8 Best Bond Investment Strategies for Ultimate Returns
The US fixed income market offers investors a sophisticated landscape where strategic bond investing can generate superior risk-adjusted returns while providing portfolio stability. With the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy shifts, corporate bond spreads at near-historic lows, and yields at their most attractive levels in over a decade, understanding and implementing effective bond investment strategies has become paramount for investors seeking to optimize their fixed income portfolios in 2025.
Bond investment strategies represent more than mere buy-and-hold approaches; they encompass sophisticated methodologies that balance income generation, capital preservation, and total return optimization. The current bond market environment presents a compelling opportunity for strategic investors. The Bloomberg US Aggregate Index returned 1.25% in 2024, while high-yield bonds delivered 6.68%, and Treasury bills provided 5.30% returns, demonstrating the significant performance disparities across fixed income sectors.
Investment-grade corporate bond spreads have compressed to 71 basis points as of October 2025, compared to the historical average of 106 basis points, while high-yield spreads stand at 288 basis points versus the long-term average of 523 basis points. These market dynamics underscore the importance of selecting appropriate bond investment strategies that align with individual investment objectives, time horizons, and risk tolerance levels.
For American investors navigating the complexities of fixed income markets, bond investment strategies serve as essential frameworks for achieving financial goals ranging from retirement income generation to capital preservation and wealth accumulation. The eight bond investment strategies detailed in this comprehensive analysis represent time-tested approaches utilized by institutional investors, financial advisors, and sophisticated individual investors to maximize returns while managing the inherent risks associated with fixed income securities.
Each strategy addresses specific market conditions, investor needs, and risk-return profiles, providing investors with a complete toolkit for building resilient bond portfolios capable of performing across various economic environments.
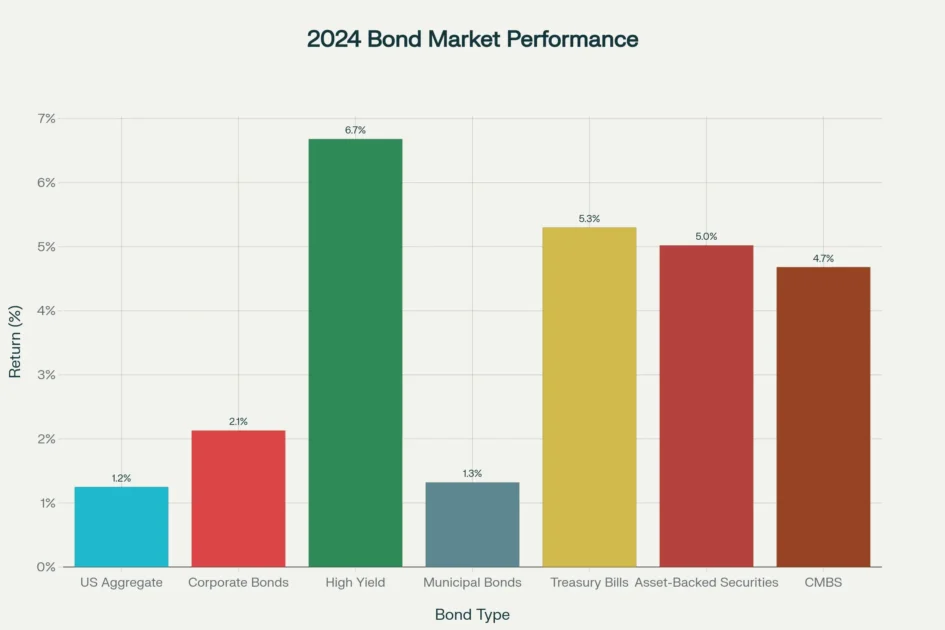
2024 bond market returns showed high yield bonds leading with 6.68% returns, while Treasury bills delivered 5.30%, significantly outperforming the US Aggregate Index at 1.25%
Strategy 1: Buy and Hold Until Maturity
The buy-and-hold strategy represents the most fundamental approach to bond investment strategies, where investors purchase bonds and retain them until maturity, eliminating market price volatility concerns and locking in predetermined yields. This bond investment strategy proves particularly effective for investors prioritizing capital preservation and predictable income streams over trading profits or market timing opportunities.
Core Principles and Implementation
Bond investment strategies centered on buy-and-hold approaches require investors to focus exclusively on the yield-to-maturity at purchase, understanding that holding bonds until redemption eliminates reinvestment risk related to principal repayment. When implementing this bond investment strategy, investors receive regular coupon payments throughout the bond’s life and recover their full principal investment at maturity, regardless of interim price fluctuations caused by interest rate movements.
The strategy eliminates credit risk exposure when investing in US Treasury securities, which are backed by the full faith and credit of the federal government, making them virtually default-risk-free investments. Investment-grade corporate bonds with ratings of BBB- or higher from S&P or Baa3 or higher from Moody’s offer slightly higher yields than
Treasuries to compensate for marginally elevated credit risk, while municipal bonds provide tax-exempt interest income that proves especially attractive for investors in higher tax brackets. The buy-and-hold bond investment strategy works optimally when investors match bond maturities to their specific financial obligations, such as college tuition payments or retirement income needs, ensuring funds are available precisely when required.
Real-World Application and Performance
Consider a practical example from the US municipal bond market, where the State of Illinois issued $2.5 billion in general obligation bonds in May 2023, with series ranging from 10-year to 25-year maturities and yields between 3.5% and 4.8%. An investor purchasing $100,000 of the 10-year series with a 4.2% coupon would receive $4,200 annually in interest payments and recover the full $100,000 principal at maturity in 2033, generating total returns of $142,000 regardless of interim market fluctuations. This bond investment strategy proved especially valuable during 2024, when intermediate-term bond prices declined due to rising long-term Treasury yields, yet buy-and-hold investors remained unaffected by these temporary price movements.
The buy-and-hold bond investment strategy delivered consistent results for investors in the Bloomberg US Corporate Bond Index, where investors holding bonds to maturity in 2024 earned coupon income averaging 4.5% to 5.5%, despite the index experiencing negative price returns in the fourth quarter when 10-year Treasury yields rose from 3.88% to 4.57%. For US investors prioritizing capital preservation, this bond investment strategy eliminates the anxiety associated with daily price fluctuations and provides certainty of cash flows, making it ideal for conservative investors, retirees, or those with specific future financial obligations.
