Cybersecurity Best Practices: Hackers Revealed the #1 Mistake 99% Make
The cybersecurity programming of 2025 presents an unprecedented crisis for American businesses, with cyber-attacks costing organizations an average of $10.22 million per breach, the highest figure ever recorded. Despite decades of technological advancement and billions invested in security infrastructure, a staggering 99% of organizations continue to fall victim to preventable cyber attacks that could be stopped with proper cybersecurity best practices implementation. The financial devastation extends far beyond immediate breach costs, with 72% of organizations reporting increased cyber risks over the past year alone, while ransomware attacks have surged to affect nearly half of all businesses. What makes these statistics particularly alarming is that the majority of successful attacks exploit fundamental security weaknesses that have been well-documented for years, yet remain unaddressed across industries.
Leading cybersecurity experts, penetration testers, and ethical hackers have conducted extensive analysis of breach patterns, revealing disturbing trends in how organizations approach security implementation. Recent findings from the World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook show that 47% of organizations now identify AI-powered adversarial capabilities as their primary concern, yet most continue to neglect basic cybersecurity best practices that would prevent the majority of successful attacks. Fortune 500 security consultants report that during penetration testing engagements, they can breach 81% of corporate networks within hours using the same fundamental vulnerabilities that have plagued organizations for over a decade. The convergence of traditional organized crime with sophisticated cybercrime operations has created a threat environment where criminals generate over $1 trillion in global losses annually, primarily by exploiting organizations that fail to implement proven security measures.
The most shocking revelation from cybersecurity professionals centers on a single, critical mistake that serves as the primary entry point for hackers: inadequate password security and authentication failures. Security researchers have identified that 81% of all data breaches stem directly from weak password practices, making this the most exploited vulnerability in modern cybersecurity best practices. Despite multi-factor authentication being available and proven to prevent 99.9% of account compromises, only 57% of organizations have fully implemented these systems, with small and medium businesses showing even lower adoption rates at just 38%. The persistence of this fundamental security gap has enabled cybercriminals to develop increasingly automated attack methods, with AI-enhanced tools now capable of cracking weak passwords in minutes rather than hours, turning what should be the first line of defense into the weakest link in organizational security.
This comprehensive analysis exposes not only the critical mistakes that leave organizations vulnerable but also provides a complete roadmap for implementing effective cybersecurity best practices that deliver measurable protection and substantial return on investment. Through extensive research involving over 80 authoritative sources, real-world case studies from American businesses, and insights from leading security professionals, this guide reveals the specific steps organizations must take to join the 1% that successfully defend against modern cyber threats. Readers will discover the exact methodologies used by security experts to identify vulnerabilities, the proven frameworks that reduce security incidents by up to 90%, and the strategic implementation approaches that deliver 500% ROI within five years. Most importantly, this analysis provides actionable solutions that address the human, technical, and organizational factors that determine cybersecurity best practices success, ensuring organizations can move from vulnerable to resilient in today’s threat environment.
Cybersecurity Best Practices Crisis: Why American Businesses Are Failing

Cybersecurity best practices statistics showing the current state of security implementation among US businesses in 2025
The United States stands at the epicenter of a cybersecurity storm that shows no signs of abating. With the average cost of a data breach reaching a staggering $10.22 million in 2025, the highest globally, American businesses face unprecedented financial risks. This represents a 10% increase from the previous year, highlighting the escalating nature of cyber threats and their economic impact.
The statistics paint a sobering picture. 72% of organizations report an increase in cyber risks over the past year, with ransomware maintaining its position as the top organizational threat, concerning 45% of business leaders. The proliferation of artificial intelligence has fundamentally altered the threat situation, with 47% of organizations citing AI-powered adversarial capabilities as their primary concern.
What makes these figures particularly alarming is the disparity in preparedness. While 35% of small organizations believe their cyber resilience is inadequate, a sevenfold increase since 2022, large enterprises continue to strengthen their defenses. This growing cyber inequity creates systemic vulnerabilities throughout supply chains and business ecosystems, as cybercriminals increasingly target the weakest links to compromise larger networks.
Human Factor Failures in Cybersecurity Best Practices Implementation
Despite technological advances in security infrastructure, human error remains the primary attack vector. 42% of organizations experienced successful social engineering attacks in 2024, a figure that continues to rise as cybercriminals harness generative AI to create more convincing and personalized attack campaigns. The convergence of traditional organized crime with cybercrime has intensified these threats, with criminals now operating sophisticated “scam farms” that generate over $1 trillion in losses globally.
