The American banking has undergone a trembling transformation in recent years, fundamentally altering how consumers interact with their financial institutions. While digital banking has become the dominant channel for everyday transactions, the full picture of consumer sentiment reveals a complex tapestry of enthusiasm, pragmatism, and persistent concerns. This comprehensive analysis examines the nuanced perspectives of US consumers toward digital banking, revealing both the remarkable adoption patterns and the underlying tensions that continue to shape the industry.
Recent surveys indicate that 89% of Americans express satisfaction with their banking experience, yet 17% remain likely to switch financial institutions in 2025. This apparent contradiction highlights the evolving expectations and sophisticated demands of today’s banking consumers, who have embraced digital convenience while maintaining high standards for service quality and security.
The Digital Transformation of American Banking
Unprecedented Adoption Rates
Digital banking usage has reached remarkable heights across the United States, with over 76% of American customers now using mobile banking applications. This represents a fundamental shift in consumer behavior, driven by the convergence of improved technology, changing lifestyle demands, and the accelerated digitization prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
These statistics strongly underscore the scale of this transformation. Mobile banking app downloads reached 2 billion in the year ending June 2025, representing a 5.1% year-over-year increase. More telling is the behavioral data: 34% of consumers use mobile banking apps daily, while 77% of Americans processed banking transactions on smartphones, tablets, or computers. This level of engagement indicates that digital banking has moved beyond mere convenience to become an integral part of daily financial management.
The shift represents more than just technological adoption; it reflects a fundamental reimagining of the banking relationship. Where customers once planned trips to physical branches around banking hours, they now expect 24/7 access to comprehensive financial services. This expectation has been largely met, with 96% of consumers rating their mobile and online banking experience as “excellent,” “very good,” or “good”.
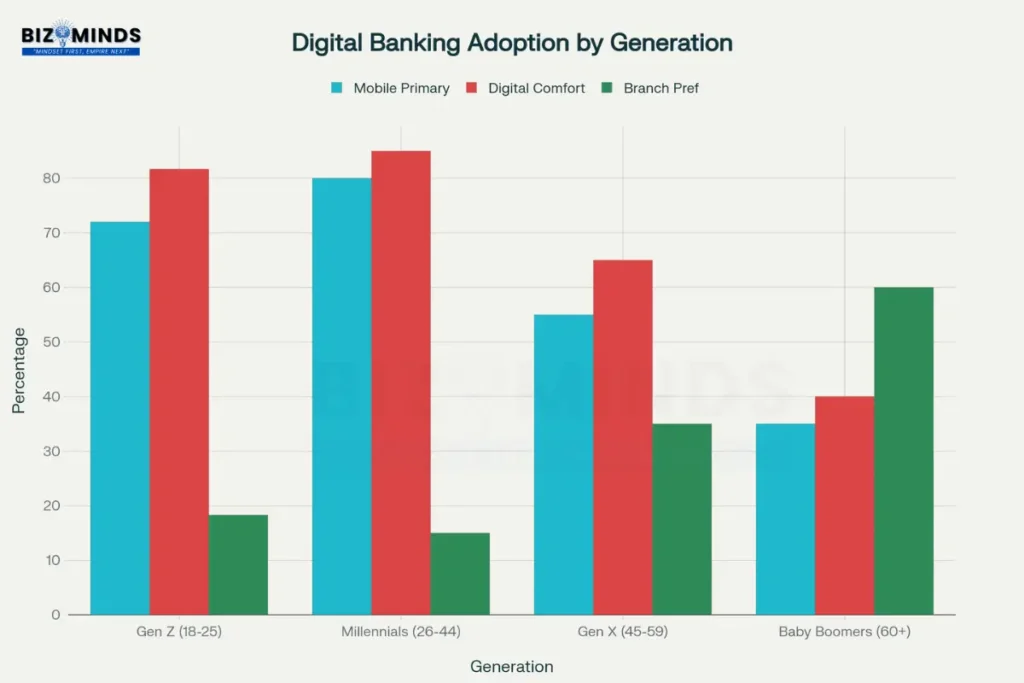
Digital banking adoption varies significantly across generations, with Millennials leading in mobile banking preferences while Baby Boomers show stronger preference for traditional branches
The Generational Divide in Digital Banking
The adoption of digital banking varies significantly across generational lines, creating distinct user profiles that banks must understand and serve differently. Millennials, currently aged 29-44, lead digital banking adoption with 80% preferring digital channels as their primary banking method. This generation, having matured during the rise of smartphones and high-speed internet, approaches banking with a distinctly digital-first mindset.
Generation Z presents a more complex picture despite their digital nativity. While 72% use digital channels primarily, they show slightly lower preference rates than millennials, possibly reflecting their still-developing financial relationships and greater likelihood to maintain flexibility in their banking choices. Notably, 32% of Gen Z consumers switched banks during job changes, and 24% did so when joining the workforce, indicating higher mobility and willingness to optimize their financial relationships.
