How AI Productivity Tools Can Radically Revolutionize Your Daily Routine
The alarm goes off at 6:30 AM, and Sarah Chen, a marketing director at a tech startup in Austin, Texas, begins what used to be a grueling daily routine. But unlike just two years ago, her workday now flows with an efficiency that seemed impossible before. Thanks to AI tools integrated throughout her workflow, she accomplishes in six hours what previously took her ten. Sarah’s story isn’t unique—it’s becoming the new normal for millions of American professionals who have embraced artificial intelligence to transform their daily work routines.
Our daily work habits are being transformed by smarter tools that help us think differently and hit our professional targets. From the bustling streets of Silicon Valley to the corporate towers of New York City, American workers are discovering that these intelligent systems don’t just automate tasks—they amplify human potential in ways that were previously unimaginable.

US AI productivity tools market projected to grow from $4.28B in 2024 to $40.5B by 2034
The Revolutionary Impact of AI Productivity Tools on American Workplaces
The numbers tell a compelling story of transformation. According to recent market analysis, the United States AI productivity tools market has reached $4.28 billion in 2024 and is projected to explode to $40.5 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate of 25.2%. This exponential growth reflects not just market enthusiasm, but the tangible impact these tools are having on everyday work experiences across America.
AI tools are fundamentally different from traditional software applications. While conventional tools require users to adapt their workflows to software limitations, AI-powered solutions adapt to human behavior, learning patterns, and preferences. They don’t just digitize existing processes—they reimagine them entirely, creating possibilities for efficiency gains that seemed like science fiction just a few years ago.
Understanding the AI Productivity Revolution
The revolution began quietly in corporate America around 2022, when generative AI technologies like ChatGPT burst onto the scene. However, the real transformation occurred when these technologies evolved from experimental novelties into sophisticated AI production tools designed specifically for workplace applications. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and OpenAI recognized that the future of work wouldn’t just involve AI as a separate tool, but as an integrated partner in daily productivity.
Research from Harvard Business School and Boston Consulting Group demonstrates the profound impact of AI productivity tools on highly skilled workers. Their comprehensive study involving over 700 consultants revealed that participants using AI showed a 38% increase in performance compared to those working without assistance. Even more remarkable was the finding that lower-skilled workers experienced the greatest benefits, with productivity gains of up to 43% when compared to their baseline performance without AI support.
When businesses implement AI production tools, the psychological benefits and changes affect workers in ways that standard efficiency data cannot capture. Workers report feeling more creative, more strategic, and less burdened by routine tasks that previously consumed valuable mental energy. Dr. Fabrizio Dell’Acqua, the lead researcher on the Harvard study, noted that AI enables professionals to “switch off their brains” from mundane activities and redirect cognitive resources toward high-value, creative problem-solving.

Productivity improvements from AI Productivity Tools across various research studies and implementations
Transforming the American Workday: From Chaos to Clarity
The transformation of daily routines through AI productivity tools becomes most apparent when we examine how these technologies reshape the fundamental structure of work itself. Traditional workdays in American offices have long been characterized by fragmented attention, endless email threads, and the constant juggling of competing priorities. AI efficiency tools are changing this reality by creating a more intentional, focused, and productive work experience.
Morning Routine Revolution
Consider how AI production tools transform the typical American morning routine. Instead of spending the first hour of the workday sorting through dozens of emails, professionals now rely on AI-powered systems like Microsoft 365 Copilot to automatically prioritize messages, summarize lengthy email threads, and even draft appropriate responses. What once required 30 minutes of careful reading and responding now takes less than 10 minutes, freeing up precious morning mental energy for more strategic thinking.
Microsoft’s internal research reveals that employees using Copilot save an average of 5.6 hours per month, with some users reporting time savings of up to 74 hours annually. For Toshiba’s 10,000 employees who deployed Microsoft 365 Copilot across their organization, the results were even more dramatic—they confirmed savings of 5.6 hours per month per employee while identifying new process improvement opportunities in procurement and document management.
The Power of Intelligent Scheduling
AI productivity tools have revolutionized how Americans manage their time and schedules. Motion, an AI-powered scheduling assistant, exemplifies this transformation by automatically organizing tasks based on priorities, deadlines, and personal working patterns. Users report saving approximately 10 hours per week that would otherwise be spent on manual calendar management and task prioritization.
