The Biggest SEO Myths Marketers Still Believe in 2025
The search engine optimization(SEO) changes has evolved dramatically, yet many marketers continue clinging to outdated beliefs that can sabotage their digital success. With Google making over 3,000 algorithm updates annually—that’s nine changes every single day—the proliferation of SEO myths has reached epidemic proportions in 2025.
The consequences extend far beyond theoretical concerns. Businesses following myth-based strategies risk algorithmic penalties, waste precious marketing budgets, and watch competitors surge ahead using evidence-based approaches. The global SEO market is expected to surge to $143.9 billion by 2030, favoring businesses that embrace proven SEO strategies while penalizing those stuck with outdated practices.
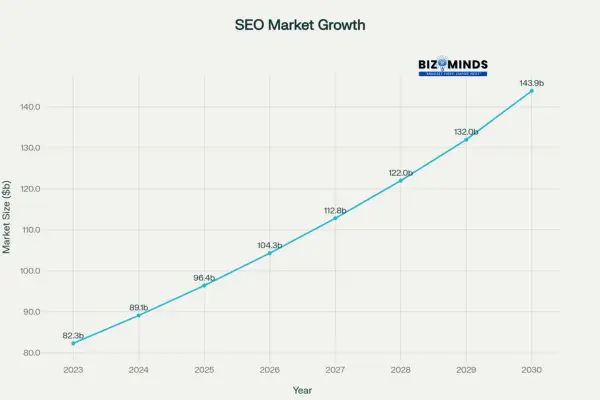
SEO Market Growth 2023-2030: Industry projected to reach $143.9 billion with consistent growth
The emotional toll on marketing teams cannot be understated. Imagine spending months implementing strategies based on SEO myths, only to watch organic traffic plummet while competitors flourish. This harsh reality affects thousands of American businesses daily, from Silicon Valley startups to Main Street retailers, all struggling with misinformation that pervades SEO education and advice.
Understanding which SEO myths persist and why they’re dangerous has become essential for survival in 2025’s competitive digital landscape. This comprehensive analysis reveals the most persistent misconceptions, their real-world consequences, and evidence-based strategies that actually drive results.
The SEO Myth Epidemic: Why False Beliefs Persist
The digital marketing industry faces an information crisis that would make even seasoned professionals skeptical. SEO myths spread faster than algorithm updates, creating a dangerous lag between Google’s actual ranking factors and widespread industry understanding.
Several psychological and structural factors contribute to this misinformation pandemic:
The Complexity Simplification Trap
Human psychology craves simple explanations for complex phenomena. Google’s algorithms consider hundreds of ranking factors, but marketers desperately want single-variable solutions. This creates fertile ground for SEO myths that promise “one weird trick” approaches to ranking success.
The emotional appeal of simplification becomes particularly pronounced during stressful periods. When organic traffic drops or competitors surge ahead, the temptation to embrace easy answers intensifies. Marketing managers facing executive pressure often gravitate toward SEO myths that promise quick fixes rather than sustainable strategies requiring patience and expertise.
Information Lag and Echo Chambers
The SEO industry operates within echo chambers where SEO myths receive repeated validation without rigorous testing. Conference speakers recycling outdated information, blog posts citing questionable sources, and social media influencers promoting unverified tactics create self-reinforcing cycles of misinformation.
This problem becomes particularly acute in smaller markets across America, where local marketing agencies may lack resources for continuous education and testing. A small business in Ohio might implement SEO myths promoted by a well-intentioned consultant who learned these techniques years ago and never updated their knowledge base.
The Cost of SEO Mythology
Real businesses suffer real consequences from SEO myths. Consider the Texas e-commerce company that spent six months implementing keyword stuffing strategies, watching their organic traffic decrease by 60% before discovering their tactics triggered algorithmic penalties. Or the California healthcare practice that invested $50,000 in low-quality backlink schemes, only to face manual penalties requiring expensive recovery efforts.