Generation X demonstrates moderate digital adoption at 55%, balanced with maintaining some preference for traditional banking relationships. This generation often seeks the security of established institutions while selectively embracing digital tools that offer clear value and convenience.
Baby Boomers show the most pronounced preference for traditional banking, with only 35% primarily using digital channels. However, this represents significant growth from previous years, with 40% of Baby Boomers now using digital banking regularly, up from 28% in 2020. This demographic values personal relationships and face-to-face service, particularly for complex financial decisions.
Channel Preference Evolution
The data reveals a clear hierarchy in banking channel preferences among American consumers. Mobile applications have become the dominant channel, with 56% of all banking interactions now occurring through mobile apps, compared to 38% five years ago. This shift represents more than convenience; it reflects changing expectations about financial service delivery.
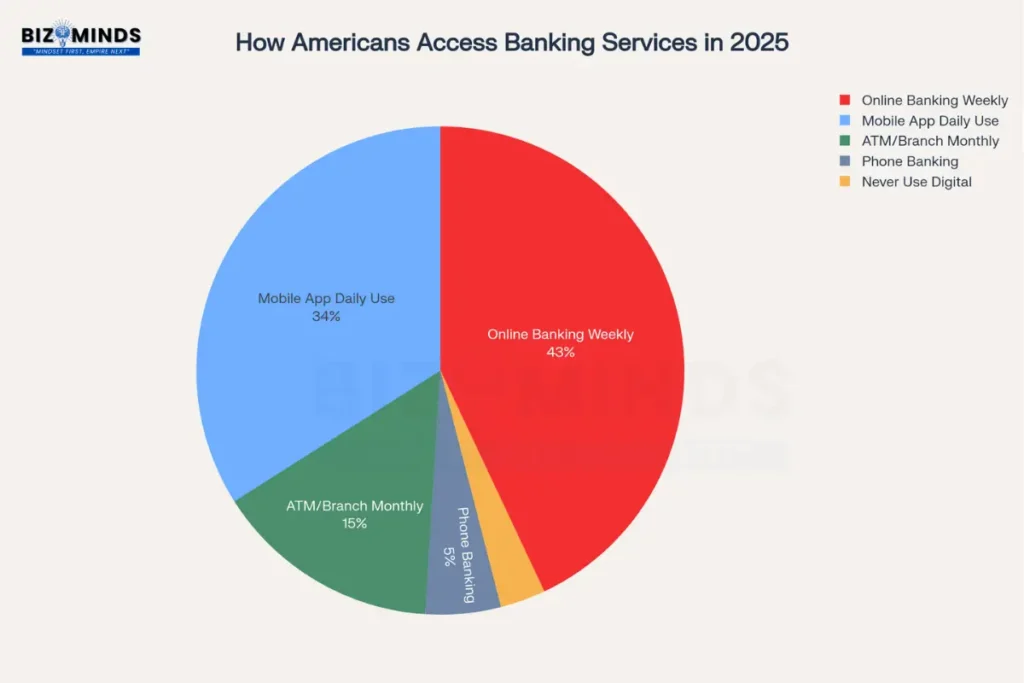
Digital channels dominate American banking habits, with 77% of consumers primarily using mobile apps and online banking for their financial needs
Digital Banking
Online banking through computers maintains strong usage, particularly for more complex transactions and detailed account management. The combination of mobile and online banking now accounts for 77% of consumer preference for account management. Traditional channels have not disappeared entirely but have been relegated to specific use cases: complex problem resolution, notary services, and situations requiring personal consultation.
Physical Banks
Physical branches now serve as the “last resort” for resolving complex issues that cannot be handled through self-service channels. Access to branch employees remains important, especially for small business customers and affluent individuals who require specialized services. However, the role has shifted from routine transaction processing to specialized advisory services and exception handling.
Trust and Security: The Foundation of Digital Banking Relationships
The Trust Hierarchy
Consumer trust in financial institutions reveals a clear hierarchy that significantly impacts digital banking adoption and satisfaction. Americans demonstrate highest trust in their primary banks, with 81% expressing confidence in their institution’s ability to keep their data secure. This trust level drops substantially when considering other institutions, with only 58% trusting other traditional banks and 45% trusting digital-only banks.
The trust differential extends to broader financial service categories. Fintech companies and technology companies both receive 44-45% trust ratings from consumers, indicating significant skepticism about newer market entrants. This trust gap represents one of the most significant challenges facing digital-first financial institutions and explains why traditional banks maintain competitive advantages despite sometimes inferior digital experiences.