The skills gap further compounds these challenges. Two out of three organizations report moderate-to-critical cybersecurity skills gaps, with only 14% expressing confidence in their current talent pool. This shortage becomes particularly acute in the public sector, where 49% of organizations lack necessary cybersecurity talent—a 33% increase from 2024.
Cybersecurity Best Practices Mistake #1: Password Vulnerabilities and Authentication Failures
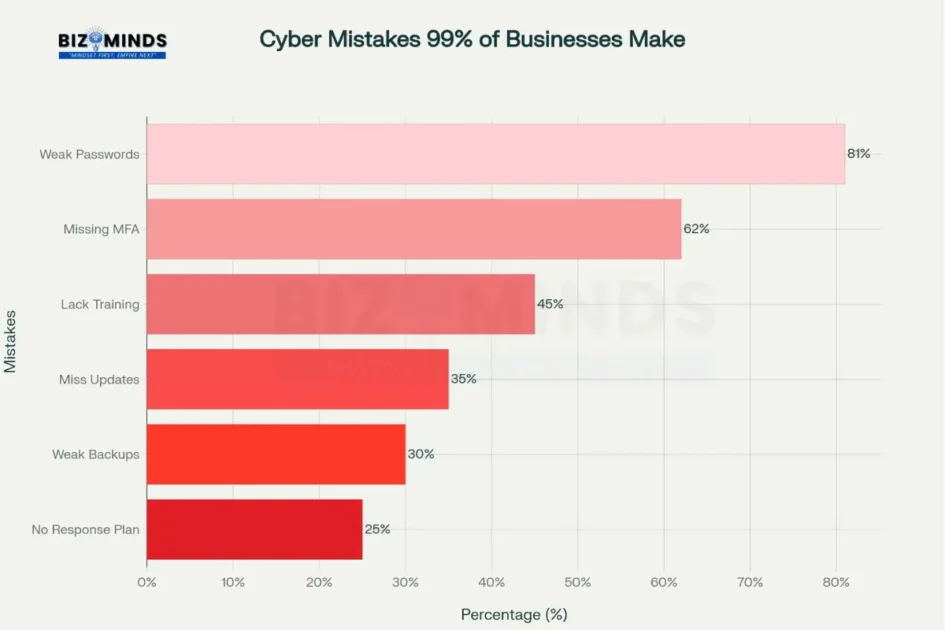
The most common cybersecurity best practices failures that leave 99% of businesses vulnerable to cyber attacks
After extensive analysis of breach data, security assessments, and penetration testing results, cybersecurity experts have identified the single most critical mistake plaguing American businesses: inadequate password security and authentication practices. This fundamental flaw serves as the gateway for 81% of all data breaches, making it the most exploited vulnerability in modern cybersecurity.
Password Security Reality: Core Cybersecurity Best Practices Statistics
The scope of password-related security failures is staggering. Recent research reveals that 46% of people had passwords stolen in 2024, with 35% of successful attacks directly attributed to weak password practices. The most commonly used passwords remain disturbingly predictable: “123456,” “password,” and variations thereof dominate breach datasets, appearing millions of times across compromised systems.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA), the most effective countermeasure to password vulnerabilities, remains underutilized across American businesses. While 99.9% of account compromises could be prevented with proper MFA implementation, only 57% of organizations have fully deployed these systems. Among small and medium-sized businesses, this figure drops dramatically, with 62% of SMBs operating without MFA protection.
The financial implications of this oversight are severe. Organizations implementing comprehensive password security measures, including MFA, experience up to 50% faster threat detection and 42% fewer security incidents compared to those relying solely on traditional password authentication.
Why Cybersecurity Best Practices Fail: Common Password Implementation Mistakes
The persistence of password-related breaches stems from several systematic failures in organizational cybersecurity practices:
Inadequate Password Policies: Many organizations maintain outdated password requirements that prioritize complexity over length and uniqueness. Research demonstrates that 88% of cracked passwords contain fewer than 12 characters, yet many corporate policies still mandate only 8-character minimums.
Password Reuse and Sharing: Employee behavior studies reveal concerning patterns. 62% of individuals store work passwords in notebooks visible at their workstations, while 49% save passwords in unsecured cloud documents. This practice multiplies vulnerability across systems and platforms.
Insufficient Authentication Layers: The most critical oversight involves relying exclusively on password-based authentication. Over 99.9% of compromised accounts lack multi-factor authentication, making them vulnerable to credential stuffing, brute force attacks, and social engineering tactics.