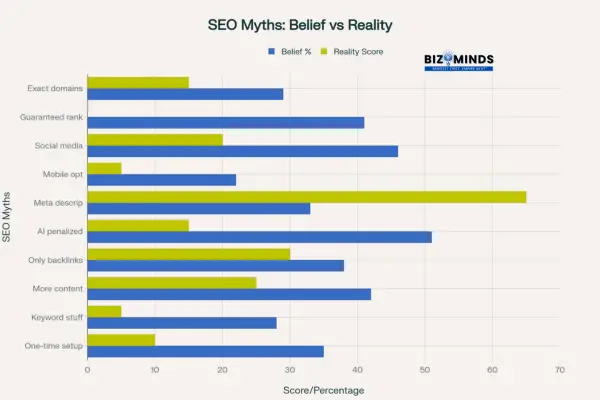
SEO Myths vs Reality: The gap between marketer beliefs and actual effectiveness in 2025
The financial impact extends beyond immediate penalties. SEO myths create opportunity costs—time and resources invested in ineffective tactics could have been allocated to strategies that actually drive results. When the average SEO professional earns $70,300 annually, wasted efforts represent significant financial losses for organizations of all sizes.
Myth #1: “SEO is a One-Time Setup Process”
Perhaps the most dangerous of all SEO myths is the belief that search engine optimization resembles website development—a project with defined completion criteria. This misconception has destroyed countless digital marketing campaigns and continues misleading marketers who should know better.
The Set-and-Forget Mentality
The appeal of one-time SEO setup stems from psychological comfort and budget convenience. Marketing managers prefer capital expenditures over ongoing operational costs, making SEO myths about permanent optimization particularly seductive. The fantasy suggests that proper initial setup ensures perpetual organic traffic growth without continued investment.
Real-world evidence demolishes this myth decisively. Google’s algorithm updates affect ranking factors continuously, competitive landscapes shift as new players emerge, and user behavior evolves with technological changes. The companies thriving in organic search understand that SEO requires ongoing attention, similar to physical fitness or relationship maintenance.
Modern SEO Realities
Successful SEO in 2025 demands systematic, ongoing optimization across multiple dimensions:
- Content Freshness: Google’s algorithms favor regularly updated content that addresses evolving user needs and industry developments
- Technical Maintenance: Website performance, security updates, and structural improvements require continuous monitoring and adjustment
- Competitive Response: As competitors improve their SEO strategies, maintaining rankings requires matching or exceeding their efforts
- Algorithm Adaptation: Each Google update potentially affects ranking factors, requiring strategy adjustments based on performance data
Consider the case of The Home Depot, which maintains dedicated SEO teams monitoring performance daily, updating content continuously, and adapting strategies based on algorithm changes. Their organic traffic success stems from treating SEO as an ongoing strategic priority rather than a completed project.
Implementation Framework
Organizations serious about dispelling this particular SEO myth should establish structured processes:
Monthly Performance Reviews: Analyze ranking changes, traffic patterns, and conversion metrics to identify optimization opportunities and potential issues requiring immediate attention.
Quarterly Strategy Updates: Assess competitive landscape changes, algorithm update impacts, and industry trend shifts that might require strategic pivots or tactical adjustments.
Annual Strategic Planning: Evaluate long-term SEO objectives, resource allocation decisions, and integration opportunities with broader marketing initiatives and business goals.
Myth #2: “Keyword Stuffing Still Works”
The persistence of keyword stuffing among SEO myths demonstrates how deeply entrenched outdated practices remain in 2025. This belief causes significant damage to websites while reflecting fundamental misunderstanding about how modern search algorithms evaluate content quality and relevance.
The Density Obsession
Keyword density obsession represents a mechanical approach to SEO that ignores user experience and content value. Marketers influenced by these SEO myths often produce content that reads awkwardly, provides little value, and triggers algorithmic penalties designed to improve search result quality.
The emotional attachment to keyword stuffing often stems from its apparent simplicity and measurability. Marketing managers can easily calculate keyword density percentages, creating false confidence in optimization efforts. This mechanical approach provides psychological comfort for teams lacking deeper SEO expertise or confidence in content quality assessment.