The true power of automated scheduling tools isn’t just saving time, but improving the quality of attention and mental clarity they foster. When AI handles the cognitive overhead of deciding what to work on next, professionals can enter what psychologists call “flow states” more readily. These deep focus periods, which are essential for creative and analytical work, become more accessible when the friction of task switching is removed through intelligent automation.
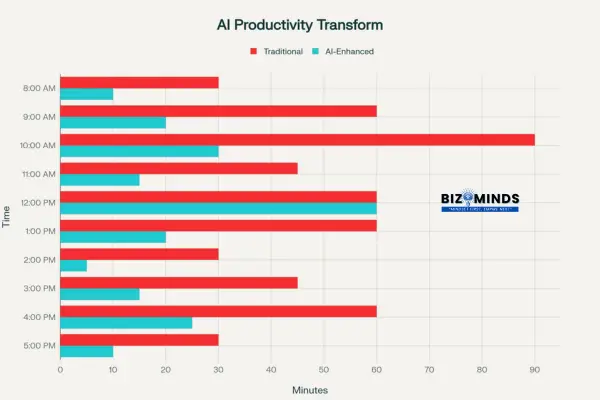
Daily workflow transformation showing time savings with AI productivity tools throughout a typical workday
Meeting Transformation through AI
Perhaps nowhere is the impact of AI production tools more immediately felt than in the realm of meetings. American professionals spend an average of 23 hours per week in meetings, yet studies consistently show that many participants feel these gatherings are unproductive. AI production tools are changing this dynamic fundamentally.
Tools like Otter.ai and Microsoft Teams’ AI features now provide real-time transcription, automatic summary generation, and action item extraction. Pennsylvania state workers using AI meeting assistance tools save an average of 95 minutes per day on routine meeting-related tasks, allowing them to deliver better services to citizens. The ripple effects extend beyond individual productivity—when meeting participants know that AI is capturing and organizing key information, they can focus more fully on creative problem-solving and strategic discussion rather than note-taking and administrative details.
Industry-Specific Applications: AI Productivity Tools across America
The adoption of AI productivity tools varies significantly across different industries, reflecting both the unique challenges and opportunities present in various sectors of the American economy. Understanding these industry-specific applications provides insight into how these technologies are reshaping the broader landscape of American business.
AI Adoption by Industry USA
| Industry | Adoption Rate | Leading US Companies | Primary Use Cases | Average ROI | Implementation Timeline |
| Technology | 79% | Microsoft, Google, Apple, Meta | Code generation, automated testing, project management | 340% | 3-6 months |
| Financial Services | 65% | JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America | Fraud detection, risk analysis, document processing | 280% | 6-12 months |
| Health & care | 58% | Mayo Clinic, Kaiser Permanente, Cleveland Clinic | Patient records, diagnosis assistance, scheduling | 220% | 9-15 months |
| Manufacturing | 52% | General Electric, Ford, Boeing, Caterpillar | Predictive maintenance, quality control, supply chain | 190% | 6-12 months |
| Retail/E-commerce | 68% | Amazon, Walmart, Target, Shopify | Customer service, inventory management, personalization | 310% | 4-8 months |
| Professional Services | 71% | McKinsey, Deloitte, PwC, Accenture | Research automation, presentation creation, client analysis | 260% | 3-6 months |
| Education | 45% | Khan Academy, Coursera, Arizona State University | Content creation, student assessment, administrative tasks | 180% | 6-9 months |
| Media & Entertainment | 63% | Netflix, Disney, Warner Bros, Spotify | Content recommendation, script writing, video editing | 250% | 4-7 months |
| Transportation | 49% | Uber, Tesla, FedEx, American Airlines | Route optimization, predictive maintenance, customer service | 200% | 8-12 months |
| Telecommunications | 61% | Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Cisco | Network optimization, customer support, service automation | 230% | 5-9 months |
Technology Sector: Leading the Innovation Charge
The technology industry leads AI adoption with a 79% implementation rate among major companies. Silicon Valley giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple haven’t just adopted AI productivity tools—they’ve fundamentally reimagined their development processes around them. Google reports that over 30% of its code is now AI-generated, representing a significant increase from 25% the previous year.
At GitHub, the impact of AI-powered coding assistance through GitHub Copilot has been transformative. Developers using the tool report 20-30% faster coding speeds, with significant improvements in code quality and reduced debugging time. The technology division of major corporations like Nykaa has seen developer productivity increase by 20% after implementing GitHub Copilot, resulting in substantial cost savings and accelerated feature releases.
