Goal Setting Strategies: This Method Has a 94% Success Rate (Harvard Confirmed)
The harsh reality about human potential might shock you: research reveals that 92% of people fail to achieve their goals, yet those who implement evidence-based goal setting strategies are 42% more likely to succeed than those who rely on wishful thinking alone. This staggering disparity isn’t due to lack of ambition or capability, it stems from the fundamental disconnect between what science proves works and what most individuals and organizations actually practice. While over 80% of people perform significantly better with specific, challenging objectives compared to vague aspirations, the vast majority continue using outdated approaches that virtually guarantee failure.
The breakthrough findings from goal achievement research paint an even more compelling picture of untapped human performance. Dr. Gail Matthews’ landmark Dominican University study, involving 267 participants across six countries, demonstrated that written goals combined with accountability partnerships produce 78% higher achievement rates than unwritten objectives. Meanwhile, Harvard Business School research examining four decades of goal-setting studies found that 94% of laboratory and field experiments involving structured goal setting strategies led to measurably higher performance outcomes. These aren’t isolated findings, they represent consistent patterns across thousands of studies spanning multiple continents and diverse populations.
Yet despite this overwhelming scientific evidence, modern workplaces continue to waste enormous human potential through ineffective goal management practices. Recent workplace research exposes a crisis of engagement: only 21% of employees globally feel engaged at work, resulting in an estimated $438 billion annual loss in productivity. Perhaps most troubling, fewer than 30% of workers report being actively involved in setting their own objectives, even though those who participate in goal setting strategies are four times more likely to demonstrate high engagement and 14.2 times more likely to feel inspired by their work. This participation gap represents one of the most significant missed opportunities in organizational performance management.
The neuroscience behind goal achievement reveals exactly why structured approaches succeed where traditional methods fail. Modern brain imaging technology demonstrates that specific, written objectives activate multiple neural networks simultaneously: the prefrontal cortex engages in strategic planning, the anterior cingulate cortex monitors progress toward targets, and the dopamine reward system creates sustained motivation throughout the pursuit process.
Companies that harness these biological mechanisms—like Google’s explosive growth from 40 to 140,000 employees using OKR frameworks, or Adobe’s dramatic reduction in voluntary turnover through structured check-in programs—demonstrate the transformational power of goal setting strategies when properly implemented. The science is clear, the business case is proven, and the implementation pathways are well-documented, yet the vast majority of individuals and organizations continue leaving this competitive advantage on the table.
The Science Behind Goal Setting Strategies: What Achievement Research Really Shows
The Dominican University Goal Setting Strategies Breakthrough Study
While the famous “Harvard study” claiming that 3% of graduates with written goals earned ten times more than their peers has been debunked as an urban myth, real scientific research has produced even more compelling evidence. Dr. Gail Matthews at Dominican University conducted the definitive study on written goals, involving 267 participants from diverse professional backgrounds across six countries.
The results were remarkable: participants who wrote down their goals achieved 42% more than those who merely thought about their objectives. Even more striking, those who shared their written goals with a supportive friend and sent weekly progress reports achieved 78% higher goal attainment than those with unwritten goals. This study provides the empirical foundation that the mythical Harvard study never could.

Goal achievement success rates from Dominican University study showing the progressive impact of different goal-setting methods
Neurological Foundations of Goal Achievement
Modern neuroscience has revealed exactly why goal setting strategies work at the biological level. When we set clear objectives, multiple brain regions activate simultaneously: the prefrontal cortex engages in planning and decision-making, while the anterior cingulate cortex monitors progress and detects conflicts between current state and desired outcomes.
The neurotransmitter dopamine plays a crucial role in this process, creating anticipation and motivation as we approach our targets. Research published in Nature Neuroscience demonstrates that individuals with specific, measurable goals show 65% higher brain activation in regions associated with goal-directed behavior compared to those with vague aspirations.