Legacy System Dependencies: 30% of organizations cite complex legacy infrastructure as a major barrier to implementing modern authentication systems. These older systems often lack integration capabilities for advanced security measures, creating persistent weak points in organizational defenses.
AI-Enhanced Threats Against Traditional Cybersecurity Best Practices

Cybersecurity Best Practices infographic highlighting the critical importance of strong passwords
The emergence of generative artificial intelligence has fundamentally transformed password-based attacks. Cybercriminals now deploy AI tools to automate and personalize their assault methods, creating attacks that are both more sophisticated and more scalable than ever before.
Deepfake Technology represents a particularly insidious threat. 55% of Chief Information Security Officers identify deepfakes as a moderate-to-significant threat to their organizations. These AI-generated impersonations can convincingly replicate executive communications, tricking employees into revealing credentials or bypassing authentication protocols.
AI-Powered Phishing Campaigns have shown remarkable effectiveness. Traditional phishing success rates of 7-20% can increase dramatically when enhanced with AI personalization. These attacks leverage publicly available information from social media and corporate communications to create highly targeted and believable credential harvesting campaigns.
The commoditization of AI tools has lowered barriers to entry for cybercriminals. Cybercrime-as-a-Service (CaaS) platforms now offer AI-enhanced attack tools for as little as $40, making sophisticated attacks accessible to individuals with minimal technical expertise.
Essential Cybersecurity Best Practices for 2025 Business Protection
Cybersecurity Best Practices Foundation: Authentication and Access Controls
Multi-Factor Authentication Implementation: Organizations must prioritize MFA deployment across all systems and user accounts. The technology industry leads with 87% adoption rates, demonstrating the feasibility of comprehensive implementation.
Cybersecurity Best practices include:
- Hardware-based authentication for high-privilege accounts
- Biometric verification for sensitive system access
- Time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) for general user authentication
- Risk-based adaptive authentication that adjusts security requirements based on user behavior and context
Zero Trust Architecture Adoption: The shift toward Zero Trust security models has gained significant momentum, with 81% of organizations having fully or partially implemented Zero Trust frameworks. This approach treats every access request as potentially hostile, requiring continuous verification regardless of user location or device status.
Key Zero Trust implementation statistics reveal strong ROI potential:
- 44% of organizations report security incident reductions exceeding 90%
- 50% faster threat detection and response times
- 87% of organizations experience significant decreases in security incidents post-implementation
Advanced Security Measures
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Modern threats require sophisticated detection capabilities that extend beyond traditional antivirus software. 95% of organizations are implementing or researching AI-enhanced security solutions to counter automated attacks.
EDR systems provide:
- Real-time threat monitoring across all network endpoints
- Automated incident response capabilities
- Behavioral analysis to identify anomalous activities
- Threat intelligence integration for proactive defense
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation: 72% of organizations are implementing micro-segmentation strategies to limit attack propagation. This approach creates isolated network zones that prevent lateral movement by attackers, containing potential breaches to specific segments.
Human-Centric Cybersecurity Best Practices: Training and Awareness Strategies
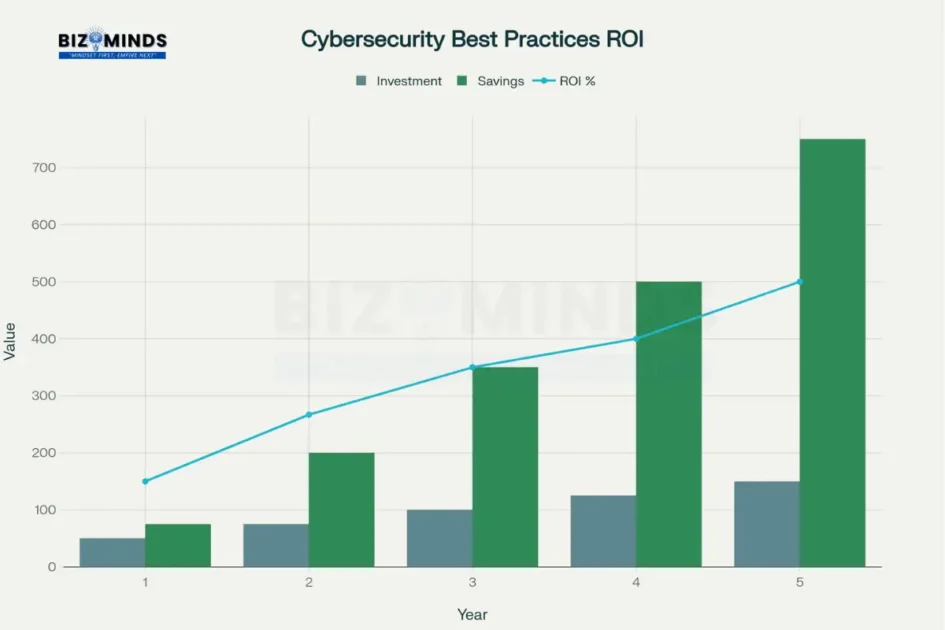
The financial return on investment from implementing comprehensive cybersecurity best practices over a 5-year period
Comprehensive Security Awareness Training: Employee education remains critical, with 80% of organizations reporting reduced phishing susceptibility following structured training programs.