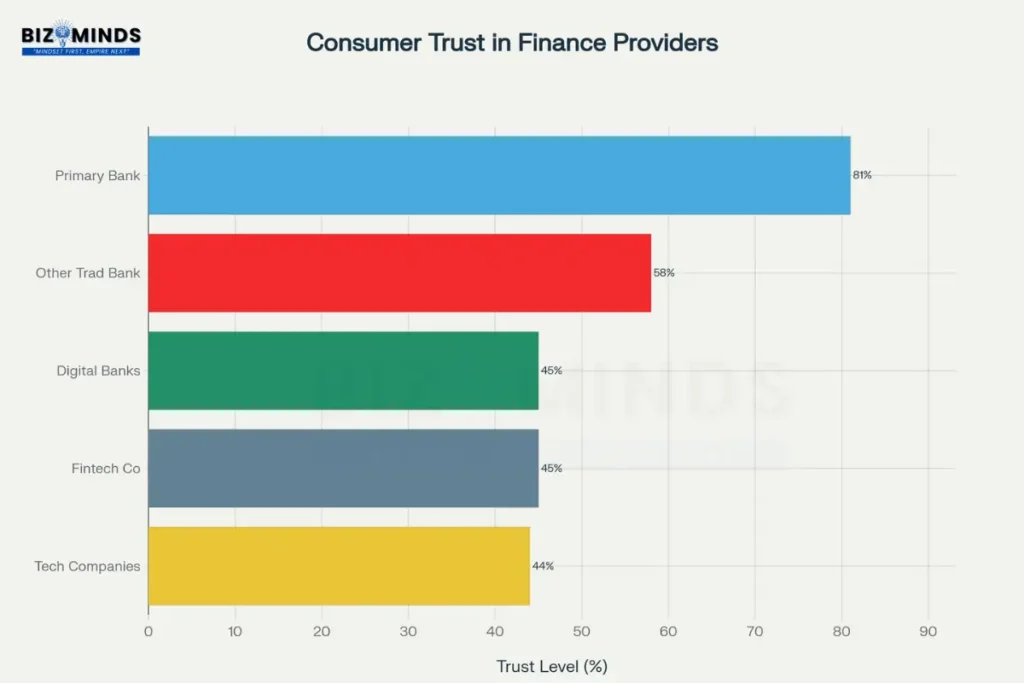
Americans show highest trust in their primary banks (81%) but significantly lower confidence in digital-only banks and fintech companies
Security Concerns and Behavioral Patterns
Despite high overall satisfaction with digital banking, security remains a paramount concern for American consumers. Identity theft tops the list of consumer concerns at 85%, followed by data breaches at 72% and fraud/scams at 68%. These concerns translate into specific behavioral patterns that banks must understand and address.
The research reveals that 19% of consumers have been informed that their personal data has been compromised in the past year. This experience shapes ongoing attitudes and behaviors, with 62% of respondents indicating they would lose confidence in their bank after a data breach, and 43% stating they would stop engaging with the institution entirely.
Interestingly, security features that were once considered burdensome have become satisfaction drivers. Multifactor authentication, previously viewed as a hindrance to the login process, now correlates with 16 points higher customer satisfaction among national banking app users. This shift reflects both improved implementation of security measures and increased consumer awareness of their importance.
The Privacy Paradox
American consumers demonstrate what researchers term a “privacy paradox” in their digital banking behavior. While 85% express concerns about identity theft and 72% worry about data breaches, 37% admit they only share personal data with financial organizations because it’s required to access products or services. This reluctant acceptance underscores the tension between desired convenience and security concerns.
The emergence of artificial intelligence in banking has intensified these concerns. Consumers are increasingly asking pointed questions about data usage: What is my data being used for? Who profits from it? What role does it play in training algorithms that affect me? These questions reflect a maturing understanding of data value and usage, requiring banks to provide more transparent and comprehensible explanations of their data practices.
Customer Experience and Satisfaction Metrics
Overall Satisfaction Trends
Customer satisfaction with digital banking has reached impressive levels, with 87% of Americans expressing satisfaction with their banking experience, up from 84% in 2023. This improvement reflects ongoing investments in digital infrastructure and user experience design. Regional banks have particularly excelled, achieving 92% satisfaction rates primarily due to personalized services, while online-only banks achieved 90% satisfaction through fee transparency and accessibility.
The satisfaction metrics reveal specific strengths and weaknesses in the digital banking experience. Ease of use scores highest at 89%, followed by overall satisfaction at 87% and app performance at 86%. Security features receive strong marks at 85%, indicating that consumer concerns about security don’t necessarily translate to dissatisfaction with current implementations.