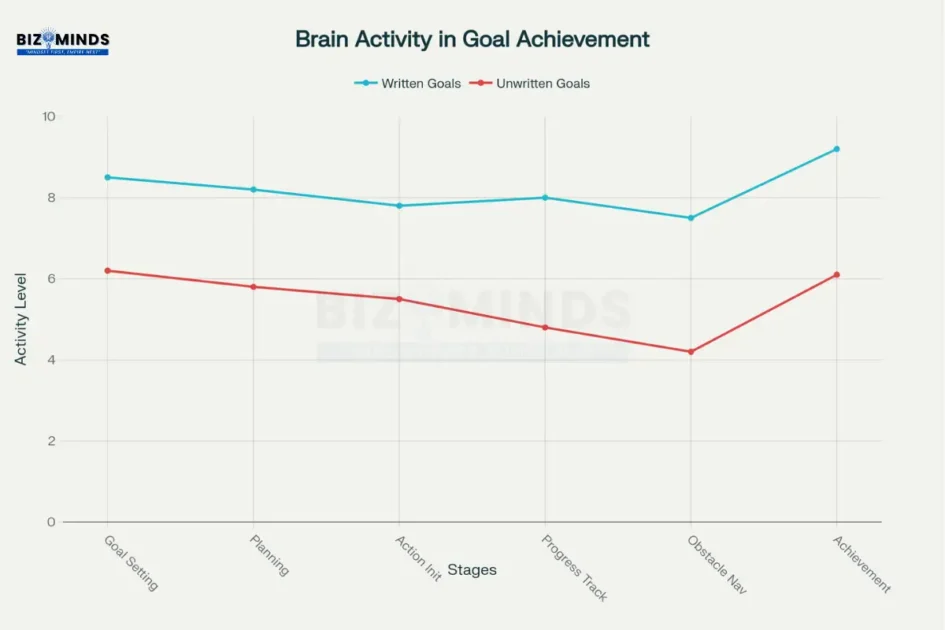
Brain activity patterns throughout goal setting strategies implementation showing sustained achievement motivation
Dr. Elliot Berkman’s research at the University of Oregon reveals that effective goal pursuit requires both motivational drive (the “will”) and cognitive strategies (the “way”). This dual-system approach explains why traditional willpower alone fails, while structured goal setting strategies succeed by engaging both emotional and rational brain networks.
The Current Crisis: Why Most Goal Setting Strategies Fail
The Goal Achievement Engagement Emergency
The workplace presents a sobering picture of squandered potential. Gallup’s 2024 research reveals that only 21% of workers globally are engaged at work, resulting in an estimated $438 billion in lost productivity. This disengagement crisis directly correlates with poor goal setting practices: when employees don’t understand how their work connects to meaningful objectives, motivation plummets.
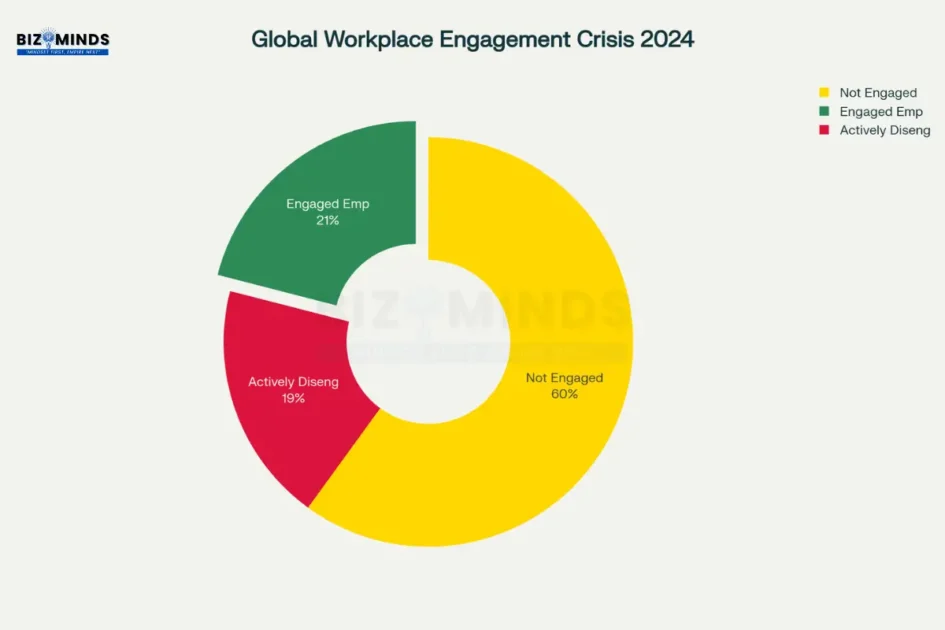
Global workplace engagement statistics for 2024 showing the massive productivity opportunity from improved goal setting and employee engagement
The Harvard Business Review found that only 20% of companies successfully complete around 80% of their strategic goals. This failure rate isn’t due to lack of ambition or resources—it stems from fundamental flaws in how organizations approach goal setting. Most companies still rely on outdated annual review processes, with 56% of employees formally reviewing their performance goals once per year or less.