Google’s Semantic Evolution
Google’s algorithms have evolved far beyond simple keyword matching, incorporating sophisticated natural language processing and semantic understanding capabilities. The search engine now evaluates content context, user intent, and topic comprehensiveness rather than keyword frequency alone.
RankBrain and BERT represent major algorithmic advances that analyze content meaning and user satisfaction signals. These systems penalize keyword stuffing while rewarding natural language that comprehensively addresses user queries and provides genuine value.
Consider how Google interprets search queries like “best pizza near me” versus “highest quality pizza restaurants in my vicinity.” Both queries express identical user intent, but effective content optimization requires semantic understanding rather than mechanical keyword repetition.
Modern Keyword Strategy
Professional SEO practitioners have abandoned keyword stuffing in favor of topic-based optimization approaches:
Semantic Keyword Integration: Using related terms, synonyms, and natural language variations that address user intent comprehensively while maintaining readable, valuable content.
Topic Cluster Development: Creating content ecosystems around central themes, with supporting pages addressing related subtopics and user questions naturally and thoroughly.
User Intent Alignment: Matching content to specific search intents—informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial investigation—rather than focusing solely on keyword inclusion metrics.
Quality Over Density: Emphasizing content depth, expertise demonstration, and user value rather than mechanical optimization metrics that ignore actual search algorithm priorities.
Myth #3: “More Content Always Equals Better Rankings”
Among the most seductive SEO myths circulating in 2025 is the belief that content volume directly correlates with search ranking improvements. Such misconceptions have fueled the rise of content farms, mass-produced AI articles, and misguided SEO strategies that drain resources without delivering real results.
The Volume Misconception
The psychological appeal of content volume stems from industrial-age thinking—more production equals better results. Marketing teams influenced by these SEO myths often prioritize publishing frequency over content quality, creating massive amounts of low-value material that fails to engage users or satisfy search algorithms.
Recent statistics reveal the harsh reality: over 97% of web pages receive zero organic traffic from Google. This sobering fact demonstrates that content creation without strategic focus and genuine value provision leads to digital obscurity rather than search success.
The emotional investment in content volume often reflects deeper organizational insecurities. Teams feeling behind competitors may believe rapid content production can compensate for strategic deficiencies, leading to SEO myths that promise quantity-based solutions to complex quality challenges.
Google’s Quality Revolution
Google’s Helpful Content System, introduced in 2022 and continuously refined, specifically targets low-value content regardless of volume. The algorithm evaluates whether content genuinely helps users solve problems, answers questions comprehensively, and demonstrates expertise rather than simply occupying web space.
The E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) has become central to content evaluation, particularly for “Your Money or Your Life” topics affecting health, finance, or safety. Content lacking these qualities faces ranking challenges regardless of publication frequency or volume.
The distinction between reliable health authorities like WebMD and generic health content farms highlights why expertise and credibility are crucial for SEO success. WebMD’s articles demonstrate medical expertise, cite authoritative sources, and undergo professional review processes. Content farms publishing hundreds of health articles weekly using AI generation or freelance writers without medical qualifications struggle to achieve meaningful rankings despite massive volume.
Strategic Content Excellence
Organizations serious about dispelling volume-based SEO myths should focus on strategic content development:
- User-First Research: Understanding audience needs, pain points, and information gaps through surveys, interviews, and behavioral analysis rather than assumptions
- Expertise Integration: Involving subject matter experts in content creation and review processes to ensure accuracy, depth, and authoritative perspective
- Comprehensive Coverage: Creating content that thoroughly addresses topics rather than surface-level treatment designed for quick publication
- Performance Optimization: Measuring content success through user engagement, conversion rates, and long-term organic traffic growth rather than publication volume metrics
A proven success story is HubSpot, which publishes fewer articles than content farms yet attracts significant organic traffic by delivering authoritative, high-value resources that thoroughly solve marketing challenges. Their content strategy prioritizes depth over breadth, expertise over volume.