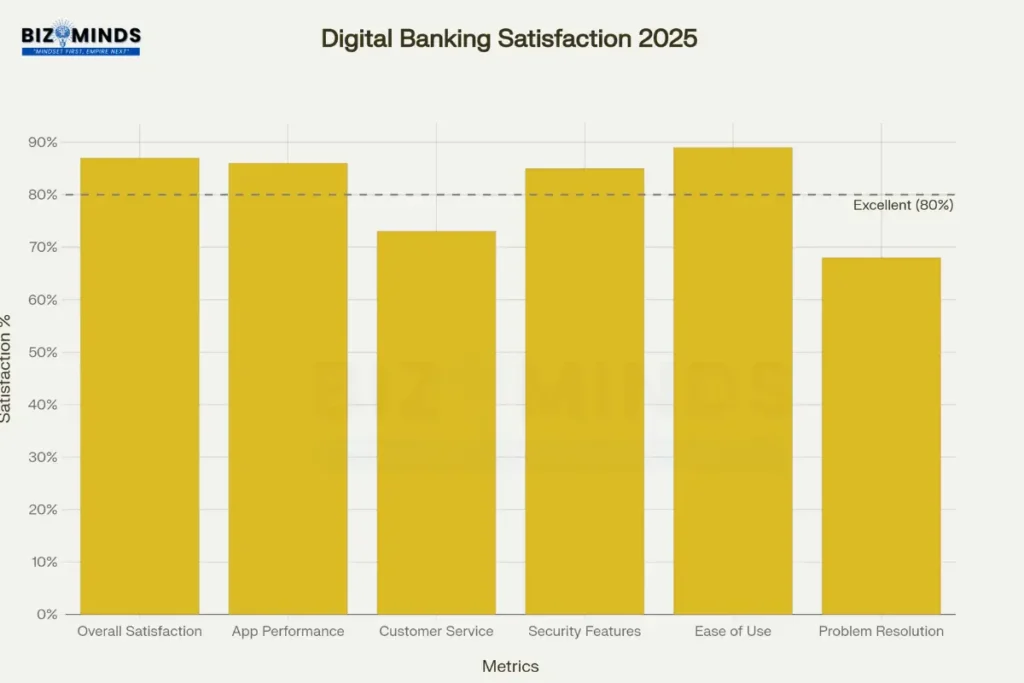
Customer satisfaction with digital banking is strong overall, with ease of use scoring highest (89%) while problem resolution remains the weakest area (68%)
However, problem resolution remains the weakest area at 68% satisfaction, highlighting a persistent challenge in digital banking delivery. This gap is particularly significant given that 61% of consumers say improved problem resolution significantly impacts their satisfaction levels. The disparity suggests that while routine transactions proceed smoothly, exception handling and complex issue resolution remain areas requiring substantial improvement.
The Experience Gap
Despite high overall satisfaction, significant experience gaps persist between consumer expectations and delivery. Research indicates that consumer demands are outpacing digital offerings in banking, with many institutions struggling to keep pace with evolving expectations shaped by experiences with leading technology companies.
The experience gap manifests in several key areas. Roughly half of customers who attempt to purchase financial products digitally defect to competitors when the process proves inadequate. This defection rate indicates that first impressions in digital experiences carry disproportionate weight in customer acquisition and retention.
Personalization represents another significant gap. While 59% of consumers want tailored financial recommendations, and 57% expect banking apps to automatically recognize international travel, many institutions have not yet delivered these capabilities. The expectations reflect consumer experiences with other digital services that provide contextual, intelligent assistance.
Mobile App Performance and Expectations
Mobile banking applications have become the primary interface between consumers and their financial institutions, making app performance critical to overall satisfaction. The 2025 J.D. Power studies show overall satisfaction with national banking apps at 669 points (on a 1,000-point scale), up 18 points from 2024.
Leading performers in mobile banking satisfaction include Bank of America (678 points), PNC (675 points), and Chase (673 points). These rankings reflect not just technical performance but comprehensive user experience design, including navigation ease, visual appeal, and information accessibility.
Consumer expectations for mobile banking continue to evolve rapidly. Four in five consumers under age 45 believe they should be able to accomplish any banking task through a mobile app. This expectation extends beyond basic transactions to include complex processes like loan applications, dispute resolution, and comprehensive financial planning tools.
The Economics of Digital Banking Transformation
Cost Efficiency and Operational Changes
The transformation to digital banking has created significant economic benefits for financial institutions while changing the cost structure of banking services. Banks that have invested in digital transformation report 20-40% reductions in operating costs through automation, process optimization, and reduced dependency on physical locations.
These cost savings have enabled banks to offer more competitive fee structures and interest rates. Digital-only banks particularly benefit from this cost advantage, often providing higher interest rates on savings accounts and lower fees compared to traditional institutions. This cost efficiency creates a competitive dynamic that pressures all institutions to optimize their digital offerings.
Branch Closure Patterns and Regional Impact
The shift to digital banking has accelerated physical branch closures across the United States. In 2025, an estimated 900-1,400 branch closures are projected in the US alone, continuing a trend that has seen an average of 1,646 branch closures annually since 2018.