Financial Services: Precision and Compliance
Financial services companies have embraced AI productivity tools with a 65% adoption rate, driven primarily by the industry’s need for precision, compliance, and risk management. JPMorgan Chase’s implementation of COIN (Contract Intelligence) represents one of the most successful applications of AI productivity enhancement. The system now accomplishes in seconds what previously required 360,000 hours of lawyer time annually, while reducing loan-servicing errors by 93%.
The transformation extends beyond large institutions to everyday banking operations. Regional banks and credit unions across America are implementing AI production tools to automate routine customer service inquiries, streamline loan processing, and enhance fraud detection capabilities. These implementations have resulted in average ROI figures of 280% within the first year of deployment.
Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care
Healthcare organizations have been more cautious in their adoption of AI production tools, with a 58% implementation rate that reflects the industry’s rightful concern for patient safety and regulatory compliance. However, when properly implemented, these tools have shown remarkable benefits. Mayo Clinic’s AI-enhanced diagnostic system improved radiologist productivity by 29.2% while reducing interpretation errors by 11%.
The administrative burden in healthcare, which traditionally consumes up to 30% of total healthcare spending, has seen efficiency improvements of 30-50% through intelligent automation of medical coding, scheduling, and documentation. For overworked healthcare professionals, AI production tools represent not just efficiency gains, but the possibility of returning focus to patient care rather than paperwork.
Manufacturing and Industrial Applications
American manufacturing companies are implementing AI productivity tools at a 52% adoption rate, with particularly strong results in predictive maintenance and quality control. General Electric’s use of AI to monitor jet engine performance across its 44,000 in-service engines demonstrates the transformative potential of these technologies. By collecting data during every flight and combining it with physical models and environmental details, GE can predict maintenance needs before problems occur, improving safety and reliability while reducing maintenance costs.
The automotive industry provides another compelling example, with companies like Ford and General Motors using AI production tools to optimize production schedules, predict equipment failures, and enhance quality control processes. These implementations have resulted in production efficiency gains of 15-35%, with some facilities reporting even higher improvements.
The Personal Transformation: Stories from American Professionals
The true measure of AI production tools lies not in corporate statistics or market projections, but in the personal transformation experienced by individual American workers. These stories reveal how AI is changing not just what we do, but how we feel about our work and our potential for professional growth.
Sarah’s Story: Marketing Director in Austin
Sarah Chen’s experience as a marketing director illustrates the profound personal impact of AI production tools. Before implementing AI assistants, Sarah’s days were consumed by routine tasks: sorting through competitor analyses, creating first drafts of marketing materials, and managing campaign schedules across multiple channels. The creative strategy work that drew her to marketing felt increasingly squeezed into the margins of her day.
After integrating AI productivity tools into her workflow, Sarah’s role evolved dramatically. AI handles the initial research and analysis, providing comprehensive competitive insights that previously required hours of manual work. Content creation tools like Jasper AI help generate first drafts of marketing copy, which Sarah then refines with her strategic expertise and brand knowledge. The result? Sarah now spends 70% of her time on strategic planning and creative direction, compared to just 30% before AI implementation.
“The most surprising thing wasn’t the time savings,” Sarah reflects. “It was how much more excited I became about my work. When AI handles the repetitive stuff, I get to focus on the problems that really matter—understanding our customers, crafting messages that resonate, and building campaigns that drive real business impact.”
David’s Journey: Financial Analyst in Chicago
David Rodriguez, a senior financial analyst at a Chicago investment firm, experienced a different but equally profound transformation. His role traditionally involved hours of data compilation, financial modeling, and report generation—work that was intellectually demanding but often repetitive. The pressure to deliver accurate analyses under tight deadlines created a constant state of stress that was affecting both his work quality and personal well-being.
The introduction of AI productivity tools transformed David’s analytical process. AI-powered data processing tools now handle initial data cleaning and basic analysis, while advanced modeling assistants help create sophisticated financial models in minutes rather than hours. Microsoft Excel’s AI features automatically identify patterns and anomalies in large datasets, allowing David to focus on interpreting results and making strategic recommendations.
“Before AI, I felt like a data processor who occasionally had insights,” David explains. “Now I feel like a strategic advisor who happens to work with data. The AI handles the mechanical work, and I focus on understanding what the numbers mean for our clients’ futures.”