Myth #4: “AI Content Will Always Be Penalized by Google”
Fear-based SEO myths surrounding artificial intelligence content have created unnecessary anxiety among marketers in 2025. This misconception stems from misunderstanding Google’s actual policies and evaluation criteria, leading to missed opportunities and strategic paralysis affecting competitive positioning.
The AI Panic
Concerns about AI content penalties reflect deeper fears about technological disruption and professional relevance. Marketing teams influenced by these SEO myths often avoid leveraging AI tools that could improve efficiency and content quality when used appropriately and strategically.
The emotional component of AI fear cannot be understated. Content creators worry about job security, while marketing managers fear algorithmic penalties that could devastate organic traffic. These legitimate concerns become distorted into SEO myths that prevent rational evaluation of AI’s role in content strategy.
Google’s Actual Position
Google’s official stance clarifies that content quality matters more than creation method. The search engine evaluates content based on helpfulness, expertise, and user value rather than whether humans or AI generated the material initially.
Comprehensive Research Findings: Ahrefs’ 2025 analysis of 600,000+ URLs found no correlation between AI content detection and lower search rankings. Additionally, 86% of high-ranking pages contain some AI-generated content elements, demonstrating that quality AI integration can support rather than harm SEO performance.
Google’s John Mueller has stated repeatedly that the company doesn’t automatically penalize AI content that provides genuine value to users. The key distinction lies in content purpose—AI-generated material designed to manipulate rankings without providing user value faces penalties, while AI content that helps users achieve their goals receives equal consideration to human-created content.
Strategic AI Integration
Professional SEO practitioners use AI tools strategically while maintaining human oversight and expertise:
Human-AI Collaboration: Using AI for research, structure, and initial drafts while adding human insight, experience, and expertise to create genuinely valuable content that demonstrates E-E-A-T qualities.
Quality Enhancement: Leveraging AI for editing, fact-checking, and optimization suggestions while ensuring final content meets user needs and provides original perspective or analysis.
Efficiency Optimization: Using AI to handle routine tasks—meta descriptions, title variations, content outlines—freeing human experts to focus on strategic thinking and value creation.
Value-First Approach: Ensuring all content, regardless of creation method, genuinely helps users solve problems, answers questions comprehensively, and provides actionable insights or information.
Myth #5: “Mobile Optimization is Optional”
Although data proves that mobile usage dominates online activity, persistent SEO myths mislead marketers into thinking mobile optimization is optional—despite Google’s mobile-first indexing that directly impacts rankings. This dangerous misconception directly threatens organic visibility and user experience in 2025’s mobile-dominant landscape.
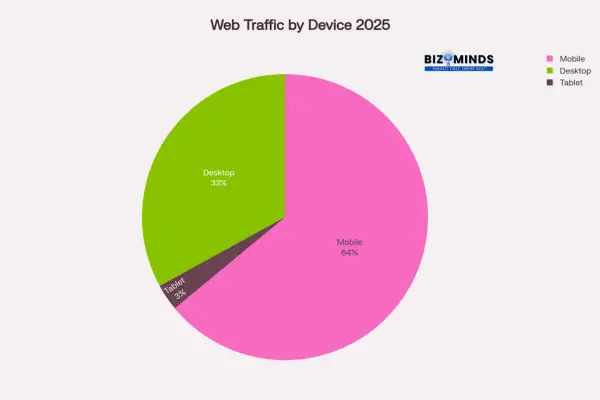
2025 Web Traffic Distribution: Mobile devices dominate with 64% of global traffic
The Desktop-First Delusion
Organizations clinging to desktop-first thinking often suffer from institutional inertia and decision-maker demographics. Because senior executives often work from desktop devices, they may lack firsthand awareness of mobile user experience, reinforcing outdated SEO myths that underestimate the critical role of mobile optimization in search rankings.
The financial consequences of mobile optimization neglect extend beyond search rankings. Poor mobile experiences directly affect conversion rates, user engagement, and brand perception among the 64% of users accessing websites via mobile devices.