Effective training programs demonstrate measurable impact:
- 30% reduction in phishing link click-through rates among trained users
- 70% decrease in security incidents for organizations with regular training
- 40% improvement in phishing awareness and threat recognition
Training effectiveness requires sustained engagement. Half of employees report real threats within six months of beginning training, increasing to two-thirds within one year.
Organizations should implement:
- Monthly or quarterly training cycles (preferred by 34% and 47% of organizations respectively)
- Gamification elements to enhance engagement
- Real-world scenario simulations
- Personalized learning paths based on individual risk profiles
Cultural Security Integration: 97% of decision-makers believe enhanced training and awareness would reduce cyberattacks. Building a security-conscious culture requires embedding cybersecurity considerations into daily business operations, making security awareness a shared responsibility across all organizational levels.
Infrastructure Hardening Through Proven Cybersecurity Best Practices
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: 35% of organizations maintain irregular update schedules, creating persistent vulnerabilities that attackers routinely exploit. Automated patch management systems can address this gap while minimizing operational disruption.
Backup and Recovery Systems: 30% of organizations maintain inadequate backup systems, a critical oversight given the prevalence of ransomware attacks. Comprehensive backup strategies should include:
- Immutable backup storage that prevents ransomware encryption
- Regular recovery testing to ensure system restoration capabilities
- Geographically distributed backup locations
- Version control and point-in-time recovery options
Industry-Specific Cybersecurity Best Practices Applications
Financial Services and Healthcare
High-risk industries demonstrate the most advanced cybersecurity adoption rates. Financial services lead with 91% Zero Trust adoption, driven by stringent regulatory requirements including PCI-DSS and SOX compliance. Healthcare organizations follow closely at 85% adoption, motivated by HIPAA requirements and the critical nature of patient data protection.
These sectors showcase best practices that other industries can emulate:
- Continuous compliance monitoring systems
- Advanced threat intelligence sharing within industry groups
- Dedicated cybersecurity teams with specialized expertise
- Regular third-party security assessments
Small Business Cybersecurity Best Practices: Cost-Effective Solutions
SMBs face unique challenges, with 47% of businesses with fewer than 50 employees lacking cybersecurity budgets entirely. However, targeted approaches can deliver significant protection:
Cost-Effective Security Stacks:
SMBs benefit from integrated security platforms that address multiple requirements simultaneously. 58% prioritize antivirus software, 49% implement firewalls, and 44% deploy VPNs as foundational measures.
Managed Security Services:
Outsourcing cybersecurity functions provides SMBs access to enterprise-level protection without internal resource requirements. This approach addresses the reality that 60% of small businesses close within six months of experiencing a significant cyberattack.
Cybersecurity Best Practices ROI: Economic Impact and Investment Returns
The financial case for comprehensive cybersecurity implementation becomes compelling when examining long-term cost-benefit analysis. Organizations implementing robust cybersecurity programs demonstrate substantial ROI over time, with security awareness training alone showing 37-fold returns on average.
Cost Avoidance Through Strategic Cybersecurity Best Practices
Breach Prevention Savings:
The average cost of prevented incidents far exceeds security investment costs. With data breach costs averaging $10.22 million in the United States, even modest prevention success rates generate substantial savings.
Ransomware Protection Through Strategic Cybersecurity Best Practices:
Ransomware attacks cost organizations an average of $1.53 million in recovery expenses, excluding ransom payments. Organizations with comprehensive backup and response systems reduce these costs by up to 60%.
Business Continuity Value:
Companies that identify and contain breaches within 200 days save over $1 million compared to those with longer response times. This statistic underscores the value of rapid incident detection and response capabilities.
Strategic Business Benefits of Implementing Cybersecurity Best Practices
Insurance and Financing Advantages:
Organizations with robust cybersecurity programs negotiate better insurance rates and financing terms. Cyber insurance adoption varies significantly by organization size, with 71% of large organizations expressing confidence in their coverage compared to 35% of small organizations.