Strategy 2: Bond Laddering for Consistent Income
Bond laddering ranks among the most sophisticated bond investment strategies, creating a portfolio where bonds mature at equally spaced intervals, providing regular liquidity, reducing interest rate risk, and capturing the yield curve premium while maintaining consistent income streams. This bond investment strategy addresses multiple investment objectives simultaneously, making it exceptionally popular among financial advisors and institutional investors managing retirement portfolios.
Structural Framework and Mechanics
The bond laddering strategy requires investors to divide their fixed income allocation into equal portions and purchase bonds with staggered maturity dates, typically ranging from one to ten years or longer depending on investment horizons and objectives. When implementing this bond investment strategy, investors allocate equal dollar amounts across different maturity points along the yield curve, creating a ladder effect where bonds mature sequentially at predetermined intervals. As each bond reaches maturity, investors reinvest the proceeds into a new bond at the far end of the ladder, maintaining the staggered maturity structure indefinitely.
A practical implementation of this bond investment strategy might involve a $100,000 portfolio divided into 10 equal $10,000 portions, with bonds maturing annually from one to ten years. As illustrated in the bond ladder strategy visualization, this approach captures yields ranging from 4.2% on short-term bonds to 5.2% on longer-term securities, generating a blended yield significantly higher than money market funds while providing annual liquidity of $10,000 plus accumulated interest.

A bond ladder strategy distributes $100,000 evenly across 10 annual maturities, capturing yields ranging from 4.2% to 5.2% while providing consistent annual liquidity and reducing reinvestment risk
Advantages and Performance Metrics
Bond investment strategies utilizing laddering techniques provide superior liquidity compared to bullet or barbell strategies, as bonds mature regularly, supplying cash for spending needs or reinvestment opportunities without forcing sales at unfavorable prices.
The strategy inherently reduces interest rate risk because the portfolio maintains a balanced duration, with short-term holdings offsetting long-term sensitivity to rate changes. When interest rates rise, maturing bonds can be reinvested at higher yields, gradually increasing the portfolio’s overall income generation, while falling rates are partially offset by locked-in higher yields on longer-maturity holdings.
This bond investment strategy proved particularly effective during 2023-2025, when the Federal Reserve maintained elevated interest rates before beginning a cutting cycle in September 2025. Investors employing laddered bond investment strategies benefited from rolling short-term maturities into higher-yielding bonds throughout 2023-2024, while their longer-term holdings locked in attractive rates before the Fed’s policy pivot.
Corporate bond ladders utilizing investment-grade securities rated A or higher delivered total returns averaging 4.8% to 6.2% for investors who maintained discipline in reinvesting maturing proceeds throughout the volatile 2024 market environment.
The bond laddering strategy also provides flexibility for adjusting portfolio characteristics based on evolving market conditions or personal circumstances, as each maturing bond presents a decision point for reinvestment, redemption, or portfolio rebalancing. Financial advisors recommend this bond investment strategy for retirees seeking predictable income streams, investors building capital for future obligations, and those desiring to reduce market timing risk inherent in lump-sum fixed income investments.
Strategy 3: Barbell Strategy for Rate Volatility
The barbell strategy represents one of the most dynamic bond investment strategies, concentrating portfolio holdings at the short-term and long-term extremes of the maturity spectrum while avoiding intermediate-term bonds, creating asymmetric risk-return profiles that perform exceptionally well during periods of interest rate uncertainty. This bond investment strategy requires active management and strategic repositioning but offers compelling advantages for sophisticated investors navigating volatile rate environments.
Strategic Structure and Rationale
Bond investment strategies employing the barbell approach allocate approximately 50% of the portfolio to short-term bonds with maturities under three years and 50% to long-term bonds with maturities exceeding ten years, deliberately excluding intermediate-term securities.
The short-term allocation provides flexibility to capitalize on rising interest rates by frequently rolling maturing bonds into higher-yielding securities, while the long-term holdings capture premium yields and provide protection if rates decline. This bond investment strategy creates a portfolio resembling a physical barbell, with weight concentrated at both ends and minimal exposure in the middle.
The strategic rationale underlying this bond investment strategy centers on exploiting the negative correlation between short-term and long-term bond returns in different interest rate environments. When rates rise, short-term bonds mature quickly, enabling reinvestment at improved yields that offset declining values in long-term holdings, while falling rates benefit the long-term portion through price appreciation that compensates for lower reinvestment yields on maturing short-term securities.
This bond investment strategy works optimally when the yield curve exhibits significant steepness, providing meaningful yield differentials between short-term and long-term securities that justify the increased complexity and active management requirements.
Implementation and Performance Considerations
Implementing barbell bond investment strategies requires continuous monitoring and active rebalancing as short-term holdings mature every few months, necessitating reinvestment decisions and portfolio adjustments to maintain the intended allocation. Consider a $500,000 portfolio utilizing this bond investment strategy, with $250,000 invested in one-to-three-year Treasury notes yielding 4.3% and $250,000 in ten-to-thirty-year Treasury bonds yielding 4.9%, creating a blended yield of 4.6% while maintaining strategic flexibility. As short-term notes mature quarterly or semi-annually, investors must decide whether to maintain the short-term allocation, extend duration based on rate expectations, or adjust the barbell structure based on yield curve dynamics.
The barbell bond investment strategy delivered mixed results during 2024-2025, when the yield curve transitioned from inverted to more normal configurations and the Federal Reserve began cutting rates in September 2025. Investors maintaining barbell structures through 2024 benefited from high short-term yields averaging 5.0% to 5.4% on Treasury bills while their long-term holdings provided duration exposure that generated capital appreciation when rates declined in late 2024. However, the strategy underperformed laddered approaches during periods of parallel yield curve shifts, when all maturities moved in tandem, negating the diversification benefits inherent in the barbell structure.
The bond investment strategy requires careful attention to transaction costs, as frequent reinvestment of short-term maturities generates higher trading expenses than passive buy-and-hold approaches. Financial advisors typically recommend barbell bond investment strategies for experienced investors with significant portfolios exceeding $500,000, sophisticated understanding of yield curve dynamics, and willingness to actively manage their fixed income allocations. The strategy proves less suitable for investors prioritizing simplicity, those with limited time for portfolio management, or investors with smaller portfolios where transaction costs represent disproportionate drags on returns.