Mobile-First Reality
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, the mobile version of your website is the primary basis for rankings and search evaluation. Websites lacking mobile optimization face inherent disadvantages regardless of desktop experience quality.
Critical Statistics:
- By 2025, mobile accounts for 64% of worldwide web traffic
- Websites optimized for mobile are 67% more likely to secure first-page rankings on Google
- Over 70% of websites now use mobile-first indexing
- Mobile traffic represents nearly 60% of global website visits
The competitive implications are severe. Companies maintaining excellent desktop experiences while neglecting mobile optimization lose market share to competitors who prioritize mobile users. This trend accelerates as younger demographics, who primarily use mobile devices, gain purchasing power and influence.
Comprehensive Mobile Strategy
Dispelling mobile optimization SEO myths requires systematic attention to multiple factors:
Technical Performance: Ensuring fast loading speeds (under 3 seconds), responsive design across all device sizes, and proper functionality on touchscreen interfaces.
Content Adaptation: Optimizing content layout, navigation structure, and user interface elements for mobile consumption patterns and interaction methods.
Local Integration: Implementing location-based features, maps integration, and local business information that mobile users frequently seek while traveling or shopping.
User Experience Focus: Prioritizing mobile user needs—quick information access, simple navigation, fast transactions—over desktop-centric design preferences.
Myth #6: “Backlinks Are the Only Ranking Factor That Matters”
The overemphasis on backlinks represents one of the most persistent and damaging SEO myths in 2025. This single-factor obsession leads to manipulative link-building practices, neglect of other critical ranking factors, and strategic imbalances that ultimately harm organic performance and user experience.
The Link-Centric Fallacy
Historical SEO success stories often emphasize backlink acquisition, creating SEO myths that suggest links represent the primary or only important ranking factor. This oversimplification appeals to marketers seeking clear, measurable optimization metrics but ignores Google’s increasingly sophisticated evaluation criteria.
The emotional appeal of backlink focus stems from its apparent logic—if other websites link to content, it must be valuable. This reasoning creates false confidence in link-building strategies while potentially overlooking content quality, user experience, and technical optimization factors that significantly impact rankings.
Google’s Holistic Approach
Modern search algorithms consider hundreds of ranking factors beyond backlinks. While quality links remain important, they function as one component within a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes content relevance, user experience signals, technical performance, and expertise demonstration.
Key Ranking Factor Categories:
- Content quality and comprehensiveness
- User experience metrics and engagement signals
- Technical performance and site speed
- Mobile optimization and accessibility
- E-E-A-T signals and authority indicators
- Freshness and content updates
- Internal linking and site structure
The relative importance of these factors varies by industry, query type, and competitive landscape. YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content prioritizes E-E-A-T signals over link quantity, while local businesses benefit more from Google Business Profile optimization than traditional backlink acquisition.
Balanced SEO Strategy
Professional practitioners avoid backlink-centric SEO myths by developing comprehensive optimization approaches:
Quality Over Quantity: Focusing on earning high-authority, relevant links through valuable content creation rather than pursuing high volumes of low-quality links through manipulative schemes.
Holistic Optimization: Balancing link building with content improvement, technical optimization, user experience enhancement, and authority building across all ranking factor categories.
Natural Link Acquisition: Creating content worthy of organic linking through research, insights, tools, or resources that genuinely help other websites and their audiences.
Relationship Building: Developing industry relationships that naturally lead to linking opportunities, collaborations, and mutual value creation rather than transactional link exchanges.
Understanding E-E-A-T: The Quality Framework Revolutionizing SEO
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) has emerged as Google’s primary content quality evaluation framework, yet many marketers continue underestimating its importance. Dispelling SEO myths about E-E-A-T requires understanding its profound impact on content strategy and ranking success.
The Experience Revolution
Google’s 2022 addition of “Experience” to the E-A-T framework fundamentally changed content evaluation criteria. The search engine now prioritizes content demonstrating firsthand experience and real-world knowledge over purely research-based material, regardless of writing quality or optimization.
