typically focus on daily, 4-hour, and 1-hour timeframes for swing trading, while day traders utilize 15-minute and 5-minute charts.
Essential Technical Indicators
Moving Averages: Simple and exponential moving averages identify trend direction and potential support/resistance levels. The 50-period and 200-period moving averages are widely used indicators to identify and analyze long-term market trends.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Momentum oscillator measuring overbought/oversold conditions, typically using 70/30 levels for signals.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Trend-following indicator showing relationship between two moving averages, useful for identifying momentum changes.
Support and Resistance: Horizontal price levels where currency pairs historically reversed direction, providing logical entry and exit points.
Multiple Timeframe Analysis
Professional traders synchronize signals across multiple timeframes. For example, identify trend direction on daily charts, then use 4-hour charts for entry timing and 1-hour charts for precise execution points.
Forex Trading Psychology and Emotional Management
Academic research reveals that emotional reactivity negatively correlates with forex trading performance. Traders exhibiting intense reactions to both gains and losses demonstrate significantly worse results than emotionally stable counterparts.
Common Psychological Challenges
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) often drives traders to make impulsive decisions without conducting proper analysis. Remedy this by maintaining watchlists and waiting for confirmed setups.
Revenge Trading: Attempting to recover losses through larger, riskier positions. This destructive pattern often compounds losses exponentially.
Overconfidence: Early success can breed excessive risk-taking. Maintain consistent position sizing regardless of recent performance.
Building Mental Discipline
Forex Trading Journals: Record every trade including entry/exit reasons, emotions, and lessons learned. Regular review identifies patterns and improvement areas.
Systematic Approaches: Develop specific criteria for trade entry, management, and exit. Eliminate discretionary decisions during emotional moments.
Realistic Expectations: Understand that professional traders often maintain 60-70% win rates while generating profits through superior risk management.
Creating Your Forex Trading Plan
Plan Components
Forex Trading Goals: Define specific, measurable objectives such as monthly return targets and maximum drawdown limits. Realistic goals for beginners include 2-5% monthly returns with maximum 10% drawdowns.
Risk Parameters: Establish position sizing rules, maximum daily loss limits, and correlation restrictions. Document these rules and review them before each trading session.
Strategy Selection: Choose 1-2 primary strategies matching your schedule and risk tolerance. Master these approaches before exploring additional methods.
Strategy Development Process
Demo Trading: Practice strategies for minimum 2-3 months using demo accounts with realistic position sizes. Many brokers offer $10,000 virtual accounts for risk-free practice.
Forward Testing: After demo success, begin live forex trading with minimal position sizes. Increase your position sizes gradually, but only after you’ve shown consistent profits to manage risk effectively.
Performance Review: Conduct weekly analysis of trading results, identifying strengths and weaknesses. Adjust strategies based on data, not emotions.
Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
Overtrading and Overleverage
Excessive Forex Trading Frequency: New traders often feel compelled to constantly trade, leading to poor decision-making and increased costs. Quality setups require patience; profitable traders often execute just 2-5 trades weekly.
Inappropriate Leverage: Using maximum available leverage multiplies both gains and losses. Conservative leverage of 10:1 or less allows for learning without catastrophic risk.
Educational and Preparation Shortfalls
Insufficient Practice: Jumping to live forex trading without adequate demo experience costs money and confidence. Successful traders typically practice for months before risking capital.
Ignoring Economic Fundamentals: Technical analysis alone provides incomplete market pictures. Understanding economic drivers enhances forex trading decisions.
Following Tips Without Analysis: Social media “gurus” and signal services rarely produce consistent results. Develop personal analytical skills rather than depending on others.
Getting Started: Step-by-Step Action Plan
Phase 1: Education and Preparation (Months 1-2)
“For a complete forex trading education, consider studying recommended books such as “Currency Trading for Dummies” and Kathy Lien’s “Day trading and Swing Trading the Currency Market”. These texts provide foundational knowledge crucial for success.
Market Analysis Practice: Spend 30-60 minutes daily studying charts, identifying support/resistance levels, and analyzing economic news impact.
Broker Research: Compare regulated American brokers, focusing on spreads, platform features, and educational resources.
Phase 2: Demo Trading (Months 2-4)
Open Demo Accounts: Register with 2-3 top brokers for platform comparison. Practice with realistic position sizes matching intended live trading capital.
Strategy Development: Focus on one trading approach, whether trend following, range trading, or breakout strategies. Document all trades with detailed reasoning.
Risk Management Implementation: Practice proper position sizing, stop-loss placement, and profit-taking techniques. These habits must become automatic before live trading.
Phase 3: Live Trading Transition (Month 5+)
Minimal Capital Start: Begin with $500-1,000 to limit initial risk while gaining live market experience. Increase capital only after demonstrating consistent profitability.
Focus on major forex pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD to benefit from optimal liquidity and tighter spreads. Avoid exotic pairs until gaining substantial experience.
Performance Tracking: Maintain detailed records of all trades, including screenshots and market conditions. Weekly performance reviews guide continuous improvement.
Advanced Considerations for Traders
Tax Implications
Forex traders face unique tax considerations under Section 988 of Internal Revenue Code, treating forex trading gains as ordinary income rather than capital gains. Seek advice from qualified tax experts to ensure compliance and optimize your forex trading tax strategies effectively.
Regulatory Updates
Stay informed about CFTC and NFA rule changes affecting forex traders. Regulatory modifications can impact available leverage, reporting requirements, and broker operations.