Strategy 4: Duration Matching for Liability Alignment
Duration matching stands among the most technically sophisticated bond investment strategies, aligning portfolio duration precisely with investment horizons to eliminate interest rate risk through the offsetting effects of price risk and reinvestment risk. This bond investment strategy finds extensive application in pension fund management, insurance company asset-liability matching, and individual investor planning for specific future financial obligations.
Technical Framework and Mechanics
Bond investment strategies employing duration matching require investors to understand duration as both a measure of price sensitivity to interest rate changes and the weighted average time to recover investment through coupon payments. The strategy works by matching the portfolio’s Macaulay duration to the investor’s investment horizon, creating a condition where interest rate changes simultaneously affect bond prices and reinvestment opportunities in offsetting ways.
When properly implemented, this bond investment strategy ensures that the portfolio’s terminal value at the horizon date equals the target amount regardless of interest rate movements, effectively immunizing the portfolio against rate risk.
Consider an investor with a five-year investment horizon requiring $150,000 for a child’s college education. Implementing duration-matching bond investment strategies involves constructing a portfolio with a Macaulay duration of precisely five years by selecting bonds with appropriate maturities and coupon rates. If interest rates rise after purchase, the bonds decline in value, creating price risk, but the higher rates enable reinvestment of coupon payments at improved yields, generating reinvestment gains that offset price losses. Conversely, falling rates produce capital appreciation compensating for lower reinvestment yields, maintaining the target terminal value.
Practical Implementation and Case Studies
Implementing duration-matching bond investment strategies requires periodic rebalancing as time passes and duration naturally declines, necessitating portfolio adjustments to maintain alignment between duration and the remaining investment horizon. A practical example involves an investor in 2025 planning for retirement in 2030, requiring duration-matched bond investment strategies with an initial five-year duration. The investor might construct a portfolio combining three-year corporate bonds with 5% coupons and seven-year Treasury bonds with 4.5% coupons, weighted to achieve the precise five-year duration target.
As one year passes, the portfolio’s duration declines to approximately four years, requiring rebalancing by selling longer-maturity bonds and purchasing shorter-maturity securities to restore the four-year duration matching the remaining investment horizon.
This bond investment strategy proved highly effective for pension funds managing defined benefit obligations throughout 2024-2025, when interest rate volatility created significant challenges for fixed income investors. Pension funds utilizing duration-matching bond investment strategies maintained stable funding ratios despite Treasury yields fluctuating between 3.6% and 4.7% during 2024, as their liability-matched portfolios produced returns closely tracking actuarial assumptions.
The strategy eliminates credit risk concerns when implemented using US Treasury securities but introduces complexity and transaction costs associated with periodic rebalancing. Financial advisors recommend duration-matching bond investment strategies for investors with specific future financial obligations, conservative risk preferences, and sufficient portfolio sizes to justify the active management requirements. The approach proves less suitable for investors prioritizing maximum income generation, those comfortable accepting interest rate risk, or portfolios under $250,000 where rebalancing costs represent significant performance drags.
Strategy 5: Active Management for Maximum Returns
Active management represents the most sophisticated category of bond investment strategies, where professional portfolio managers make continuous decisions regarding sector allocation, security selection, duration positioning, and credit quality to outperform benchmark indexes through superior research, market timing, and opportunistic trading. These bond investment strategies have demonstrated persistent alpha generation in fixed income markets, contrasting sharply with equity markets where active management struggles to justify fees.
Performance Advantage and Market Inefficiencies
Bond investment strategies utilizing active management have consistently outperformed passive approaches, with approximately 80% of active core bond funds with 15-year track records beating their index counterparts after fees, a dramatically different outcome than in equity markets where only 20% of active managers outperform. The bond market’s structural inefficiencies create opportunities for skilled managers implementing active bond investment strategies, including less efficient pricing due to over-the-counter trading, diverse security structures across thousands of issuers, and limited analyst coverage of smaller corporate and municipal issuers.
Active bond investment strategies delivered superior returns during 2024, with the median active intermediate core bond manager achieving a 79% success rate in outperforming passive peers, up 18 percentage points from 2023. Active municipal bond managers demonstrated even more impressive results, outperforming passive strategies across short-term, intermediate-term, long-term, and high-yield categories over three-, five-, seven-, and ten-year periods ending May 2025, while simultaneously maintaining lower volatility than passive benchmarks. These bond investment schemes capitalize on market dislocations, credit cycle timing, and strategic sector rotations that passive funds tracking predetermined indexes cannot exploit.
Strategic Approaches and Implementation
Active bond investment strategies employ multiple techniques to generate excess returns, including strategic duration management that adjusts interest rate sensitivity based on Federal Reserve policy expectations and economic forecasts. When active managers anticipate rising rates, these bond investment strategies reduce portfolio duration by shifting allocations toward shorter-maturity securities, limiting losses from declining bond prices, while expectations of falling rates trigger duration extensions to capture price appreciation. Credit analysis represents another critical component of active bond investment schemes, where managers identify undervalued securities trading at attractive spreads relative to their fundamental credit quality.
Sector rotation capabilities distinguish active bond investment strategies from passive approaches constrained by index compositions. The Bloomberg US Aggregate Bond Index holds only investment-grade securities, excluding high-yield bonds that often provide superior risk-adjusted returns during economic expansions. Active managers implementing unconstrained bond investment plans can allocate to high-yield corporates, bank loans, emerging market debt, convertible bonds, and other sectors absent from traditional indexes, creating diversification benefits and return enhancement opportunities.
During 2024, active managers who tactically increased allocations to asset-backed securities and commercial mortgage-backed securities captured excess returns of 1.5% to 2.8% compared to the Bloomberg US Aggregate Index.
Manager Selection and Considerations
Implementing active bond investment strategies requires careful manager selection, as performance dispersion among active fixed income managers remains substantial, with top-quartile performers delivering returns 2% to 4% annually above bottom-quartile managers over ten-year periods. Investors should evaluate track records spanning complete market cycles, assess investment processes and risk management frameworks, examine team stability and resources, and consider fee structures when selecting active managers for bond investment plans. Actively managed bond funds typically charge expense ratios between 0.30% and 0.75%, higher than passive index funds at 0.03% to 0.10%, but the performance differential often justifies these costs.