This shift affects content across all industries but particularly impacts review sites, travel blogs, how-to guides, and any content where personal experience provides unique value. A restaurant review written by someone who actually dined at the establishment now significantly outranks one compiled from online research, regardless of writing skill or SEO optimization.
Industry-Specific E-E-A-T Applications
Different content types require varying E-E-A-T emphasis, creating nuanced optimization requirements that challenge simplistic SEO myths about universal strategies:
YMYL Content (Your Money or Your Life): Health, finance, legal, and safety content requires maximum E-E-A-T demonstration, with particular emphasis on author credentials, source citations, and factual accuracy.
Product Reviews: Must demonstrate actual product usage, comparison testing, and real-world evaluation rather than specification regurgitation or affiliate marketing focused content.
Technical Guides: Require demonstrated expertise through detailed explanations, troubleshooting scenarios, and insights that only experienced practitioners could provide.
News and Current Events: Demand timely updates, source verification, author expertise in relevant topics, and editorial oversight for accuracy and bias minimization.
Building E-E-A-T Signals
Organizations serious about E-E-A-T optimization must implement systematic approaches:
- Author Expertise Documentation: Creating comprehensive author bios, credential verification, and portfolio demonstration that establishes subject matter authority
- Source Citation and Verification: Linking to authoritative sources, primary research, and credible references that support content claims and provide additional value
- Experience Integration: Including personal anecdotes, case studies, original research, and firsthand insights that demonstrate direct experience with topics
- Trust Signal Implementation: Adding contact information, physical addresses, customer service access, and transparency about business operations and content creation processes
Local SEO Myths: Not Just for Brick-and-Mortar Businesses
One of the most limiting SEO myths in 2025 suggests that local optimization only benefits businesses with physical locations. This misconception prevents service-based businesses, consultants, and online companies from capturing valuable local search traffic and building community connections.
Expanding Local Relevance
Local SEO benefits extend far beyond traditional retail stores and restaurants. Service area businesses—contractors, consultants, lawyers, accountants—often serve specific geographic regions and benefit significantly from local optimization strategies.
Statistical Reality: 46% of monthly Google searches have local intent, representing millions of potential customers seeking local solutions. Businesses ignoring local SEO due to SEO myths about physical location requirements miss substantial traffic and conversion opportunities.
The evolution of remote work and digital services hasn’t eliminated geographic preferences. Consumers often prefer working with local service providers due to familiarity, trust, cultural understanding, and potential for in-person meetings when necessary.
Local Strategy for Digital Businesses
Smart organizations dispel location-based SEO myths through comprehensive local optimization:
Community Content Creation: Developing content addressing local issues, events, and interests that demonstrates community connection and regional expertise.
Local Partnership Development: Building relationships with local organizations, chambers of commerce, and industry associations that create natural linking and citation opportunities.
Geographic Keyword Integration: Targeting location-specific keywords naturally within content while avoiding keyword stuffing or forced geographic references.
Review and Reputation Management: Actively managing online reviews across Google, Yelp, and industry-specific platforms that influence local search visibility and consumer trust.
The Immediate Results Fallacy
Expecting quick SEO wins is one of the most dangerous myths in digital marketing. This belief fosters unrealistic timelines, organizational disappointment, and early abandonment of strategies, ultimately derailing the long-term success SEO is built to achieve.
The Instant Gratification Trap
Digital advertising’s immediate feedback loops create unrealistic expectations for SEO timelines. Marketing managers accustomed to PPC campaigns that generate traffic within hours struggle with SEO’s gradual, compound growth patterns.
The pressure for quick results intensifies during economic uncertainty or competitive challenges. Executives facing revenue pressure may embrace SEO myths promising rapid ranking improvements rather than investing in sustainable, long-term strategies.
SEO’s Compound Nature
Genuine SEO results rarely happen overnight—most sites see noticeable ranking improvements within 3–6 months, but achieving significant gains often takes 12–18 months of steady effort. This timeline reflects how search engines evaluate content, build trust, and assess long-term value rather than immediate optimization changes.