Technology and Platform Evolution
Modern trading platforms increasingly integrate artificial intelligence and algorithmic trading tools. Stay current with technological advances while maintaining focus on fundamental trading principles.
Resources for Continued Learning
Educational Materials
Books: Beyond introductory texts, advanced reading includes “Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques” by Steve Nison and “Beat the Odds in Forex Trading” by Igor Toshchakov.
Online Resources: CFTC and NFA websites provide regulatory updates and investor education. Major broker educational sections offer free webinars and market analysis.
Academic Sources: Journal of Stock & Forex Trading publishes peer-reviewed research on trading strategies and market behavior. Academic insights enhance practical trading knowledge.
Professional Development
Trading Communities: Join reputable forex forums and local trading groups for peer learning and idea exchange. Avoid groups promoting unrealistic returns or “guaranteed” systems.
Continuing Education: Attend forex seminars, webinars, and conferences to stay current with market developments and advanced strategies.
Conclusion
Forex trading in the market presents unique opportunities fueled by technological advancements, strong regulatory protections, and a wealth of educational resources. By mastering fundamental concepts—such as pips, spreads, leverage, and position sizing—you establish the groundwork for disciplined trading. A thorough understanding of market sessions and strategic timing ensures you capitalize on peak liquidity and volatility, while robust risk management rules protect your capital through prudent stop-loss placement and conservative risk-per-trade limits.
Selecting a well-regulated U.S. broker with competitive pricing, advanced trading platforms, and comprehensive educational support is crucial to your long-term success. Top providers like OANDA, FOREX.com, tastyfx, Interactive Brokers, and Charles Schwab combine stringent CFTC/NFA oversight with features tailored to both novice and experienced traders.
As you progress from demo practice to live trading, maintain emotional discipline by adhering to a detailed trading plan, recording each trade in a journal, and avoiding common pitfalls such as overtrading and revenge trading. Continuous learning—from academic research, industry webinars, and peer communities—will refine your strategies and deepen your market insight.
Ultimately, consistent profitability in forex emerges not from chasing quick gains but from systematic study, rigorous risk controls, and adaptability in response to evolving market conditions. Armed with the knowledge and frameworks outlined in this guide, you are well-positioned to develop a sustainable, growth-oriented approach to currency trading that aligns with your financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQ
1. How much money do I need to start forex trading in the US?
Most American brokers accept minimum deposits of $250-500, though starting with $1,000-2,000 provides better flexibility for proper position sizing. Remember that 74-89% of retail traders lose money, so only trade capital you can afford to lose completely.
2. Is forex trading legal in the United States?
Yes, forex trading is completely legal and regulated by the CFTC and NFA. American residents must trade with properly registered brokers maintaining required regulatory capital.
3. What are the best currency pairs for beginners?
Prioritize trading major USD pairs such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CAD to leverage the best liquidity and tightest spreads in the forex trading market. These pairs offer tight spreads, high liquidity, and predictable behavior patterns suitable for learning.
4. How many hours per day should I spend trading forex?
Quality over quantity matters most. Successful part-time traders often spend 1-2 hours daily on analysis and trade management. Full-time traders may monitor markets 4-6 hours during active sessions.
5. What’s the difference between demo and live trading?
Demo trading uses virtual money without emotional pressure, while live trading involves real capital and psychological stress. Practice on demo for 2-3 months before transitioning to live trading with minimal position sizes.
6. How do I manage risk in forex trading?
Never risk more than 1-2% of account capital per trade, always use stop-loss orders, maintain positive risk-reward ratios of at least 1:2, and diversify across non-correlated currency pairs.
7. Can I trade forex part-time while working a regular job?
Absolutely. Many successful traders work part-time, focusing on swing trading with daily and 4-hour chart analysis. The 24-hour market allows trading around work schedules.
8. What key economic indicators should traders watch most closely?
Monitor Federal Reserve announcements, Non-Farm Payrolls, CPI inflation data, GDP releases, and unemployment figures. These directly impact USD strength across all major pairs.
9. How long does it take to become profitable in forex trading?
Most successful traders require 6-24 months of consistent practice and learning. Expect initial losses during the learning period; focus on education and risk management rather than immediate profits.
10. Should I use trading signals or copy trading services?
Develop personal analytical skills rather than depending on signals. While educational signal services exist, sustainable success requires understanding market analysis and developing independent trading judgment.
11. What’s the best time for traders to do forex trading in USA?
The London-New York trading overlap from 8:00 AM to 12:00 PM EST offers peak liquidity and volatility for major currency pairs, while the New York session (8:00 AM to 5:00 PM EST) consistently drives activity in USD pairs.
12. How do taxes work for American forex traders?
Forex gains are typically taxed as ordinary income under Section 988, not capital gains rates. Keep detailed trading records and consult tax professionals familiar with trader tax situations for proper compliance and potential elections.
Forex trading presents significant opportunities for dedicated American traders willing to invest time in proper education, practice, and risk management. Success requires patience, discipline, and realistic expectations rather than dreams of quick wealth. Start small, learn continuously, and prioritize capital preservation over profit maximization during your development phase.
The American forex market continues expanding with improved regulation, technology, and educational resources. By following systematic approaches outlined in this guide, beginning traders can navigate currency markets more effectively while avoiding common pitfalls that derail trading careers. Remember that consistent profitability develops gradually through experience, proper risk management, and emotional discipline rather than luck or speculation.