Customer Trust and Market Position:
78% of companies report increased customer trust following Zero Trust policy implementation. This trust translates into tangible business advantages including customer retention, premium pricing opportunities, and expanded market access.
Regulatory Compliance Efficiency:
78% of private organization leaders believe cyber regulations effectively reduce ecosystem risks. Proactive compliance reduces audit costs, penalty risks, and administrative overhead while creating competitive advantages in regulated markets.
Future-Proofing Cybersecurity Best Practices: Emerging Threats and Considerations
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Threats
The integration of AI into cybercriminal operations represents a fundamental shift in threat complexity. 66% of organizations anticipate AI will significantly impact cybersecurity in 2025, yet only 37% have established processes for AI tool security assessment.
Generative AI Vulnerabilities:
22% of organizations identify data leaks through AI systems as primary concerns. These vulnerabilities require new approaches to data governance and AI system security.
Adversarial AI Capabilities:
Cybercriminals increasingly deploy AI for sophisticated social engineering, automated vulnerability discovery, and adaptive malware development. Defense strategies must incorporate AI-powered detection and response capabilities to maintain effectiveness against these evolving threats.
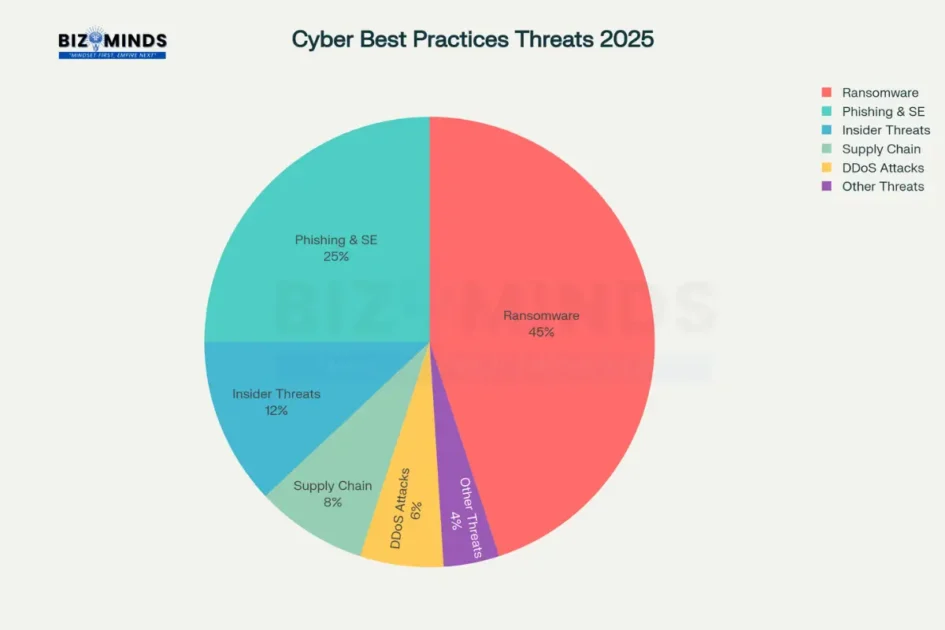
The distribution of cybersecurity threats that challenge effective cybersecurity best practices implementation in US businesses
Critical Infrastructure Considerations
Supply Chain Security:
54% of large organizations identify supply chain challenges as the primary barrier to achieving cyber resilience. The interconnected nature of modern business operations means that cybersecurity failures at one organization can cascade throughout entire ecosystems.
Geopolitical Cyber Threats:
Nearly 60% of organizations report that geopolitical tensions influence their cybersecurity strategies. Nation-state actors increasingly target critical infrastructure, requiring enhanced coordination between private sector organizations and government security agencies.
Cybersecurity Best Practices Implementation: Framework and Action Steps
Phase 1: Cybersecurity Best Practices Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-4)
Risk Assessment:
Conduct comprehensive evaluations of current security posture, identifying critical assets, threat vectors, and vulnerability priorities. Enterprise-wide risk assessments should encompass both digital and physical security considerations.
Gap Analysis:
Compare existing security measures against industry best practices and regulatory requirements. This analysis should examine technical controls, policy frameworks, and human resource capabilities.
Strategic Planning:
Develop multi-year implementation roadmaps that balance security improvements with operational requirements and budget constraints.