The closure patterns reveal important regional and demographic disparities. Rural areas face disproportionate impact, with 1 in 4 branches closing in low-population ZIP codes. This creates potential “banking deserts” where access to in-person financial services becomes limited, particularly affecting populations that rely heavily on traditional banking relationships.
Major banks have led the closure trend, with Wells Fargo closing almost 300 branches in 2023 and Bank of America closing about 100. However, some institutions are beginning to stabilize their branch networks. JPMorgan Chase reported minimal net closures, with 22 openings against 14 closures in recent periods, suggesting that optimization may be reaching completion for some institutions.
The Investment in Digital Infrastructure
Banks have invested hundreds of billions of dollars in digital technology, with a considerable share focused on enhancing self-service and digital customer experiences. However, this investment has sometimes created operational silos instead of integrated experiences, potentially hindering bankers’ ability to assist customers during critical moments.
The investment priorities reflect changing consumer expectations and competitive pressures. Financial institutions are particularly focused on artificial intelligence implementation, with 46% of banks using AI reporting improved customer experiences through faster and more efficient services. These investments aim to provide personalized banking experiences that can compete with both traditional competitors and emerging fintech challengers.
Regional and Demographic Variations
Geographic Patterns in Digital Adoption
Digital banking adoption shows significant geographic variation across the United States, with certain metropolitan areas leading in both adoption rates and innovation. San Francisco maintains its position as the global fintech capital, driven by its highly skilled workforce, early technology adoption, and strong venture capital support.
New York City ranks second in digital banking adoption, benefiting from its fusion of traditional finance expertise and rapid digital innovation. Los Angeles, Seattle, Boston, Chicago, Austin, Miami, Denver, and Philadelphia complete the top ten cities for digital banking adoption, each contributing unique factors such as tech-savvy populations, university-led innovation, or business-friendly regulatory environments.
These geographic patterns reflect broader economic and demographic factors that influence digital banking adoption. Cities with higher education levels, stronger technology sectors, and younger demographics consistently show higher digital banking usage rates. This geographic clustering creates both opportunities and challenges for financial institutions seeking to optimize their service delivery models.
Demographic Influences on Banking Behavior
Beyond generational differences, various demographic factors significantly influence digital banking adoption and satisfaction. Income levels show strong correlation with digital banking usage, with higher-income households more likely to engage with mobile banking than those with lower incomes. Education plays a similar role, with college-educated individuals more than twice as likely to use mobile banking as their primary account access method compared to those with only a high school diploma.
These demographic patterns have important implications for financial inclusion and service design. Lower-income and less-educated populations may face barriers to digital banking adoption, potentially creating inequitable access to the cost savings and convenience benefits of digital services. Financial institutions must consider these factors when designing digital experiences and maintaining traditional service channels.
Competitive Landscape and Market Dynamics
Traditional vs. Digital Banking Challengers
The competitive environment in American banking reflects a complex dynamic between established traditional institutions and emerging digital challengers. While traditional banks maintain dominant market positions, digital-only banks and fintech companies are gaining significant market share, particularly among younger demographics.
Almost 20% of European respondents now use direct banks or neobanks as their main financial service provider, and similar trends are emerging in the US market. This shift represents a fundamental challenge to traditional banking models, as digital challengers often provide superior customer experiences despite lacking the trust levels associated with established institutions.
Digital challengers excel in several key areas that appeal to modern consumers. They typically offer streamlined account opening processes that can be completed in minutes rather than days, transparent fee structures without hidden charges, and innovative features like real-time spending insights and automated savings tools. These advantages appeal particularly to younger consumers who prioritize convenience and transparency over institutional reputation.
The Emergence of Hybrid Banking Models
Recognizing the competitive threat from digital-only institutions, many traditional banks are developing hybrid models that combine digital innovation with traditional strengths. These models aim to provide the convenience and efficiency of digital banking while maintaining the trust and specialized services associated with established institutions.
Successful hybrid models integrate advanced digital capabilities with selective physical touchpoints. This might include flagship branches in key markets, specialized advisory services for complex financial needs, and partnerships with fintech companies to enhance digital capabilities. The goal is to serve diverse customer segments while maintaining competitive relevance in an evolving market.
Consumer Expectations and Future Trends
The Evolution of Consumer Expectations
Consumer expectations for digital banking continue to evolve rapidly, shaped by experiences with leading technology companies and emerging digital services. Modern consumers expect banking services to be as intuitive and responsive as their favorite consumer applications, creating pressure for continuous innovation and improvement.
Key expectation areas include personalization, with consumers wanting financial services tailored to their specific circumstances and goals. Real-time insights and proactive recommendations are becoming standard expectations rather than premium features. Consumers also expect seamless integration across devices and platforms, allowing them to start transactions on one device and complete them on another without friction.