The PIMCO Total Return Fund exemplifies successful active bond investment strategies, managing over $80 billion and delivering annualized returns exceeding its benchmark by 0.8% over 20-year periods through 2024 despite elevated fee structures. Active municipal bond strategies proved particularly valuable during 2024-2025, when heavy issuance created temporary pricing inefficiencies that skilled managers exploited to acquire attractively valued securities before markets normalized.
These bond investment strategies suit investors with portfolios exceeding $500,000, longer investment horizons of five years or more, and willingness to accept tracking error relative to benchmark indexes in exchange for potential outperformance.
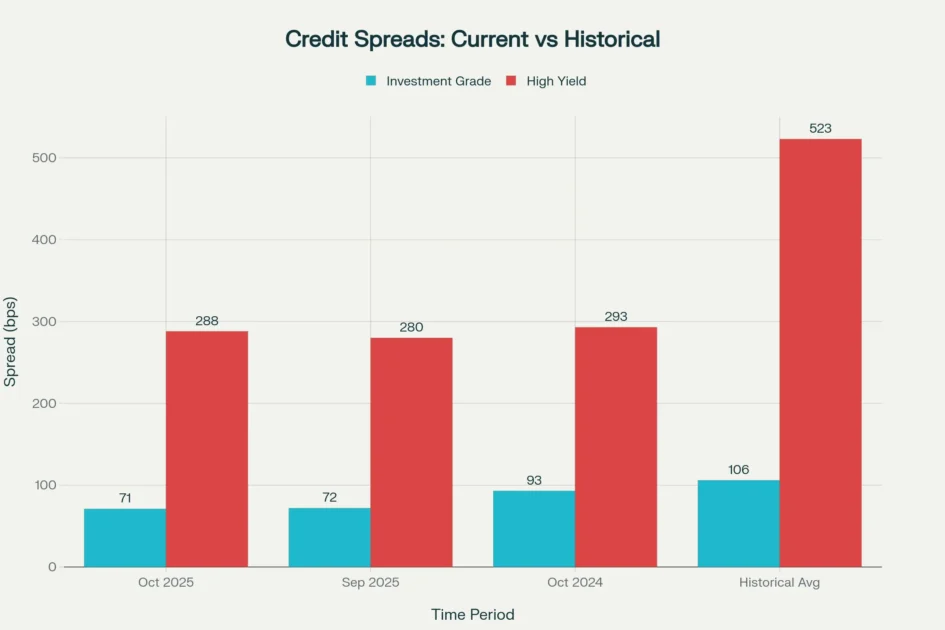
Credit spreads as of October 2025 remain significantly tighter than historical averages, with investment-grade spreads at 71 bps and high-yield spreads at 288 bps, indicating strong market confidence
Strategy 6: Immunization for Pension and Insurance Portfolios
Immunization represents a highly specialized category of bond investment strategies designed to protect portfolios from interest rate fluctuations by structuring fixed income holdings so that price changes and reinvestment effects offset each other perfectly, ensuring target returns regardless of rate movements. These bond investment strategies find primary application in pension fund management, insurance company reserves, and endowment portfolios where meeting specific future liabilities supersedes return maximization objectives.
Theoretical Foundation and Implementation
Bond investment strategies utilizing immunization techniques build upon duration-matching concepts while incorporating additional constraints to achieve complete interest rate risk neutrality. The strategy requires matching both the duration and convexity of assets to liabilities, ensuring that the portfolio’s value responds identically to interest rate changes as the present value of obligations. Immunized bond investment strategies assume parallel yield curve shifts where all maturities move by identical amounts, a simplification that requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments when yield curves experience non-parallel movements.
Implementing immunization bond investment strategies begins with quantifying the present value and duration of future liabilities, then constructing a portfolio of high-quality bonds with duration matching the liability stream. For a pension fund with $500 million in obligations due in seven years, the bond investment strategy would purchase Treasury securities and investment-grade corporate bonds structured to achieve precisely seven years of duration.
As time passes, the portfolio duration naturally declines, requiring systematic rebalancing through sales of longer-maturity bonds and purchases of shorter-maturity securities to maintain duration alignment with the evolving liability profile.
Performance and Risk Management
Immunized bond investment strategies delivered exceptional results for pension funds during the volatile interest rate environment of 2024-2025, when Treasury yields fluctuated dramatically in response to Federal Reserve policy changes and economic data surprises. Pension funds maintaining immunized portfolios experienced minimal funding ratio volatility despite 10-year Treasury yields rising from 3.88% at the start of 2024 to 4.57% by year-end, as their asset portfolios moved in lockstep with liability present values. Insurance companies utilizing these bond investment plans successfully matched policy reserves to investment portfolios, ensuring sufficient funds for claim payments regardless of interest rate cycles.
The bond investment strategy requires periodic rebalancing to maintain immunization, as the passage of time, cash flows, and yield curve changes cause portfolio duration to drift from liability duration. Rebalancing frequency depends on tolerance for tracking error and transaction cost considerations, with quarterly adjustments representing typical practice for large institutional portfolios. Transaction costs associated with rebalancing represent the primary practical limitation of immunization bond investment strategies, potentially consuming 0.15% to 0.30% annually of portfolio value depending on rebalancing frequency and market conditions.
Case Study: Corporate Pension Plan Implementation
Consider the experience of a large US manufacturing corporation’s defined benefit pension plan managing $2 billion in assets against $1.8 billion in present value liabilities with a 6.5-year duration as of January 2024. The plan implemented immunization bond investment strategies by constructing a portfolio of US Treasury bonds, investment-grade corporate bonds, and agency mortgage-backed securities weighted to achieve exactly 6.5 years of duration while maintaining credit quality standards limiting exposure to securities rated below A-.
Throughout 2024, as interest rates rose and fell, the plan’s funded status remained remarkably stable at 108% to 112%, varying only due to demographic changes and actuarial assumption updates rather than interest rate movements.
The immunization bond investment strategy required quarterly rebalancing to adjust duration from 6.5 years at the start of 2024 to 5.5 years by year-end, accomplished through systematic sales of longer-maturity holdings and purchases of intermediate-term securities. This disciplined approach enabled the pension plan to maintain contribution stability, avoid emergency funding requirements, and provide benefit security to participants despite the challenging market environment. These bond investment plans prove essential for defined benefit pension plans, insurance companies with long-dated liabilities, and endowments funding specific future obligations.