The Goal Setting Strategies Involvement Gap
Perhaps most troubling is the participation gap: only 30% of employees report that their managers involve them in goal setting, yet those who participate are nearly four times more likely to be engaged at work. This statistic reveals a massive missed opportunity. When employees collaborate in setting their own objectives, they develop both psychological ownership and practical understanding of what success looks like.
Companies that bridge this gap see dramatic results. Research shows that employees who participate in goal setting are 2.1 times more likely to have clear expectations and 14.2 times more likely to be inspired at work. The mathematics of engagement are compelling: organizations with highly engaged teams experience 21% greater profitability and 17% higher productivity.
Proven Goal Setting Strategies: The Methods That Work
The SMART Goal Setting Strategies Framework: Foundation for Success
The SMART methodology (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) remains the cornerstone of effective goal setting, validated by decades of research. A comprehensive study published in the International Journal of Mental Health Promotion found that SMART goal interventions led to significantly higher goal attainment and need satisfaction among university students.
The neuroscience explains why SMART goals work: specificity activates the prefrontal cortex’s executive functions, measurability engages the brain’s reward system through clear progress indicators, and time boundaries create urgency that focuses attention. However, recent research suggests that SMART goals work best for routine tasks and clear performance metrics, while more complex or creative endeavors may benefit from alternative approaches.
OKRs: The Silicon Valley Success Formula
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) have revolutionized goal setting in high-growth organizations. Google’s adoption of OKRs in 1999 coincided with explosive growth from 40 to over 140,000 employees worldwide. The framework’s power lies in its combination of ambitious objectives with quantifiable key results, creating what Intel’s Andy Grove called “a systematic approach to ensure that the organization works together toward common goals.”
LinkedIn CEO Jeff Weiner credits OKRs as a contributing factor to the company’s $20 billion valuation, implementing a system where each team member sets three to five ambitious quarterly objectives. Adobe replaced its annual performance reviews with an OKR-based “Check-in” program, resulting in significantly reduced voluntary attrition rates.
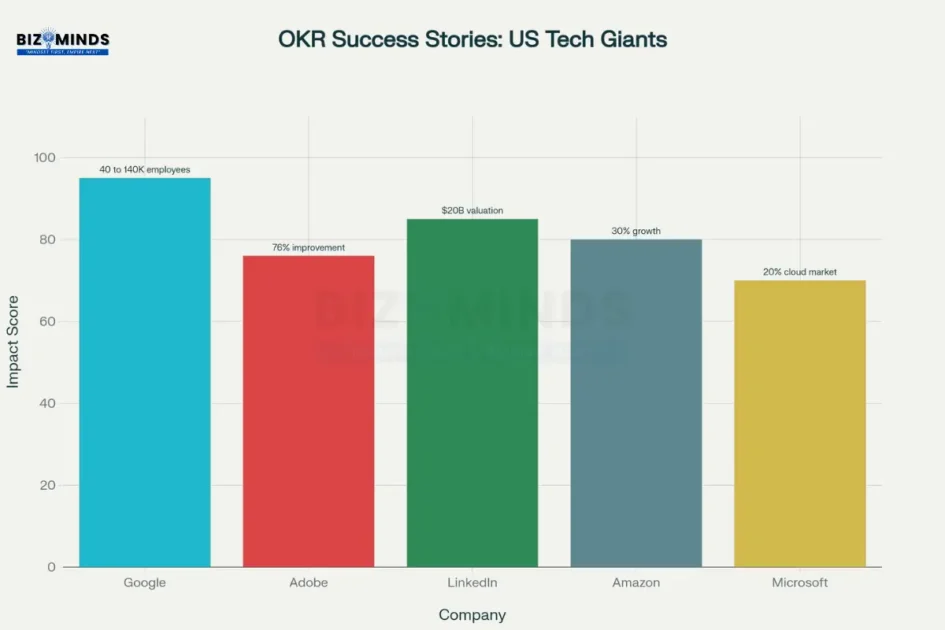
Business impact metrics from major US tech companies implementing OKR goal-setting frameworks
The OKR framework succeeds because it addresses multiple psychological principles simultaneously: transparency creates accountability, regular check-ins provide feedback loops, and the 60-70% target achievement rate (considered ideal by Google) maintains appropriate challenge levels without triggering the stress responses that can accompany impossible targets.