The compound effect means early SEO investments often show minimal visible results while building foundation elements—technical optimization, content depth, authority signals—that enable dramatic improvements over time. Understanding this pattern helps organizations maintain commitment during slow initial progress periods.
Managing Expectations Professionally
Dispelling immediate results SEO myths requires transparent communication and realistic goal setting:
Leading Indicator Monitoring: Tracking early signals like crawl rate increases, indexing improvements, and content engagement rather than focusing solely on ranking changes.
Progressive Milestone Setting: Establishing quarterly objectives that build toward annual goals rather than expecting dramatic monthly improvements.
Educational Investment: Helping stakeholders understand SEO timelines, competitive factors, and algorithm evaluation processes that affect result timing.
Long-term ROI Focus: Emphasizing SEO’s exceptional long-term return on investment—$22 for every $1 spent according to industry research—rather than short-term ranking fluctuations.
The Future of SEO: Preparing for Continued Evolution
As Google continues refining its algorithms and user behavior evolves, dispelling current SEO myths prepares organizations for future changes and opportunities in search optimization.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI will increasingly support content creation, optimization, and strategy development while requiring human oversight for quality and value assurance.
Voice Search Evolution: Conversational queries and voice assistants will require content optimization for natural language and question-answering formats.
Visual Search Growth: Image and video optimization will become increasingly important as visual search capabilities expand and user adoption increases.
Entity-Based Understanding: Google’s knowledge graph evolution will emphasize entity recognition, relationships, and semantic understanding over traditional keyword matching.
Adaptive Strategy Development
Professional SEO practitioners prepare for future changes by building flexible frameworks rather than rigid tactics:
Continuous Learning Investment: Staying updated with official Google communications, industry research, and algorithm change announcements.
User-Centric Focus: Prioritizing user experience and value creation over search engine manipulation, ensuring strategies remain effective regardless of algorithm changes.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Using analytics, testing, and performance measurement to guide strategy adjustments rather than following unverified SEO myths or industry speculation.
Quality Foundation Building: Establishing strong technical infrastructure, content quality standards, and authority signals that withstand algorithm updates and competitive pressure.
Conclusion: Embracing Evidence-Based SEO in 2025
The proliferation of SEO myths in 2025 represents more than mere misinformation—it reflects an industry struggling to adapt to rapid technological change while maintaining competitive advantage. Organizations that successfully separate fact from fiction will dominate organic search results while competitors waste resources on obsolete tactics.
The emotional and financial pressure around digital marketing continues to intensify as the global SEO market surges toward an estimated $143.9 billion by 2030, highlighting the growing importance of strategic, results-driven optimization. Companies falling victim to SEO myths don’t simply lose rankings—they forfeit market share, customer acquisition opportunities, and competitive positioning that become increasingly difficult to recover.
Success in modern SEO requires intellectual humility, continuous learning, and commitment to user value over algorithmic manipulation. The most persistent SEO myths often appeal to our desire for simple solutions to complex challenges, but Google’s algorithms reward comprehensive, sustainable approaches that prioritize user experience and genuine expertise.
The path forward demands evidence-based decision making, regular strategy auditing, and willingness to abandon comfortable beliefs when data contradicts them. Organizations embracing this approach will find themselves rewarded with sustainable organic growth, while those clinging to SEO myths will watch competitors surge ahead using strategies grounded in reality rather than wishful thinking.
The choice remains clear: continue believing comforting SEO myths that promise easy solutions, or embrace the challenging but rewarding path of evidence-based optimization that actually drives results. In 2025’s competitive landscape, this decision will determine which businesses thrive and which struggle to maintain visibility in an increasingly sophisticated search environment.
You can also read:
Our most read & best Article on Marketing Strategy in the USA: 7 Digital Marketing Strategies US Companies Swear By
Frequently Asked Questions about SEO Myths
Q1: Why do SEO myths persist despite algorithm updates and industry education?