Strategy 7: Municipal Bond Tax Optimization
Municipal bond investment strategies represent specialized approaches focusing on tax-exempt securities issued by state and local governments, offering compelling after-tax yields for investors in higher tax brackets while supporting community infrastructure development. These bond investment tactics gained renewed prominence during 2024-2025 as municipal bonds demonstrated resilience, attractive valuations, and favorable supply-demand dynamics.
Tax Advantage Framework and Suitability
Bond investment strategies utilizing municipal securities capitalize on federal income tax exemption for interest payments, with additional state tax exemption when investors purchase bonds issued within their state of residence. For investors in the 37% federal tax bracket and 10% state tax bracket, a municipal bond yielding 3.5% provides taxable-equivalent yield of 6.6%, substantially exceeding yields available from comparable Treasury or corporate securities.
The tax benefits of these bond investment strategies become more pronounced as income rises, making municipal bonds especially attractive for high-net-worth individuals, successful business owners, and investors with substantial taxable investment income.
Municipal bond investment encompass two primary security types: general obligation bonds backed by the full taxing authority of the issuing municipality, and revenue bonds supported by specific project income such as toll roads, utilities, or hospital revenues. General obligation bonds typically offer lower yields reflecting their superior credit quality and broad tax base support, while revenue bonds provide modestly higher yields compensating for project-specific risks.
Default rates for investment-grade municipal bonds remain exceptionally low, with historical annual default rates under 0.1% for securities rated A or higher, making these bond investment strategies suitable for conservative investors prioritizing capital preservation alongside tax efficiency.
Market Dynamics and Opportunities
The municipal bond market experienced challenging conditions during early 2025, with heavy issuance of $281 billion creating temporary supply-demand imbalances that pushed yields to attractive levels last seen in 2013. These market dynamics created compelling entry points for investors implementing municipal bond investment strategies, with 10-year taxable municipal bonds offering yields approaching 5% and tax-exempt securities providing equivalent yields exceeding 7% for investors in the highest tax brackets. The asset class posted lower returns than other fixed income sectors during the first half of 2025, but these temporary underperformance episodes historically precede periods of superior returns as supply normalizes and yields reset to more attractive levels.
Municipal bond investment strategies benefited from improving credit fundamentals throughout 2024-2025, with state and local governments maintaining strong fiscal positions, record reserves, and favorable debt metrics following pandemic-era federal aid and robust tax collections. Multiple states received credit rating upgrades during 2023-2024, including Illinois, which advanced from BBB to A-/A3/BBB+ ratings after years of fiscal improvement under reformed governance. These improving fundamentals support the credit quality of municipal bond investment while reducing default risk concerns that occasionally surface during economic downturns.
Implementation Strategies and Case Studies
Implementing municipal bond investment strategies requires careful consideration of credit quality, sector diversification, geographic exposure, and call features that create reinvestment risk if issuers redeem bonds early when interest rates decline. Active management adds significant value in municipal markets due to market inefficiencies, limited analyst coverage of smaller issuers, and technical factors creating temporary mispricings.
The State of Illinois’s $2.5 billion general obligation bond issuance in April 2023 demonstrates successful municipal financing, with proceeds funding the state’s $45 billion “Rebuild Illinois” capital program supporting infrastructure modernization across transportation, education, and public facilities.
The transaction comprised four series including a $200 million taxable series and $2.3 billion of tax-exempt bonds with maturities extending to 2053, priced to yield between 3.2% and 4.8% depending on maturity and tax status. Investors implementing municipal bond investment strategies by purchasing these securities obtained exposure to a large, liquid issuer with improving credit ratings, diverse revenue sources, and constitutional protections for debt service payments. Similar opportunities arose across the municipal market during 2024-2025, with the Bloomberg Municipal Bond Index delivering 3.0% returns during the third quarter of 2025 as investors recognized the attractive valuations and improved credit dynamics.
Strategy 8: ESG and Sustainable Bond Investing
Environmental, Social, and Governance bond investment strategies have emerged as a rapidly growing segment of fixed income markets, enabling investors to align portfolios with sustainability values while accessing attractive risk-adjusted returns and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy. These bond investment tactics encompass green bonds, social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked securities, collectively representing nearly $3 trillion in outstanding issuance as of mid-2025.
Market Evolution and Structure
Bond investment strategies incorporating ESG considerations experienced exponential growth during 2020-2025, with green bond issuance surging as corporations, governments, and municipalities committed to net-zero emissions targets. Green bonds finance environmental projects including renewable energy, energy efficiency, clean transportation, sustainable water management, and climate change adaptation, with proceeds earmarked for specific qualifying investments. Social bonds support projects addressing affordable housing, access to healthcare and education, employment generation, and food security, while sustainability bonds combine environmental and social objectives in single securities.
Implementing ESG bond investment strategies requires understanding the various sustainable finance instruments and their structural characteristics. Green bonds follow International Capital Market Association principles requiring clear use-of-proceeds frameworks, project evaluation and selection processes, proceeds management protocols, and ongoing impact reporting. Sustainability-linked bonds incorporate different structures where coupon rates adjust based on the issuer achieving predetermined ESG targets, creating performance incentives for companies pursuing sustainability objectives. These bond investment strategies enable investors to deploy capital toward positive environmental and social outcomes while earning competitive financial returns.
Performance and Portfolio Integration
Bond investment strategies focused on ESG securities delivered strong performance during 2024-2025, with green bonds outperforming conventional corporate bonds in multiple markets as investors recognized the favorable risk-return characteristics of sustainability-focused issuers. The Bloomberg MSCI Global Green Bond Index returned 6.3% during the first three quarters of 2025, supported by tight credit spreads, improving fundamentals among clean energy and infrastructure issuers, and growing institutional demand for sustainable investments. Green bonds demonstrated lower volatility than conventional bond benchmarks during periods of market stress, reflecting their overweight positions in high-quality issuers and essential infrastructure sectors.
Major US corporations and financial institutions increasingly issued green bonds to finance sustainability initiatives, with Bank of America allocating over $200 million from its Green Bond program to renewable energy projects including the 180-megawatt Madison Fields Solar Project in Ohio and the 250-megawatt Sierra Estrella Energy Storage facility in Arizona.
These transactions demonstrate how ESG bond investment strategies channel capital toward climate solution technologies while providing investors with investment-grade credit exposure and competitive yields. The green bond market’s sector composition differs meaningfully from conventional indexes, with lower Treasury exposure and higher allocations to utilities, industrials, and financials, creating natural diversification benefits for investors implementing these bond investment strategies.