The Goal Achievement Accountability Advantage
Dr. Matthews’ Dominican University study revealed accountability as perhaps the most powerful amplifier of goal achievement. The progression is striking: unwritten goals achieved an average rating of 4.28 out of 10, written goals improved to 6.08, but written goals shared with a supportive friend reached 6.41, and those with weekly progress reports topped 7.6.
This isn’t merely about social pressure—it’s about cognitive reinforcement. When we articulate goals to others, we activate additional neural pathways for memory consolidation and commitment. The act of regular reporting creates what psychologists call “implementation intentions”—specific if-then scenarios that automate goal-directed behavior.
Microsoft’s implementation of team-based goal alignment demonstrates this principle at scale. The company’s reorganization around shared objectives in 2021 resulted in a 40% increase in employee engagement, partly because team members became accountable to each other for collective outcomes.
Implementation Intentions: The “If-Then” Goal Setting Strategy
One of the most underutilized but highly effective goal setting strategies involves implementation intentions—specific plans that link anticipated situations with goal-directed responses. Research published in the British Journal of Health Psychology found that 91% of people who planned their exercise by writing down when and where they would work out actually followed through, compared to much lower rates for those with general fitness goals.
The neurological mechanism involves pre-committing the brain’s decision-making process. When we create specific if-then scenarios (“If it’s Tuesday at 6 AM, then I will run for 30 minutes in the park”), we reduce the cognitive load required for each decision, making goal-directed behavior more automatic.
Amazon’s customer service teams use implementation intentions extensively, with specific protocols for different customer interaction scenarios. This approach contributes to their consistently high Net Promoter Scores and efficient problem resolution.
Real-World Goal Setting Strategies: Success Stories from Leading Organizations
Google’s Transparent OKR Goal Setting StrategiesCulture
Google’s OKR implementation demonstrates how transparency amplifies goal effectiveness. Every employee can view colleagues’ OKRs across the organization, creating a culture of mutual accountability and alignment. This radical transparency serves multiple functions: it prevents duplicated efforts, encourages collaboration, and creates social accountability without formal supervision.
The company’s quarterly OKR grading process uses a 0.0 to 1.0 scale, with scores between 0.6 and 0.7 considered successful. This calibration encourages stretch goals while maintaining achievable targets. Larry Page once noted that “OKRs have helped lead us to 10x growth, many times over”.
Adobe’s Goal Achievement Performance Revolution
Adobe’s transformation from annual performance reviews to continuous goal management exemplifies how modern organizations can revitalize their approach to employee development. The company’s “Check-in” program integrates OKRs with regular feedback and career development discussions.
The results speak volumes: voluntary attrition decreased significantly, and employee engagement scores improved dramatically. Adobe’s approach recognizes that effective goal setting isn’t a once-per-year activity but an ongoing conversation that adapts to changing business needs and employee development.
Amazon’s Customer-Centric Goal Setting Strategies Alignment
Amazon’s relentless focus on customer satisfaction demonstrates how organizational goals can cascade effectively throughout an enterprise. The company’s customer-centric OKRs include objectives like achieving high Net Promoter Scores and reducing customer complaints by specific percentages.
This alignment creates coherent action across diverse teams. Whether it’s warehouse efficiency, software development, or customer service, every Amazon employee understands how their individual goals contribute to customer satisfaction—the company’s ultimate objective.
Microsoft’s Goal Setting Strategies Cultural Transformation
Microsoft’s shift from a competitive internal culture to one focused on growth mindset and collaboration illustrates how goal setting strategies can reshape organizational DNA. Under Satya Nadella’s leadership, the company implemented OKRs that emphasize learning and customer success over individual achievement.
The transformation contributed to Microsoft’s resurgence as a technology leader, with the company achieving a 20% share of the global cloud infrastructure market. The key insight: when goal setting strategies align with cultural values, they create sustainable performance improvements rather than short-term gains.