The rise of artificial intelligence has created new expectations for intelligent assistance and automated financial management. Consumers increasingly expect their financial institutions to provide proactive insights, automated savings optimization, and predictive assistance for financial planning. These expectations reflect a broader shift toward anticipatory rather than reactive financial services.
Emerging Technology Integration
The integration of emerging technologies in banking continues to accelerate, driven by consumer expectations and competitive pressures. Artificial intelligence applications are expanding beyond chatbots to include sophisticated financial planning tools, fraud detection systems, and personalized product recommendations.
Biometric authentication has gained significant consumer acceptance, with 71% preferring fingerprint or facial recognition features. This preference reflects both security concerns and convenience expectations, as biometric systems provide both enhanced security and streamlined access to accounts.
The integration of banking services with broader financial ecosystems is becoming increasingly important. Consumers expect their banking applications to connect seamlessly with investment platforms, budgeting tools, and payment systems. This integration requires sophisticated API development and partnership strategies that many institutions are still developing.
Challenges and Pain Points in Digital Banking
Persistent Problem Areas
Despite high overall satisfaction levels, several persistent problem areas continue to challenge digital banking delivery. Problem resolution remains the lowest-scoring satisfaction area at 68%, indicating significant room for improvement in exception handling and customer support.
Complex transaction processing represents another ongoing challenge. While routine transactions like transfers and bill payments generally work smoothly, more complex processes like dispute resolution, loan modifications, and account problem resolution often require multiple touchpoints and extended resolution times.
The integration between digital and human-assisted channels remains problematic for many institutions. When customers need to escalate issues from digital channels to human representatives, the transition often lacks context sharing and requires customers to repeat information, creating frustration and inefficiency.
Digital Divide Concerns
The shift toward digital banking has created concerns about financial inclusion and access equity. Populations that are less comfortable with technology, have limited internet access, or prefer human interaction for cultural or accessibility reasons may face reduced access to banking services as physical branches close.
Rural areas face particular challenges, as they experience disproportionate branch closures while often having limited high-speed internet access necessary for effective digital banking. This creates potential barriers to financial services for rural populations who may lack both digital access and physical branch alternatives.
Older populations, while increasingly adopting digital banking, still show strong preferences for human interaction and face-to-face service for complex financial decisions. As banks optimize their operations around digital channels, ensuring adequate service options for these populations remains an important consideration.
Industry Response and Innovation
Financial Institution Adaptation Strategies
Financial institutions are responding to evolving consumer expectations through various adaptation strategies. Many traditional banks are accelerating digital transformation investments while selectively maintaining physical presence in strategic markets. This approach aims to serve diverse customer segments while optimizing operational efficiency.
Investment in customer experience design has become a priority across the industry. Banks are hiring user experience professionals, conducting extensive customer research, and implementing design thinking methodologies to improve their digital offerings. These efforts focus on reducing friction, improving intuitive navigation, and creating more engaging customer interactions.
Partnership strategies with fintech companies have become increasingly common, allowing traditional banks to integrate innovative capabilities without building them entirely in-house. These partnerships can provide access to specialized technologies, rapid implementation timelines, and expertise in emerging financial services.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
The digital transformation of banking occurs within a complex regulatory environment that continues to evolve. Regulators are balancing the need to encourage innovation with consumer protection requirements, creating both opportunities and constraints for digital banking development.
Data privacy regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, requiring banks to implement robust data protection measures while maintaining user experience quality. The growing importance of transparency in data usage practices reflects both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for understanding how their information is used.
Cybersecurity regulations continue to evolve in response to emerging threats and attack vectors. Banks must invest in advanced security technologies while ensuring these measures don’t create excessive friction for legitimate users. The balance between security and usability remains a critical design challenge.
Looking Forward: The Future of Digital Banking
Anticipated Trends and Developments in Digital Banking
The future of digital banking in the United States appears to be characterized by continued innovation, increasing personalization, and deeper integration with broader financial and lifestyle ecosystems. Artificial intelligence applications will likely become more sophisticated, providing predictive financial advice and automated financial management tools.
Open banking initiatives may accelerate, allowing consumers to aggregate their financial relationships across multiple institutions through single interfaces. This development could reduce institutional switching costs while increasing competition for customer engagement and primary banking relationships.
The integration of banking services with emerging payment technologies, cryptocurrency platforms, and digital asset management tools will likely continue. These integrations reflect changing consumer expectations about comprehensive financial service delivery.
Strategic Implications for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions must navigate several strategic imperatives to remain competitive in the evolving digital banking situation. Investment in digital capabilities must continue while maintaining appropriate risk management and regulatory compliance. This requires sophisticated resource allocation decisions and careful balance between innovation and stability.