Maria’s Experience: Small Business Owner in Phoenix
Maria Gonzalez owns a boutique marketing agency in Phoenix with just eight employees. For small business owners like Maria, AI productivity tools have been particularly transformative because they provide access to capabilities that were previously available only to large corporations with substantial resources.
Maria’s agency now uses AI for client research, content creation, social media management, and project coordination. Tools like Motion help optimize her team’s schedules and workloads, while AI writing assistants help create high-quality content for clients across diverse industries. The impact has been substantial—her agency now handles 40% more clients with the same team size, while maintaining higher quality standards and shorter turnaround times.
As Maria observes, AI technology has eliminated barriers and provided small businesses with the same advantages as larger competitors. “We can now compete with agencies that have 50 or 100 employees because our AI tools multiply our team’s capabilities. It’s not just about efficiency—it’s about being able to deliver enterprise-quality work as a small business.”
Implementation Strategies: Making AI Productivity Tools Work for You
Successfully implementing AI production tools requires more than simply purchasing software licenses. American companies that have achieved the greatest success with these technologies follow specific strategies that maximize both adoption rates and return on investment.
Start with Clear Objectives
The most successful AI production tools implementations begin with a clear understanding of specific productivity challenges. Rather than adopting AI for its own sake, successful organizations identify particular pain points where AI can make the greatest impact. These might include:
- Email overwhelm: Average knowledge workers spend 2.5 hours daily managing email
- Meeting inefficiency: Professionals spend 23 hours weekly in meetings, with 67% considering them unproductive
- Content creation bottlenecks: Marketing teams spend 40% of their time on routine content tasks
- Data analysis delays: Analysts spend 60% of their time gathering and cleaning data rather than interpreting it
- Scheduling conflicts: Managers spend 90 minutes weekly coordinating schedules and resolving conflicts
Phased Implementation Approach
Companies achieving the highest success rates with AI production tools typically follow a phased approach that allows for learning and adjustment. The implementation phases generally include:
Phase 1: Pilot Programs (Months 1-2)
Select a small group of enthusiastic early adopters to test AI production tools in controlled environments. Focus on tools that address the most pressing productivity challenges identified in the planning phase. Companies like Honeywell have seen success with this approach, reporting that pilot users save an average of 92 minutes per week within the first month of implementation.
Phase 2: Department-Wide Rollout (Months 3-4)
Expand successful pilots to entire departments, incorporating lessons learned from early users. Implement robust training initiatives and dedicated support systems that enable smooth transition and user adoption. Microsoft’s research indicates that companies providing formal AI training see 22% higher productivity gains compared to those relying on self-directed learning.
Phase 3: Organization-Wide Integration (Months 5-6)
Deploy AI production tools across the entire organization, with customized training programs for different roles and departments. Establish metrics and monitoring systems to track adoption and impact.
Training and Change Management
The success of AI production tools still depends heavily on human expertise and oversight during implementation. Organizations achieving the highest adoption rates invest significantly in training and change management initiatives. Key strategies include:
Comprehensive Training Programs: Companies like Telstra have deployed AI tools to 21,000 employees with remarkable success, reporting that 90% of users see improved work experiences. Their success stems partly from extensive training programs that help employees understand not just how to use AI tools, but how to integrate them effectively into their specific workflows.
Peer Learning Networks: Organizations that establish formal peer learning networks see higher adoption rates and more creative applications of AI production tools. These networks allow successful users to share best practices and help overcome implementation challenges.
Leadership Modeling: When executives and managers actively use and advocate for AI production tools, adoption rates increase significantly. Microsoft and Google have both made AI proficiency a core job requirement, with managers expected to incorporate AI usage into performance evaluations.
Measuring Success: ROI and Impact Assessment
Successful implementation of AI production tools requires comprehensive measurement systems that track both quantitative metrics and qualitative improvements. American companies leading in AI adoption have developed sophisticated frameworks for assessing the impact of these technologies.