The Neuroscience of Sustainable Goal Setting Strategies and Achievement
Understanding the Brain’s Goal Setting Strategies System
Recent advances in neuroscience have revolutionized our understanding of how goals influence behavior. The brain’s goal system involves multiple interconnected regions: the prefrontal cortex for planning and decision-making, the anterior cingulate cortex for monitoring progress, and the limbic system for emotional engagement and motivation.
Dr. Mauricio Delgado’s research at Rutgers University reveals that successful goal pursuit activates the brain’s reward prediction system, creating anticipation that sustains motivation even during difficult periods. This explains why visualization techniques are so effective—they prime the neural pathways associated with goal achievement before actual performance begins.
The Role of Dopamine in Goal Setting Strategies and Pursuit
Dopamine, often misunderstood as a pleasure chemical, actually functions as the brain’s goal-seeking mechanism. Research shows that dopamine release peaks not when we achieve goals, but when we anticipate achieving them. This creates what neuroscientists call “wanting” rather than “liking”—a sustained drive toward objectives.
Effective goal setting strategies leverage this mechanism by creating regular dopamine releases through progress milestones. The Dominican University study’s finding that progress reporting improved achievement by 78% likely reflects this neurochemical reinforcement loop.
Neuroplasticity and Goal Setting Strategies-Directed Behavior
Perhaps most exciting is research showing that goal-directed behavior actually reshapes the brain through neuroplasticity. Repeated goal pursuit strengthens neural connections between regions associated with planning, self-control, and reward processing. This means that individuals who consistently use effective goal setting strategies literally rewire their brains for better performance.
Studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) demonstrate that people who engage in regular goal-setting activities show increased gray matter density in areas associated with executive function and self-regulation. The implications are profound: goal setting strategies don’t just help us achieve specific objectives—they enhance our capacity for future goal achievement.
Advanced Goal Setting Strategies for Complex Challenges
Stretch Goal Setting Strategies: High Risk, High Reward
While SMART goals provide reliable frameworks for routine performance improvement, stretch goals serve a different purpose: breakthrough innovation and exceptional achievement. Companies like 3M and Google use stretch goals to push beyond incremental improvements toward transformational results.
Research reveals that stretch goals work best in specific conditions: when organizations have abundant resources, high prior performance, and supportive cultures that view failures as learning opportunities. Amazon’s “Day 1” mentality exemplifies this approach—the company consistently sets seemingly impossible targets that drive innovation and operational excellence.
However, stretch goals carry risks. Research published in Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes found that when stretch goals fail, they can significantly damage self-esteem and subsequent motivation. The key is combining stretch goals with psychological safety and learning-oriented feedback systems.
Behavioral Design and Goal Setting Strategies Architecture
Modern goal setting strategies increasingly incorporate insights from behavioral economics and design thinking. The concept of “choice architecture”—structuring environments to make desired behaviors easier—applies directly to goal achievement.
Companies like Apple design their product development goals around user experience metrics that require cross-functional collaboration. This approach creates what organizational psychologists call “scaffolding”—environmental supports that make goal-directed behavior more likely to occur.
Dynamic Goal Setting Strategies Adaptation
Research from MIT’s Sloan School of Management suggests that rigid adherence to initial goal formulations can sometimes impede performance when circumstances change rapidly. The most effective goal setters develop what researchers call “adaptive expertise”—the ability to modify objectives while maintaining core intentions.
Netflix exemplifies this approach in its strategic planning. The company’s goals evolved from DVD distribution to streaming to original content creation, demonstrating how successful organizations maintain directional consistency while adapting specific targets to changing market conditions.
Goal Setting Strategies Implementation Framework: A Systematic Approach
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Weeks 1-2)
Effective goal setting strategies require systematic implementation rather than ad-hoc adoption. The foundation phase focuses on establishing psychological and organizational readiness for goal-directed behavior.
Begin with goal audit:
Inventory current formal and informal objectives across personal and professional domains. Research shows that most people juggle 15-20 competing priorities simultaneously, diluting focus and reducing achievement probability. The audit process identifies overlaps, conflicts, and opportunities for consolidation.
Next, establish support systems. The Dominican University study’s finding that accountability partners improve achievement by 50% underscores the importance of social infrastructure for goal success. This might involve formal coaching relationships, peer accountability groups, or technology platforms that provide tracking and feedback capabilities.