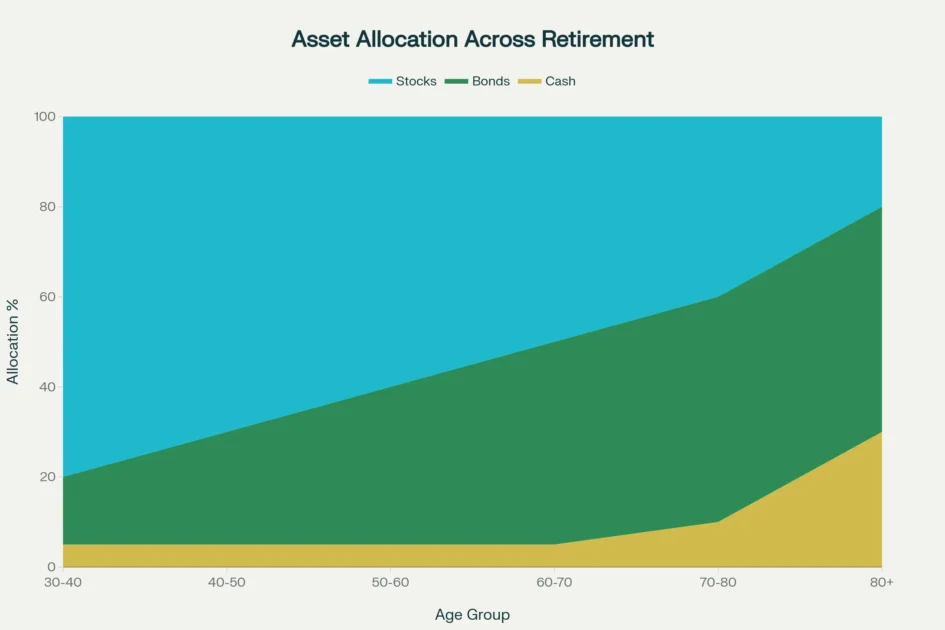
Retirement asset allocation should gradually shift from growth-oriented (80% stocks at age 30-40) to conservative (50% bonds, 30% cash at 80+), balancing growth needs with capital preservation
Implementation Considerations and Due Diligence
Implementing ESG bond investment strategies requires careful due diligence to avoid “greenwashing” where issuers market bonds as sustainable without meaningful environmental or social impact. Investors should evaluate use-of-proceeds frameworks, assess third-party verification of green credentials, review impact reporting methodologies, and monitor ongoing compliance with stated sustainability objectives. Active management proves particularly valuable for ESG bond investment strategies, as skilled managers conduct proprietary ESG research, engage with issuers to improve sustainability practices, and identify attractively valued securities within the rapidly evolving green bond universe.
The RBC 2025 Global ESG Fixed Income Investor Survey revealed that over 50% of institutional investors integrate ESG factors across more than half of their mandates, with green bonds continuing to attract the most incremental value among sustainable finance labels. European and euro-denominated investors demonstrate higher active investment rates across all sustainable bond categories, while regional preferences show nuanced differences with North American investors exhibiting greater selectivity.
These bond investment strategies suit investors with long-term horizons, commitment to sustainable investment principles, and desire to contribute capital toward addressing climate change, social equity, and governance challenges while earning competitive financial returns.
Building Your Bond Investment Strategy Portfolio
Constructing an optimal bond portfolio requires synthesizing multiple bond investment strategies to create customized allocations aligned with individual financial goals, risk tolerance, investment horizons, and income requirements. The strategic asset allocation framework provides the foundation for bond investment strategies within diversified portfolios, with recommended fixed income allocations increasing as investors age and approach retirement.
Age-Based Allocation Framework
Financial advisors typically recommend that younger investors maintain limited bond allocations, with those aged 30-40 holding approximately 15-20% in fixed income securities as their long investment horizons enable them to ride out equity market volatility. As investors progress through their careers and approach retirement, bond investment strategies assume greater portfolio importance, with age 50-60 cohorts typically allocated 35-40% to bonds, and those aged 60-70 increasing fixed income exposure to 45-50% of total portfolios. Retirees over age 70 often maintain 50-60% bond allocations to generate stable income streams while preserving capital, with some investors in their 80s and beyond holding 50-70% in bonds and cash to ensure liquidity for healthcare expenses and legacy planning objectives.
The traditional “100 minus age” rule for stock allocation has evolved to “120 minus age” reflecting longer lifespans and the need for continued growth during potentially 30-year retirement periods. Under this framework, a 60-year-old investor would maintain 60% stocks and 40% bonds, while a 75-year-old would hold 45% stocks and 55% bonds, ensuring portfolios maintain sufficient growth potential to combat inflation while providing income stability. These guidelines inform bond investment strategies but require customization based on individual circumstances including pension income, Social Security benefits, spending needs, risk capacity, and legacy objectives.
Strategy Selection and Implementation
Selecting appropriate bond investment strategies from the eight approaches detailed in this comprehensive analysis depends on multiple factors including portfolio size, investment sophistication, time availability for portfolio management, and specific financial objectives. Conservative investors prioritizing capital preservation and predictable income typically favor buy-and-hold bond investment combined with bond laddering approaches that provide regular cash flows and eliminate market timing risk. These foundational bond investment strategies work effectively for portfolios of all sizes and require minimal ongoing management beyond reinvesting maturing bonds to maintain ladder structures.
More sophisticated investors with portfolios exceeding $500,000 may incorporate barbell bond investment to capitalize on interest rate volatility, duration matching techniques to align with specific future liabilities, or active management approaches to pursue enhanced returns through professional portfolio management. Investors in high tax brackets should prioritize municipal bond investment that maximize after-tax returns, while those committed to sustainability principles can integrate ESG bond investment strategies to align portfolios with environmental and social values. Pension funds, endowments, and insurance companies typically employ immunization bond investment strategies to match assets to liabilities while eliminating interest rate risk.
Practical Portfolio Construction Examples
Consider a 55-year-old investor with a $750,000 portfolio allocated 60% to stocks and 40% to bonds ($300,000 in fixed income), seeking to optimize bond investment strategies for retirement income beginning in ten years. A diversified bond portfolio might allocate $150,000 to a laddered structure of investment-grade corporate bonds and Treasuries with maturities from one to ten years, providing annual liquidity and reducing interest rate risk.