Quantitative Metrics
Time Savings: The most immediate and measurable benefit of AI production tools is time savings. Leading companies track time savings across different categories:
- Email processing: Average reduction of 64% in time spent sorting emails
- Meeting preparation: 70% reduction in prep time through AI-generated summaries and agendas
- Content creation: 85% of users report faster creation of high-quality first drafts
- Data analysis: 27% faster information retrieval compared to traditional methods
Productivity Improvements: Beyond time savings, AI production tools deliver measurable productivity improvements:
- Overall productivity increase of 40% among regular AI users
- When workers use AI assistance, their task completion efficiency rises by 73% compared to traditional methods
- Quality improvements in 68% of AI-enhanced deliverables
Cost Reduction: The financial impact of AI production tools extends throughout organizations:
- Average operational cost reduction of 20-25% through automation
- Reduced need for outsourcing routine tasks, saving $4,000 per employee annually
- Decreased training time for new employees by 50% when AI tools are integrated into workflows
Qualitative Benefits
While quantitative metrics provide clear evidence of AI production tools effectiveness, qualitative benefits often prove equally valuable:
Enhanced Job Satisfaction: 57% of Copilot users report that AI tools help them enjoy their work more. This improvement in job satisfaction translates to lower turnover rates and higher employee engagement scores.
Increased Creativity: 72% of users report that AI assists with idea generation and creative processes. By handling routine tasks, AI production tools free mental capacity for creative and strategic thinking.
Reduced Stress: Workers report feeling less overwhelmed and more in control of their workload when AI handles routine task management and scheduling. This stress reduction contributes to better work-life balance and improved mental health.
Skill Development: Rather than replacing human capabilities, AI production tools often help employees develop new skills and expand their expertise. Finance professionals using AI tools report learning new analytical techniques, while marketers discover creative approaches they might not have considered without AI assistance.
Overcoming Challenges and Resistance
Despite the compelling benefits of AI production tools, implementation is not without challenges. Successful organizations anticipate and address these obstacles proactively, turning potential resistance into opportunities for growth and learning.
Addressing Technology Concerns
Data Privacy and Security: American companies are particularly sensitive to data privacy concerns, especially given increasing regulatory scrutiny and consumer awareness. Successful AI production tools implementations address these concerns through:
- Clear data governance policies that specify how AI tools access and use information
- Selection of AI providers with strong privacy commitments and transparent data handling practices
- Regular security audits and compliance assessments
- Employee education about data protection best practices when using AI tools
Integration Complexity: Many organizations worry about the technical complexity of integrating AI productivity tools with existing systems. Leading implementations address this through:
- Careful vendor selection prioritizing tools with robust integration capabilities
- Phased rollout approaches that allow for testing and refinement
- Partnership with experienced implementation consultants when necessary
- Investment in IT infrastructure upgrades when required
Managing Cultural Resistance
Job Displacement Fears: Perhaps the most significant challenge in implementing AI productivity tools is addressing employee concerns about job security. Research indicates that 35% of workers worry about workforce displacement from AI technologies. Successful organizations address these concerns by:
- Ensure messaging highlights that AI tools serve to empower human capabilities instead of replacing human roles
- Providing evidence from early implementations showing job enhancement rather than elimination
- Offering reskilling and upskilling opportunities to help employees adapt to AI-enhanced roles
- Involving employees in AI tool selection and implementation processes
Resistance to Change: Some employees resist adopting AI productivity tools due to comfort with existing workflows or skepticism about technology benefits. Organizations overcome this resistance through:
- Demonstrating immediate, tangible benefits through pilot programs
- Providing comprehensive training and support during transition periods
- Recognizing and celebrating employees who successfully adopt AI tools
- Making AI proficiency part of performance evaluation and career advancement criteria
Looking Forward: The Future of AI Productivity Tools
As AI productivity tools continue to evolve, American workplaces are poised for even more dramatic transformations. Understanding emerging trends and preparing for future developments will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantage.
Emerging Technologies and Capabilities
Multimodal AI Integration: The next generation of AI productivity tools will seamlessly integrate text, voice, image, and video capabilities. Google’s upcoming AI Ultra for Business includes tools like Flow for AI filmmaking and Whisk for image-to-video creation, suggesting a future where AI assists with increasingly sophisticated creative tasks.
Predictive Workflow Optimization: Advanced AI productivity tools will anticipate user needs and proactively suggest optimizations. Rather than simply responding to requests, these systems will identify productivity bottlenecks and recommend solutions before problems occur.
Collaborative AI Agents: Future AI productivity tools will feature multiple specialized agents that collaborate on complex projects, much like human teams. These agents will coordinate their activities, share information, and collectively deliver comprehensive solutions to business challenges.