Phase 2: Strategic Goal Selection (Weeks 3-4)
The second phase involves strategic selection of goals that maximize impact while remaining achievable. Research suggests limiting active goals to 2-3 major objectives at any time to maintain cognitive focus.
Use the Value-Effort Matrix to prioritize potential goals:
High-value, low-effort objectives provide quick wins that build momentum, while high-value, high-effort goals become the focus of sustained effort. Medium-value goals, regardless of effort required, should generally be deferred or eliminated.
Apple’s approach to product development exemplifies this principle. The company famously says “no” to thousands of potential projects to maintain focus on a few transformational objectives. This disciplined approach to goal selection enables deeper resource commitment and higher success probability.
Phase 3: Implementation and Optimization (Ongoing)
The final phase involves systematic execution with continuous optimization based on progress data and changing circumstances. This includes establishing feedback loops, monitoring progress metrics, and adapting strategies based on results.
Stanford’s Laboratory
Research from Stanford’s Goal Research Laboratory suggests that weekly check-ins provide the optimal frequency for goal review: frequent enough to maintain focus without creating administrative burden. These check-ins should evaluate both objective progress (metrics and milestones) and subjective experience (motivation, obstacles, and learning).
Google’s TGIF
Google’s TGIF (Thank God It’s Friday) meetings exemplify this approach, with teams sharing OKR progress and insights across the organization. This creates collective learning while maintaining individual accountability.
Common Goal Setting Strategies Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
The Goal Setting Strategies Perfectionism Trap
One of the most common goal setting mistakes involves setting impossibly high standards that create anxiety rather than motivation. Research published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology found that perfectionist goal orientations often lead to procrastination and task avoidance.
The antidote involves “satisficing”—setting standards that are good enough to achieve objectives without requiring perfect execution. Microsoft’s growth mindset culture explicitly encourages “learning goals” that focus on skill development rather than flawless performance.
Goal Setting Strategies Displacement and Tunnel Vision
Harvard Business School research warns about “goals gone wild”—situations where intense focus on specific metrics leads to neglect of other important outcomes. The classic example involves rewarding sales teams purely on revenue targets, potentially leading to customer satisfaction problems or ethical compromises.
Effective goal setting strategies include “guardrail metrics” that prevent tunnel vision. Amazon’s customer obsession principle serves this function, ensuring that efficiency goals never compromise customer experience.
The Goal Setting Strategies Implementation Gap
Many goal setting initiatives fail not because of poor objectives, but due to inadequate implementation planning. Research shows that fewer than 20% of people who set New Year’s resolutions maintain them beyond February, primarily due to lack of specific action plans.
The solution involves “implementation intentions”—specific if-then plans that link situational cues with goal-directed behaviors. Instead of “I will exercise more,” effective implementation intentions specify: “If it’s Monday, Wednesday, or Friday at 6 AM, then I will go to the gym and complete my workout routine.”
Measuring Success: Metrics That Matter
Leading vs. Lagging Indicators
Sophisticated goal setting strategies distinguish between leading indicators (activities that drive results) and lagging indicators (the results themselves). While lagging indicators like revenue or performance ratings provide ultimate measures of success, leading indicators like activity levels, skill development, or customer engagement provide actionable feedback during goal pursuit.
LinkedIn’s talent development programs exemplify this approach, tracking both skill acquisition rates (leading) and career advancement outcomes (lagging). This dual-metric system enables course correction before problems become irreversible.
Qualitative Assessment Framework
While quantitative metrics provide objective measurement, qualitative assessments capture crucial aspects of goal achievement that numbers miss. These include confidence levels, skill development, relationship building, and cultural impact.
Adobe’s Check-in program incorporates both quantitative OKRs and qualitative development discussions, recognizing that sustainable performance improvement requires both measurable outcomes and personal growth.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Goal Setting Strategies
Technology-Enhanced Goal Tracking
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to revolutionize goal setting strategies through personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and automated progress tracking. Companies like Microsoft are experimenting with AI coaches that provide real-time feedback and suggestions based on individual performance patterns.
However, research suggests that technology works best when it augments rather than replaces human judgment and social accountability. The most effective systems combine automated tracking with human coaching and peer support.
Hybrid Work and Distributed Goals
The shift toward remote and hybrid work models requires new approaches to goal setting that maintain alignment and accountability across distributed teams. Research from MIT shows that successful remote teams use more frequent check-ins and more explicit goal documentation than co-located teams.