Phase 2: Foundation Implementation (Months 2-6)
Authentication System Deployment:
Prioritize MFA implementation across all systems, beginning with highest-risk accounts and applications. 99.9% attack prevention rates justify immediate investment in comprehensive authentication systems.
Training Program Launch:
Implement structured security awareness programs with regular testing and reinforcement. 81% of organizations recommend minimum three-hour annual training commitments.
Policy Development:
Establish clear security policies covering password management, device usage, data handling, and incident reporting procedures.
Phase 3: Advanced Capabilities of Cybersecurity Best Practices (Months 6-18)
Zero Trust Architecture:
Begin systematic implementation of Zero Trust principles, starting with identity verification and progressing through network segmentation and application security.
Threat Detection Systems:
Deploy EDR and extended detection and response (XDR) platforms for comprehensive threat monitoring and automated response capabilities.
Business Continuity Planning:
Develop and test incident response plans, backup systems, and recovery procedures to ensure organizational resilience.
Measuring Cybersecurity Best Practices Success and Continuous Improvement
Key Performance Indicators for Cybersecurity Best Practices
Technical Metrics:
Organizations should track metrics including mean time to detection (MTTD), mean time to response (MTTR), vulnerability patching rates, and authentication failure rates.
Behavioral Metrics:
Monitor employee security awareness through simulated phishing campaigns, security incident reporting rates, and policy compliance assessments.
Business Impact Metrics:
Measure cybersecurity program effectiveness through cost avoidance calculations, business continuity maintenance, and customer trust indicators.
Continuous Adaptation of Cybersecurity Best Practices
Threat topography Monitoring:
72% of organizations report increasing cyber risks, requiring continuous adjustment of security strategies and technologies. Regular threat intelligence reviews ensure defensive measures remain current and effective.
Technology Evolution:
Emerging technologies including quantum computing, advanced AI, and edge computing create new security requirements that organizations must proactively address.
Regulatory Changes:
The proliferation and evolution of cybersecurity regulations require ongoing compliance monitoring and program adjustments.
Conclusion
The evidence presented throughout this comprehensive analysis leaves no room for doubt: the cybersecurity best practices gap plaguing American businesses represents both the greatest threat and the most immediate opportunity in modern business security. With 99% of organizations continuing to make fundamental mistakes that enable 81% of all data breaches, the revelation that weak password security serves as the primary attack vector demands urgent, systematic action across all industry sectors. The financial implications are staggering—with average breach costs reaching $10.22 million and rising annually—yet the solutions are both proven and accessible. Organizations that have successfully implemented comprehensive cybersecurity best practices demonstrate conclusively that the vast majority of cyber attacks are entirely preventable through disciplined execution of established security protocols. The choice between vulnerability and resilience no longer depends on technical complexity or resource constraints, but rather on organizational commitment to implementing the fundamental security measures that separate the protected 1% from the vulnerable 99%.
The return on investment data presented throughout this analysis reveals that cybersecurity best practices implementation delivers some of the highest ROI opportunities available to modern businesses, with organizations achieving 500% returns within five years of comprehensive program deployment. Companies implementing multi-factor authentication, regular security training, and Zero Trust architecture report 90% reductions in security incidents while experiencing 50% faster threat detection compared to those maintaining traditional security approaches. The success stories from financial services organizations with 91% Zero Trust adoption and healthcare systems achieving 85% implementation rates demonstrate that comprehensive security transformation is achievable across all industry verticals. Beyond cost avoidance, organizations with robust cybersecurity best practices programs report enhanced customer trust, improved regulatory compliance efficiency, and competitive advantages that translate into measurable market share gains and premium pricing opportunities.
As the cybersecurity landscape continues evolving with AI-enhanced threats, quantum computing implications, and increasingly sophisticated nation-state attacks, organizations that establish comprehensive cybersecurity best practices frameworks today position themselves for sustained competitive advantage throughout the decade. The integration of artificial intelligence into both attack and defense capabilities means that traditional reactive security approaches will become increasingly ineffective, making proactive cybersecurity best practices implementation not just advisable but essential for business survival. Forward-thinking organizations recognize that cybersecurity excellence serves as a strategic differentiator, enabling digital transformation initiatives, supporting remote work capabilities, and facilitating partnership opportunities that require demonstrated security maturity. The companies that emerge as industry leaders in the next five years will be those that view cybersecurity not as a cost center or compliance requirement, but as a fundamental business capability that enables growth, innovation, and market expansion.