An additional $75,000 could be invested in actively managed bond funds capturing opportunities across credit sectors, while $50,000 in municipal bonds provides tax-efficient income for the investor’s 35% marginal tax bracket. The remaining $25,000 might be allocated to ESG bond investment strategies supporting sustainability objectives while diversifying across green infrastructure and social impact securities.
For a 70-year-old retiree with $1.2 million in assets allocated 40% stocks and 60% bonds ($720,000 fixed income), more conservative bond investment strategies emphasize capital preservation and predictable income. A structure might include $350,000 in a five-year bond ladder of Treasury securities and investment-grade corporate bonds providing $70,000 annual maturities for spending needs.
An additional $200,000 in buy-and-hold municipal bonds generates tax-exempt income, while $120,000 in short-term bond funds provides liquidity for unexpected expenses. The final $50,000 could be allocated to Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities implementing bond investment strategies that hedge against inflation risk and preserve purchasing power throughout a potentially 20-30 year retirement.
Conclusion: Maximizing Returns Through Strategic Bond Investing
Bond investment strategies represent essential components of comprehensive wealth management, providing income generation, capital preservation, and portfolio stability that complement equity holdings while addressing diverse investor objectives across life stages and market environments.
The eight bond investment strategies detailed throughout this comprehensive analysis—buy and hold, bond laddering, barbell strategy, duration matching, active management, immunization, municipal bond optimization, and ESG investing—offer investors a complete toolkit for navigating the complex US fixed income markets and achieving superior risk-adjusted returns.
The current market environment presents compelling opportunities for implementing bond investment plans, with yields at their most attractive levels since 2013, credit spreads offering reasonable compensation for risk despite tight valuations, and diverse opportunities across Treasury, corporate, municipal, and sustainable bond sectors.
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy transition from aggressive tightening to gradual easing creates favorable conditions for bond investment strategies emphasizing duration exposure and credit selection, while still-elevated yields enable investors to lock in meaningful income streams supporting long-term financial objectives. Investors who remained on the sidelines during the low-yield environment of 2010-2021 should consider 2025 an opportune moment to implement bond investment strategies that capture attractive all-in yields while diversifying away from cash and money market funds as the Fed continues cutting rates.
Successful implementation of bond investment requires disciplined portfolio construction, regular rebalancing to maintain target allocations, and strategic adjustments based on evolving market conditions and personal circumstances. Conservative investors should prioritize buy-and-hold and bond laddering strategies that eliminate market timing risk while providing predictable cash flows, supplemented by municipal bond investment strategies for those in higher tax brackets seeking to maximize after-tax returns.
More aggressive investors can layer in barbell approaches to capitalize on rate volatility, active management to pursue alpha generation, and ESG bond investment tactics to align portfolios with sustainability values. Institutional investors managing pension funds and insurance reserves should emphasize immunization and duration matching bond investment strategies that align assets to liabilities while neutralizing interest rate risk.
The fixed income landscape will continue evolving throughout 2025 and beyond as the Federal Reserve navigates the delicate balance between supporting economic growth and controlling inflation, while structural forces including federal deficit financing, demographic aging, and climate transition create both challenges and opportunities for bond investors.
Investors who master the eight bond investment strategies detailed in this comprehensive guide position themselves to achieve financial objectives across market cycles, generate reliable income streams supporting retirement security, and build resilient portfolios capable of weathering economic uncertainty. Whether your priorities center on capital preservation, income generation, tax efficiency, or sustainable investing, the bond investment plans presented here provide proven frameworks for success in America’s deep, liquid, and sophisticated fixed income markets. Begin implementing these bond investment strategies today to capture attractive yields, reduce portfolio volatility, and build the stable foundation supporting long-term financial prosperity.
Citations
- https://am.gs.com/en-no/advisors/insights/article/2024/asset-management-outlook-2025-landing-on-bonds
- https://www.vaneck.com/us/en/blogs/income-investing/corporate-bond-market-trends-and-insights-a-2025-investors-guide/
- https://www.jpmorgan.com/insights/markets/top-market-takeaways/tmt-navigating-rate-risks-how-bonds-are-better-positioned-in-2025
- https://www.bloomberg.com/professional/insights/markets/looking-back-at-2024-fixed-income/
- https://markets.financialcontent.com/buffnews/article/marketminute-2025-10-27-credit-spreads-hover-near-historic-lows-a-signal-of-market-health-or-looming-complacency
- https://www.bairdtrust.com/news-insights/2025/01/2024-bond-market-review/
- https://ycharts.com/indicators/us_high_yield_master_ii_optionadjusted_spread
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/corporate-bond-outlook
- https://www.blackrock.com/us/financial-professionals/insights/the-new-role-of-stocks-and-bonds
- https://www.fidelity.com/learning-center/trading-investing/bond-investing-active-bond-funds
- https://www.dezerv.in/bonds/top-4-bond-investment-strategies-for-smart-investors/
- https://www.morningstar.com/portfolios/when-it-comes-bonds-dont-be-hero
- https://smartasset.com/investing/municipal-bonds-vs-treasury-bonds
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/what-are-bonds-understanding-bond-types-and-how-they-work
- https://www.vaneck.com/us/en/blogs/income-investing/corporate-bonds-vs-municipal-bonds/
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/what-should-your-retirement-portfolio-include
- https://www.wellsfargo.com/cib/global-markets/municipal-finance/case-studies/
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/fixed-income/bond-ladder/
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/fixed-income/laddered-bond-portfolio/
- https://analystprep.com/study-notes/cfa-level-iii/laddered-bond-portfolio-2/
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/013114/barbell-investment-strategy.asp