Customer experience differentiation will become increasingly important as basic digital banking capabilities become commoditized. Banks must identify unique value propositions that extend beyond transaction processing to comprehensive financial partnership and advisory services.
The development of trust-building capabilities will remain crucial, particularly for institutions seeking to compete with established traditional banks. This requires transparent communication, consistent service delivery, and proactive security measures that reassure consumers about data protection and financial safety.
Conclusion
The comprehensive analysis of US consumer sentiment in 2025 reveals a financial services landscape in remarkable transition, where technological adoption meets evolving expectations and persistent concerns. American customers have embraced online channels with unprecedented enthusiasm, with 77% now preferring internet and mobile tools for routine transactions and apps processing over 2 billion downloads annually. Yet beneath this widespread shift lies a nuanced story of generational preferences, trust hierarchies, and experience gaps that continue to shape the industry’s evolution.
These innovations have fundamentally transformed the American banking experience, creating both opportunities and challenges for institutions navigating this technological revolution. While overall satisfaction reaches impressive heights at 87%, the data highlights critical areas requiring attention—particularly problem resolution, which lags at 68%. The trust differential between primary banks (81%) and digital-only platforms (45%) underscores the enduring value of longstanding relationships, even as consumers increasingly favor online convenience. This dynamic suggests that successful strategies must balance innovation with relationship-building, recognizing that technology alone cannot overcome loyalty gaps.
Generational differences present both immediate challenges and long-term opportunities for financial providers. Millennials lead usage with 80% channel preference, while Baby Boomers maintain stronger in-branch loyalty at 60%, creating diverse service expectations within single institutions. As younger, tech-native generations mature, organizations must navigate this transition carefully, maintaining service quality across multiple touchpoints while optimizing for predominantly online interactions. The 17% of consumers likely to switch providers in 2025 demonstrates that satisfaction with current offerings doesn’t guarantee loyalty in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Security remains the most significant barrier to deeper engagement, with 85% of consumers expressing identity theft concerns and 72% worried about data breaches affecting their accounts. However, the research reveals a positive correlation between robust safeguard measures and customer satisfaction, suggesting that transparent, well-implemented protections enhance rather than hinder the user experience. As institutions continue investing in artificial intelligence, biometric authentication, and advanced fraud prevention, addressing these concerns through both technological solutions and clear communication is essential for maintaining confidence in online services.
Looking ahead, the future of financial services in America will likely be defined by increased personalization, AI-driven insights, and ecosystem connectivity, as customers expect their providers to offer comprehensive, intelligent partnerships rather than merely transaction processing. The organizations that succeed will master the delicate balance between technological innovation and human connection, leveraging tools to enhance rather than replace meaningful customer relationships. As digital channels become the dominant way Americans bank, the winners will be determined not just by their systems but by their ability to earn and maintain trust while delivering exceptional experiences across every touchpoint.
Frequently Asked Questions
How secure is digital banking compared to traditional banking?
Digital banking employs multiple layers of security including encryption, multifactor authentication, and real-time fraud monitoring. While 85% of consumers express concerns about identity theft, 86% believe their banks take proactive steps to protect them from fraud. Digital banking transactions often have more comprehensive audit trails and faster fraud detection capabilities than traditional paper-based transactions.
Will physical bank branches disappear completely?
Physical branches are unlikely to disappear entirely but will continue to evolve in function and number. Banks are projected to close 900-1,400 branches in 2025, but remaining branches increasingly focus on complex services, advisory relationships, and specialized transactions that require human expertise. Rural areas may face greater challenges in maintaining branch access.
Which generation prefers digital banking most?
Millennials lead digital banking adoption with 80% preferring digital channels as their primary banking method. Surprisingly, Generation Z shows slightly lower preference at 72%, possibly due to their developing financial relationships and desire for flexibility. Baby Boomers show the lowest digital preference at 35% but are rapidly increasing their adoption rates.
What are the main barriers preventing people from switching to digital banking?
The primary barriers include security concerns (cited by 42% of non-digital users), preference for branch access (45%), and lack of familiarity with digital tools. Additionally, 41% cite the hassle of switching accounts as a major obstacle, while 27% feel uncertain about the benefits of changing their banking relationship.
How do digital-only banks compare to traditional banks in customer satisfaction?
Digital-only banks achieve 90% customer satisfaction rates, compared to 87% for traditional banks overall. However, traditional banks maintain significant trust advantages, with 81% of consumers trusting their primary bank compared to only 45% trusting digital-only banks. The satisfaction advantage for digital banks primarily stems from transparent fee structures and user-friendly interfaces.
What digital banking features do consumers value most?
Ease of use ranks highest in consumer preferences at 89% satisfaction, followed by app performance (86%) and security features (85%). Consumers particularly value real-time transaction notifications, mobile check deposit, and integrated budgeting tools. However, 59% want more personalized financial recommendations, indicating significant opportunity for enhanced services.