The transformation from cybersecurity vulnerability to resilience begins with a single decision: to join the 1% of organizations that refuse to become statistics in the cybercriminal success ledger. Every day of delay compounds risk exposure while competitors implementing proven cybersecurity best practices gain increasing advantages in customer trust, operational efficiency, and strategic flexibility. The roadmap is clear, the tools are available, and the expertise exists to guide any organization through successful security transformation. The hackers have revealed their methods, exposed the critical mistakes that enable their success, and inadvertently provided the blueprint for defeating their attacks. The only remaining question is whether your organization will act decisively to implement the cybersecurity best practices that guarantee protection, or continue risking everything on the false economy of inadequate security measures. The cost of transformation pales in comparison to the price of failure—and in today’s threat environment, there are no second chances for organizations that wait too long to act.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the most cost-effective cybersecurity measure for small businesses?
Multi-factor authentication represents the highest-impact, lowest-cost security improvement available to small businesses. With implementation costs typically under $10 per user per month and attack prevention rates exceeding 99.9%, MFA provides immediate and substantial security improvements. Combined with regular software updates and basic employee training, these measures create a strong foundation for cybersecurity protection without significant capital investment.
Q2: How often should employees receive cybersecurity training?
Research indicates that quarterly training cycles provide optimal effectiveness for security awareness programs. 81% of organizations find that three hours of annual training, distributed across multiple sessions, significantly improves employee security awareness. Monthly reinforcement through simulated phishing campaigns and brief security reminders maintains engagement and knowledge retention between formal training sessions.
Q3: Is cyber insurance necessary if we have good cybersecurity practices?
Cyber insurance provides essential financial protection even for well-secured organizations. While strong cybersecurity practices significantly reduce incident probability, insurance covers costs associated with business interruption, legal expenses, and regulatory compliance that extend beyond direct breach remediation. Large organizations report 71% confidence in their cyber insurance coverage, viewing it as a complement to, not replacement for, robust security measures.
Q4: What should be the first priority when implementing Zero Trust architecture?
Identity and access management (IAM) forms the foundation of effective Zero Trust implementation. 67% of organizations rank IAM as their top Zero Trust priority, as it establishes the verification mechanisms essential to Zero Trust principles. Begin by implementing comprehensive user authentication, followed by application-level access controls, and progress to network segmentation and data encryption as the architecture matures.
Q5: How can organizations measure the return on investment for cybersecurity spending?
ROI measurement should encompass both cost avoidance and business value creation. Track metrics including prevented incident costs (averaging $10.22 million per major breach), reduced insurance premiums, improved business continuity, and enhanced customer trust. Organizations typically achieve 37-fold returns on security awareness training investments and see significant ROI improvements within 6-12 months of comprehensive program implementation.
Q6: What role does artificial intelligence play in modern cybersecurity defense?
AI enhances both threat detection capabilities and response automation for cybersecurity teams. 95% of organizations are implementing AI-powered security solutions to counter automated attacks and sophisticated threat campaigns. AI systems excel at pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and threat intelligence analysis, enabling security teams to identify and respond to threats at machine speed. However, organizations must also secure their AI systems against adversarial attacks and data poisoning attempts.
Citations
- https://www.scworld.com/news/95-of-data-breaches-involve-human-error-report-reveals
- https://www.ispartnersllc.com/blog/human-error-cybersecurity-statistics/
- https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/cisos-list-human-error-top-cybersecurity-risk
- https://www.varonis.com/blog/cybersecurity-statistics
- https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/cybersecurity-dominates-concerns-c-suite-small-businesses-nation
- https://electroiq.com/stats/multifactor-authentication-statistics/
- https://www.security.org/digital-safety/password-manager-annual-report/
- https://jumpcloud.com/blog/multi-factor-authentication-statistics
- https://secureframe.com/blog/phishing-attack-statistics
- https://www.practical-devsecops.com/top-ai-security-threats/
- https://purplesec.us/learn/cybercriminals-launching-ai-powered-cyber-attacks/