A: SEO myths persist due to several psychological and structural factors. The complexity of Google’s algorithms creates demand for simple explanations, while information lag between algorithm changes and industry understanding allows outdated practices to continue circulating. Additionally, the emotional appeal of “quick fix” solutions during stressful periods makes marketers susceptible to myth-based strategies promising immediate results.
Q2: How can I identify whether an SEO strategy is based on myths or legitimate practices?
A: Legitimate SEO practices focus on user value, align with Google’s official guidelines, and emphasize long-term sustainability over quick tricks. Be skeptical of strategies promising “guaranteed rankings,” requiring payment for specific positions, or emphasizing manipulation over value creation. Always verify claims against official Google documentation, peer-reviewed research, and credible industry sources with track records of accuracy.
Q3: What’s the most dangerous SEO myth affecting businesses in 2025?
A: The belief that “SEO is a one-time setup process” causes the most long-term damage because it prevents organizations from investing in ongoing optimization required for sustained success. This myth leads to neglected websites, outdated strategies, and gradual ranking declines as competitors implement continuous improvement approaches.
Q4: How do I convince leadership to abandon SEO myths they believe in?
A: Present data-driven evidence from credible sources, including Google’s official documentation and peer-reviewed research. Share case studies demonstrating myth-based strategy failures and evidence-based success stories. Consider bringing in external SEO consultants or attending industry conferences to provide third-party validation of modern best practices.
Q5: Are there any SEO myths that contain partial truth?
A: Yes, many SEO myths contain kernels of truth that make them particularly dangerous. For example, “backlinks matter” is true, but the myth “backlinks are the only ranking factor” oversimplifies Google’s holistic evaluation approach. Similarly, “keywords are important” is accurate, but “keyword stuffing works” represents a harmful distortion of keyword optimization principles.
Q6: How often should I audit my SEO strategy for myth-based practices?
A: Conduct comprehensive SEO audits quarterly, with monthly performance reviews to identify potential issues. Additionally, review strategies immediately following major Google algorithm updates or significant ranking changes. Stay informed about industry developments through reputable sources and be prepared to adjust tactics based on new information.
Q7: What is the role of E-E-A-T in debunking common SEO myths and improving search quality?
A: E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) provides a framework for evaluating content quality that directly contradicts many SEO myths focusing on technical manipulation over value creation. Understanding E-E-A-T helps marketers prioritize expertise demonstration and user value over outdated tactics like keyword stuffing or link schemes.
Q8: Can small businesses compete with larger companies despite believing some SEO myths?
A: Small businesses can compete effectively by focusing on local optimization, niche expertise, and personalized user experiences that larger companies struggle to replicate. However, SEO myths can be particularly damaging for small businesses with limited resources, making accurate information and efficient strategy implementation even more critical for success.
Q9: How do I stay updated on SEO best practices without falling for new myths?
A: Follow official Google communications through Search Central Blog, Google Search Liaison Twitter account, and official documentation. Subscribe to trusted SEO sources known for their rigorous editorial standards and thorough fact-checking processes. Attend industry conferences featuring speakers with verifiable track records and avoid sources making extraordinary claims without substantial evidence.
Q10: What should I do if my current SEO agency promotes myth-based strategies?
A: Address concerns directly by requesting evidence supporting their strategies and comparing their recommendations against Google’s official guidelines. If they cannot provide credible justification or continue promoting debunked tactics, consider finding agencies with stronger technical knowledge and ethical practices. Your business success depends on evidence-based optimization approaches.
Q11: How do algorithm updates affect the relevance of different SEO myths?
A: Algorithm updates often target specific manipulative practices, making certain SEO myths more dangerous over time. For example, Google’s Helpful Content System specifically penalizes low-value content, making content volume myths particularly harmful. Stay informed about update purposes and affected practices to understand which myths pose increased risks.
Q12: What resources can help me distinguish between SEO facts and myths?
A: Rely on Google’s official documentation, peer-reviewed research from academic institutions, and industry studies from reputable organizations like Moz, Ahrefs, and Search Engine Land. Cross-reference claims across multiple credible sources and be particularly skeptical of extraordinary promises or strategies that seem too good to be true.