Citations
- https://www.driveresearch.com/market-research-company-blog/banking-trends-statistics/
- https://cheqly.com/us-digital-banking-trends-2025/
- https://www.meridianlink.com/blog/why-consumer-sentiment-toward-banking-needs-work/
- https://www.absrbd.com/post/digital-banking-statistics
- https://sdk.finance/what-is-digital-banking/
- https://www.bankrate.com/banking/digital-banking-trends-and-statistics/
- https://sensortower.com/blog/consumer-banking-apps-and-advertising-trends-2025
- https://www.alkami.com/blog/attracting-millennials-starts-with-digital-banking-solutions/
- https://sbs-software.com/insights/banks-attract-millennials-financial-guidance/
- https://thefinancialbrand.com/news/demographics/how-generational-differences-and-life-events-are-shaping-consumers-financial-decisions-189100
- https://rfppl.co.in/subscription/upload_pdf/single-pdf(-27%E2%80%9335)-1746784738.pdf
- https://coinlaw.io/consumer-banking-satisfaction-statistics/
- https://www.teradata.com/insights/data-analytics/bank-branches-in-digital-age
- https://bankingjournal.aba.com/2025/03/survey-most-customers-trust-their-banks-to-keep-their-data-secure/
- https://cpl.thalesgroup.com/digital-trust-index
- https://isjem.com/download/cybersecurity-risks-in-digital-banking-a-financial-perspective/
- https://www.jdpower.com/business/press-releases/2025-us-banking-and-credit-card-mobile-app-satisfaction-studies
- https://usercentrics.com/resources/state-of-digital-trust-report/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/garydrenik/2024/09/17/consumer-demands-outpacing-digital-offerings-in-banking/
- https://www.backbase.com/press/state-of-banking-european-consumer-survey
- https://www.customerexperiencedive.com/news/millennials-drive-growing-expectations-digital-banking/751225/
- https://smartdev.com/customer-experience-in-traditional-banks-vs-digital-only-banks/
- https://coinlaw.io/bank-branch-closure-statistics/
- https://www.bankdirector.com/article/banks-cut-branches-as-digital-banking-drives-growth/
- https://thefinancialbrand.com/news/banking-branch-transformation/trends-2024-is-record-breaking-pace-of-bank-branch-closures-easing-173198
- https://www.statista.com/topics/2614/mobile-banking/
- https://www.aba.com/about-us/press-room/press-releases/national-survey-consumers-are-happy-with-their-bank
- https://www.ijrti.org/papers/IJRTI2503077.pdf
- https://ijrpr.com/uploads/V6ISSUE4/IJRPR41614.pdf
- https://coinlaw.io/online-banking-usage-statistics/
- https://www.fico.com/en/latest-thinking/ebook/2025-consumer-survey-usa-fraud-identity-and-digital-banking
- https://www.ijprems.com/uploadedfiles/paper/issue_3_march_2025/38954/final/fin_ijprems1741960394.pdf
- https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/industry/banking/document/Accenture-Global-Banking-Consumer-Study-2025-Report.pdf
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/consumer-packaged-goods/our-insights/the-state-of-the-us-consumer
- https://www.decta.com/company/media/pros-and-cons-of-digital-banks-vs-traditional-banks
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1042957325000300
- https://www.conference-board.org/topics/consumer-confidence/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1394885/mobile-banking-penetration-in-us/
- https://aitd.amity.edu/blog/digital-banking-trends-in-an-overview/
- https://www.alkami.com/resources/research/reports/the-2025-generational-trends-in-digital-banking-study/
- https://buildfire.com/app-statistics/
- https://appcircle.io/blog/most-popular-banking-apps-in-the-us-2025-data-analysis
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2444569X22000105
- https://appinventiv.com/blog/mobile-app-download-and-usage-statistics/
- https://www.fiserv.com/en/insights/articles-and-blogs/are-your-banking-customers-digitally-engaged.html
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1097139/consumer-trust-score-of-banks-worldwide-by-country/
- https://livebank24.com/digital-banking/measuring-success-key-metrics-for-evaluating-customer-service-in-digital-banking/
- https://theuxda.com/blog/banks-will-cut-millions-of-jobs-in-the-next-decade
- https://www.accenture.com/in-en/insights/banking/consumer-study-banking-advocacy-powering-growth
- https://theacsi.org/industries/finance-and-insurance/banks/
- https://www.philadelphiafed.org/-/media/frbp/assets/community-development/reports/banking-deserts-report-feb-2024.pdf
- https://www.spglobal.com/market-intelligence/en/news-insights/articles/2025/5/pace-of-us-bank-branch-closures-picks-up-in-q1-2025-88699893
- https://www.capgemini.com/insights/research-library/world-retail-banking-report/