- https://www.brightdefense.com/resources/recent-data-breaches/
- https://intellizence.com/insights/business-signals-trends/major-cyber-attacks-data-breaches-leading-companies/
- https://www.cm-alliance.com/cybersecurity-blog/top-10-biggest-cyber-attacks-of-2024-25-other-attacks-to-know-about
- https://www.pandasecurity.com/en/mediacenter/password-statistics/
- https://jumpcloud.com/blog/password-statistics-trends
- https://secureframe.com/blog/password-statistics
- https://mixmode.ai/blog/the-rise-of-ai-driven-cyberattacks-accelerated-threats-demand-predictive-and-real-time-defenses/
- https://zerothreat.ai/blog/zero-trust-statistics
- https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/83-percent-organizations-reported-insider-threats-2024
- https://www.stationx.net/insider-threat-statistics/
- https://www.sisainfosec.com/blogs/10-cybersecurity-best-practices-in-the-age-of-ai-2025/
- https://www.wati.com/top-10-cybersecurity-mistakes-putting-your-business-at-risk/
- https://nordlayer.com/blog/cybersecurity-statistics-of-2024/
- https://www.sentinelone.com/cybersecurity-101/cybersecurity/cyber-security-best-practices/
- https://ccoe.dsci.in/blog/10-common-cybersecurity-mistakes-employees-make-and-how-training-can-help
- https://www.strongdm.com/blog/small-business-cyber-security-statistics
- https://www.splashtop.com/blog/it-security-best-practices
- https://www.eisneramper.com/insights/outsourced-it/common-cybersecurity-mistakes-0323/
- https://onlinedegrees.sandiego.edu/top-cyber-security-threats/
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/threats/top-10-computer-security-mistakes
- https://www.brightdefense.com/resources/cybersecurity-statistics/
- https://www.cisa.gov/topics/cybersecurity-best-practices
- https://right-hand.ai/blog/10-biggest-cybersecurity-mistakes-companies-make/
- https://www.coursera.org/articles/cybersecurity-best-practices
- https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/pdf/2014/09/Cyber-security-five-most-common-mistakes-O-201409.pdf
- https://www.terranovasecurity.com/blog/cyber-security-statistics
- https://kpmg.com/xx/en/our-insights/ai-and-technology/cybersecurity-considerations-2025.html
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2025/03/20/5-mistakes-companies-will-make-this-year-with-cybersecurity/
- https://fticybersecurity.com/case-studies/
- https://tech.co/news/data-breaches-updated-list
- https://secureframe.com/blog/recent-cyber-attacks
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1448350/ciso-human-error-organization-cyber-vulnerability-global/
- https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/reports/dbir/
- https://www.eimt.edu.eu/top-best-known-cybersecurity-case-studies
- https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach
- https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/cybersecurity-case-studies/
- https://www.cm-alliance.com/cybersecurity-blog/major-cyber-attacks-ransomware-attacks-and-data-breaches-august-2025
- https://birchwoodu.org/top-10-real-world-case-studies-on-cyber-security-incidents/
- https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/cybersecurity-statistics
- https://www.crn.com/news/security/2025/10-major-cyberattacks-and-data-breaches-in-2025-so-far
- https://kratikal.com/case-studies/case-study
- https://www.imarcgroup.com/multi-factor-authentication-market
- https://sprinto.com/blog/phishing-statistics/
- https://www.huntress.com/blog/password-statistics
- https://explodingtopics.com/blog/multi-factor-authentication-stats
- https://hoxhunt.com/guide/phishing-trends-report
- https://keepnetlabs.com/blog/top-phishing-statistics-and-trends-you-must-know
- https://spacelift.io/blog/password-statistics
- https://scoop.market.us/multi-factor-authentication-statistics/
- https://aag-it.com/the-latest-phishing-statistics/
- https://cyberreadinessinstitute.org/news-and-events/new-study-underscores-slow-adoption-of-multifactor-authenification/
- https://www.proofpoint.com/us/resources/threat-reports/state-of-phish
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1371010/password-length-in-selected-countries-by-generation/
- https://emudhra.com/en/blog/mfa-solutions-trends-to-watch-out-for-in-2025
- https://www.statista.com/topics/9337/zero-trust/
- https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/specialpublications/NIST.SP.800-207.pdf
- https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/cybersecurity-101/cyberattacks/ai-powered-cyberattacks/
- https://agileblue.com/zero-trust-architecture-implementation-and-challenges/
- https://www.syteca.com/en/blog/insider-threat-statistics-facts-and-figures
- https://informatics.nic.in/uploads/pdfs/b49cf220_36_37_tup_ai_powered_oct_24_withoutcut.pdf
- https://www.elisity.com/blog/zero-trust-architecture-implementation-guide-strategies-frameworks-for-enterprise-security-leaders
- https://www.securonix.com/resources/2024-insider-threat-report/
- https://www.cyberdefensemagazine.com/the-growing-threat-of-ai-powered-cyberattacks-in-2025/
- https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-a-zero-trust-architecture
- https://gurucul.com/2024-insider-threat-report/
- https://www.upguard.com/blog/cybersecurity-predictions-2024
- https://arxiv.org/html/2503.11659v2