Preparing for Continued Evolution
Skills Development: As AI productivity tools become more sophisticated, human skills requirements will continue evolving. Successful professionals will focus on developing:
- AI prompt engineering and optimization skills
- Strategic thinking and creative problem-solving capabilities
- Emotional intelligence and interpersonal communication
- Adaptability and continuous learning mindsets
Organizational Adaptation: Companies that thrive with AI productivity tools will develop organizational structures and cultures that maximize human-AI collaboration:
- Flatter organizational hierarchies that enable rapid decision-making and adaptation
- Cross-functional teams that leverage diverse AI tool expertise
- Continuous learning cultures that embrace technological change
- Performance management systems that reward AI-enhanced productivity
Ethical Considerations: As AI productivity tools become more powerful and pervasive, organizations must address ethical considerations:
- Ensuring AI tools enhance rather than replace human judgment in critical decisions
- Maintaining transparency about AI usage in customer-facing processes
- Addressing potential biases in AI-generated content and recommendations
- Balancing efficiency gains with human values and relationships
Conclusion: Embracing the AI Productivity Revolution
The adoption of AI productivity tools in U.S. workplaces marks not just a tech upgrade but a fundamental evolution in how work, productivity, and human capability are perceived. From the technology corridors of Silicon Valley to the financial districts of New York, from small businesses in Phoenix to manufacturing facilities in Detroit, AI productivity tools are enabling professionals to accomplish more meaningful work with greater efficiency and satisfaction.
The evidence is overwhelming: AI productivity tools deliver substantial productivity improvements, cost savings, and quality enhancements across industries and job functions. More importantly, they’re helping American workers rediscover the aspects of their jobs that originally drew them to their careers—the creative, strategic, and interpersonal elements that make work fulfilling rather than merely transactional.
As we look toward the future, the question is not whether AI productivity tools will continue to transform American workplaces, but how quickly and effectively organizations will adapt to maximize their benefits. The companies and professionals who embrace this transformation thoughtfully, with attention to both technological capabilities and human values, will find themselves at the forefront of a new era of productivity and professional fulfillment.
The revolution is not just about working faster or cheaper—it’s about working smarter, with greater purpose, and with enhanced ability to create value for customers, colleagues, and society. For American professionals willing to embrace the possibilities of AI productivity tools, the future of work has never looked more promising.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What exactly are AI productivity tools and how do they differ from regular software?
AI productivity tools are software applications that use artificial intelligence to learn from your behavior, predict your needs, and automatically handle routine tasks. Unlike traditional software that requires you to adapt to its interface and workflows, AI tools adapt to your working style. For example, while a traditional calendar app simply stores appointments, an AI-powered scheduling tool like Motion automatically finds optimal meeting times, blocks focus periods, and adjusts your schedule when priorities change. The key difference is that AI tools get smarter over time, learning your preferences and improving their assistance without requiring manual configuration.
2. Are AI productivity tools safe to use with confidential business information?
Leading AI productivity tools designed for business use implement enterprise-grade security measures including data encryption, secure cloud storage, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Companies like Microsoft and Google invest billions in security infrastructure for their AI tools. However, it’s important to review each tool’s privacy policy and data handling practices. Many tools offer on-premises deployment options for organizations with strict data security requirements. Always ensure your organization’s IT department approves any AI tool before using it with sensitive information.
3. How affordable are AI productivity tools for small enterprises, and what is their typical price?
AI productivity tools range from free basic versions to enterprise solutions costing hundreds per user monthly. For small businesses, popular tools cost between $5-30 per user per month. For example, ChatGPT Plus costs $20 monthly, Grammarly Premium is $12 monthly, and Notion AI is $8 per member monthly. Many AI platforms feature no-cost entry levels with essential features, helping small enterprises test AI technology without heavy upfront spending. The ROI typically justifies these costs—businesses report saving 4-10 hours per employee weekly, which translates to thousands in productivity value.
4. Will AI productivity tools eliminate jobs or just change how we work?
Research consistently shows that AI productivity tools enhance rather than eliminate jobs, though they do change job requirements. A Harvard/MIT study found that AI tools primarily automate routine tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-value activities like strategy, creativity, and relationship building. While some specific tasks may become obsolete, new roles emerge that require human judgment, emotional intelligence, and AI collaboration skills. Companies implementing AI tools typically see job transformation rather than job elimination, with employees moving into more strategic and satisfying roles.