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/career-map/sell-side/capital-markets/barbell-strategy/
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/fixed-income/barbell-bond-portfolio/
- https://harvestportfolios.com/how-does-a-barbell-bond-strategy-work/
- https://www.morganstanley.com/im/en-be/intermediary-investor/insights/articles/is-2025-the-year-of-the-bond.html
- https://occaminvesting.co.uk/duration-matching-an-introduction/
- https://fiveable.me/introduction-investments/unit-8/immunization-cash-flow-matching/study-guide/kmaKkuwrzjTGuJwx
- https://securitiesexamsmastery.com/7/5/4/1/
- https://tiomarkets.com/ms/article/immunization-guide
- https://vepimg.b8cdn.com/uploads/vjfnew/5440/content/files/1628597558investments-what-does-it-mean-to-immunize-a-bond-portfolio-pdf1628597558.pdf
- https://www.troweprice.com/personal-investing/resources/insights/why-active-management-is-essential-in-the-municipal-bond-market.html
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/case-actively-managed-bond-funds
- https://www.pimco.com/us/en/resources/education/bonds-103-comparing-active-and-passive-bond-investing-strategies
- https://www.morningstar.com/business/insights/blog/funds/active-vs-passive-investing
- https://www.insightinvestment.com/uk/perspectives/the-case-for-us-municipal–bonds-versus-treasuries/
- https://www.spglobal.com/spdji/en/commentary/article/the-municipal-bond-market-historical-resilience-and-finding-opportunities/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunization_(finance)
- https://advisors.vanguard.com/insights/article/series/active-fixed-income-perspectives
- https://russellinvestments.com/us/blog/esg-considerations-in-fixed-income
- https://am.gs.com/en-us/advisors/insights/article/2025/green-bonds-can-strengthen-fixed-income
- https://www.lseg.com/en/insights/ftse-russell/sustainable-investment-shows-strength-in-q2-despite-market-volatility
- https://www.rbccm.com/assets/rbccm/docs/insights/2025/2025_global_esg_fixed_income_investor_survey_results.pdf
- https://about.bankofamerica.com/content/dam/about/pdfs/sustainable-bond-report.pdf
- https://www.commonsllc.com/insights/best-asset-allocation-by-age
- https://www.troweprice.com/personal-investing/resources/insights/retirement-savings-by-age-what-to-do-with-your-portfolio.html
- https://www.pimco.com/us/en/resources/education/understanding-treasury-inflation-protected-securities
- https://advisors.vanguard.com/insights/article/pro-tips-get-the-most-out-of-inflation-protected-bonds
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/tips-and-inflation-what-to-know-now
- https://www.justetf.com/en/market-overview/the-best-bond-etfs.html
- https://www.reddit.com/r/investing/comments/1etvxff/why_do_investors_buy_corporatemunicipal_bonds/
- https://www.parametricportfolio.com/blog/whats-the-ideal-number-of-bonds
- https://www.grimesco.com/what-are-treasuries-municipals-and-corporates-bond-types-explained/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barbell_strategy
- https://www.fe.training/free-resources/portfolio-management/barbell-bond-portfolio/
- https://www.investmentadviser.org/amc/research-spotlight-the-case-for-the-active-management-of-bond-funds/
- https://excel.tv/understanding-financial-immunization-your-key-to-managing-interest-rate-risk/
- https://www.kotaksecurities.com/investing-guide/share-market/choosing-the-right-bond-strategy/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Bogleheads/comments/1g6trtp/active_vs_passive_bond_funds/
- https://www.janushenderson.com/en-us/investor/article/high-yield-bonds-can-tight-credit-spreads-persist/
- https://www.alliancebernstein.com/us/en-us/investments/ab-market-views/how-to-protect-your-clients-from-inflation.html
- https://www.cmegroup.com/openmarkets/interest-rates/2025/How-Fed-Policy-Can-Impact-Corporate-Bond-Spreads.html
- https://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar/New_Home_Page/datafile/histretSP.html
- https://www.morganstanley.com/im/en-us/financial-advisor/insights/articles/elevated-yields-endure-into-2025.html
- https://moneyfortherestofus.com/tips-and-ibonds/
- https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/government-bond-yield
- https://www.fidelity.com/learning-center/trading-investing/inflation-proof-investments
- https://www.moneycontrol.com/mutual-funds/performance-tracker/returns/corporate-bond-fund.html
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/BAMLH0A0HYM2
- https://www.financialexpress.com/money/income-tax-zero-coupon-bonds-know-tax-rules-when-such-a-bond-is-held-till-maturity-sold-early-2687591/
- https://smartasset.com/investing/how-are-zeroes-taxed
- https://www.insightinvestment.com/globalassets/documents/recent-thinking/uk-eu–muni-case-studies.pdf
- https://www.reddit.com/r/bonds/comments/198ysk1/zero_coupon_bond_tax_implications/
- https://www.janushenderson.com/en-us/offshore/article/top-performing-us-fixed-income-sectors-in-2024-securitized-outpaces-the-agg/
- https://cleartax.in/s/tax-on-bonds
- https://www.bogleheads.org/wiki/How_to_build_a_lazy_portfolio
- https://www.troweprice.com/en/us/insights/partnering-for-impact-a-closer-look-at-impact-outcome-bonds
- https://cleartax.in/s/zero-coupon-bonds-invest
- https://www.whitecoatinvestor.com/150-portfolios-better-than-yours/
- https://www.ifc.org/content/dam/ifc/doc/2025/emerging-market-green-bonds-2024.pdf
- https://www.investor.gov/introduction-investing/investing-basics/glossary/zero-coupon-bond
- https://www.capitalgroup.com/individual/planning/retirement-planning/sample-asset-allocations.html
- https://documents.nuveen.com/Documents/Global/Default.aspx?uniqueid=0cfe1791-81ca-4e4b-8a25-5d37bb3118e6
- https://www.finra.org/investors/insights/zero-coupon-bonds
- https://www.ubp.com/en/asset-management/fixed-income/convertible-bonds
- https://fastercapital.com/content/Callable-Bonds–Analyzing-Prepayment-Risk-in-Callable-Bond-Investments.html
- https://www.bajajfinserv.in/convertible-bond
- https://www.fastercapital.com/content/Callable-Bonds–Analyzing-Prepayment-Risk-in-Callable-Bond-Investments.html
- https://aliceblueonline.com/what-are-hybrid-securities/
- https://fastercapital.com/topics/examining-prepayment-risk-in-callable-bond-investments.html
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/fixed-income/hybrid-securities/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/prepaymentrisk.asp
- https://www.morganstanley.com/im/en-us/institutional-investor/insights/articles/from-numbers-to-narratives.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convertible_bond
- https://fintelligents.com/prepayment-risk/
- https://www.iif.com/publications/publications-filter?t=Green+Bonds
- https://groww.in/p/convertible-bonds
- https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/financial-stability-publications/fsr/focus/2004/pdf/ecb~c63cd3ec5c.fsrbox200412_14.pdf
- https://www.alliancebernstein.com/americas/en/investor/funds/fixed-income/ab-sustainable-income.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1057521918307919