5. Which AI productivity tools should beginners start with?
For beginners, start with AI productivity tools that address your biggest daily challenges. If email overwhelm is your issue, try Google’s Smart Reply or Microsoft Copilot for Outlook. For writing assistance, Grammarly offers immediate value with minimal learning curve. ChatGPT is excellent for research, brainstorming, and general productivity tasks. For meeting management, Otter.ai provides transcription and summaries. Start with one tool, master it completely, then gradually add others. This approach prevents overwhelm and allows you to experience tangible benefits quickly.
6. How can I measure whether AI productivity tools are actually helping my productivity?
Assess AI productivity tools by considering measurable data alongside user experience and feedback. Quantitatively, measure time savings on specific tasks (like email processing or report writing), work completion rates, and overall daily productivity. Most AI tools provide usage analytics showing time saved and tasks completed. Qualitatively, assess your stress levels, job satisfaction, and ability to focus on strategic work. Keep a simple log for two weeks before and after implementing AI tools, noting daily accomplishments and energy levels. Many users report that while time savings are valuable, the reduction in mental fatigue is equally important.
7. What skills should I develop to work effectively with AI productivity tools?
To maximize AI productivity tools, develop these key skills: prompt engineering (crafting effective instructions for AI), critical thinking (evaluating AI outputs for accuracy and relevance), and digital literacy (understanding how AI works and its limitations). Communication skills become more important as AI handles routine tasks and you focus on strategic work. Learn to think in terms of workflows rather than individual tasks—AI tools excel when integrated into comprehensive work processes. Most importantly, maintain a growth mindset and willingness to experiment with new tools and approaches.
8. How do I convince my team or boss to adopt AI productivity tools?
Present AI productivity tools adoption as a business case focused on specific, measurable benefits. Identify your organization’s biggest productivity pain points and research which AI tools address those issues. Propose a small pilot program with measurable goals, such as reducing meeting prep time by 50% or increasing content creation efficiency by 30%. Share success stories from similar companies in your industry. Start by implementing free or low-cost tools to demonstrate value before requesting budget for premium solutions. Focus on how AI tools will help the team accomplish strategic objectives rather than just saving time.
9. Can AI productivity tools work effectively for creative industries?
AI productivity tools are particularly powerful for creative industries because they handle routine tasks that consume creative energy. Designers use AI for initial concept generation, color palette suggestions, and asset organization, freeing time for strategic design thinking. Writers use AI for research, first drafts, and editing, then apply their expertise for refinement and brand voice. Marketing teams use AI for campaign ideation, content variations, and performance analysis. The key is using AI as a creative partner that handles mechanical work while humans focus on strategy, brand alignment, and emotional resonance.
10. What are the top mistakes businesses make when implementing AI productivity tools initially?
Common mistakes with AI productivity tools include trying to implement too many tools simultaneously, expecting AI to work perfectly without guidance, and not investing time in learning prompt engineering. Many users also make the mistake of using AI tools in isolation rather than integrating them into comprehensive workflows. Another frequent error is not establishing clear boundaries—knowing when to rely on AI versus human judgment. Finally, some users become overly dependent on AI for tasks that require human creativity or emotional intelligence. Start slowly, learn each tool thoroughly, and maintain critical thinking about when AI assistance is appropriate.
11. How do AI productivity tools handle different industries’ compliance requirements?
Enterprise AI productivity tools are designed with industry compliance in mind. Healthcare AI tools comply with HIPAA regulations, financial services tools meet SOX and other banking requirements, and legal industry tools maintain attorney-client privilege protections. Major providers like Microsoft and Google offer compliance certifications and detailed documentation about data handling practices. Many tools provide audit trails showing how data is processed and stored. For highly regulated industries, look for tools that offer on-premises deployment or private cloud options. Always work with your compliance team to evaluate any AI tool before implementation.
12. What’s the future outlook for AI productivity tools in American workplaces?
The future of AI productivity tools in American workplaces looks exceptionally promising, with the market projected to grow from $4.28 billion to $40.5 billion by 2034. Emerging trends include multimodal AI that combines text, voice, and visual capabilities, predictive workflow optimization that anticipates needs before they arise, and collaborative AI agents that work together on complex projects. We’ll see AI tools becoming more specialized for specific industries and job functions while remaining easy to use. The focus will shift from basic automation to intelligent collaboration, where AI tools become true partners in strategic thinking and creative problem-solving.