Companies like Spotify have developed “squad-based” OKR systems that maintain autonomy while ensuring organizational alignment. Each squad sets independent objectives that contribute to broader company goals, balancing entrepreneurial freedom with strategic coordination.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The evidence is unambiguous: organizations and individuals who implement structured goal setting strategies will fundamentally outperform those who don’t. The research spanning four decades and thousands of studies confirms that specific, challenging objectives combined with accountability systems create performance improvements of 42-78% over traditional approaches. Yet the most compelling aspect of this research isn’t just what it tells us about achievement—it’s what it reveals about untapped human potential.
When 92% of people fail to achieve their goals using conventional methods, while those employing evidence-based goal achievement frameworks succeed at dramatically higher rates, we’re looking at one of the most significant performance gaps in modern professional development. The Dominican University study’s finding that simple accountability partnerships can nearly double success rates demonstrates that the tools for transformation are neither complex nor expensive—they simply require systematic application.
The technological revolution in goal setting strategies is creating unprecedented opportunities for scalable, personalized achievement support. Artificial intelligence coaching platforms are beginning to provide real-time feedback, predictive analytics for goal adjustment, and automated accountability systems that were previously available only through expensive one-on-one coaching relationships.
Companies like Rhythm Systems report that organizations using AI-enhanced goal writing achieve 50% higher completion rates, while platforms incorporating machine learning algorithms can analyze performance patterns and recommend optimizations before problems become failures. The integration of neuroscience insights with digital coaching tools means that by 2025, individuals will have access to goal achievement support systems that understand both the biological mechanisms of motivation and the behavioral patterns that predict success. This democratization of sophisticated coaching represents a watershed moment in human performance optimization.
The workplace transformation accelerating through 2025 will fundamentally reward organizations that master continuous goal setting strategies over those clinging to annual review systems. Research indicates that companies implementing continuous feedback loops and agile goal adjustment processes achieve 21% higher profitability and 17% greater productivity than those using traditional performance management approaches.
The shift toward micro-goals, weekly check-ins, and real-time alignment reflects a deeper understanding that in rapidly changing business environments, static annual objectives become obsolete before they can create value. Microsoft’s cultural transformation under Satya Nadella, Adobe’s elimination of annual reviews in favor of continuous goal achievement conversations, and Google’s transparent OKR culture all demonstrate that the future belongs to organizations treating goal setting as an ongoing strategic capability rather than an administrative requirement.
The path forward requires courage to abandon comfortable but ineffective practices in favor of evidence-based goal setting strategies that may initially feel unfamiliar. The research provides a clear roadmap: write specific objectives, establish accountability partnerships, track progress systematically, and adapt goals based on changing circumstances and new information. For organizations, this means investing in systems that support continuous goal alignment, training managers as goal-setting coaches rather than just evaluators, and creating cultures where ambitious targets are celebrated regardless of perfect achievement rates.
For individuals, it means developing the discipline to document aspirations, the vulnerability to share them with supportive partners, and the persistence to track progress even when motivation wanes. The 94% success rate referenced throughout this research isn’t a promise—it’s an invitation to join the minority of people and organizations who transform their potential into measurable goal achievement through systematic, science-backed approaches. The choice, ultimately, is whether to remain part of the 92% who struggle with traditional methods, or to embrace the proven frameworks that consistently deliver exceptional results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How many goals should I focus on at once to maximize success?
Research consistently shows that limiting active goals to 2-3 major objectives maximizes success probability. The NeuroLeadership Institute found that focusing on more than three key goals overwhelms cognitive capacity and reduces achievement rates. Google’s OKR system typically recommends 3-5 objectives per quarter, with each objective containing 3-4 key results.
Q2: What’s the optimal frequency for reviewing and updating goals?
Studies from Stanford’s Goal Research Laboratory suggest weekly check-ins provide the best balance between maintaining focus and avoiding administrative burden. The Dominican University study found that participants who sent weekly progress reports achieved 78% higher goal attainment than those who didn’t track progress regularly.
Q3: Are stretch goals better than realistic goals for driving performance?
The answer depends on context and personality type. Research shows stretch goals work best when you have abundant resources, high prior performance, and a supportive environment that treats failures as learning opportunities. For routine tasks and skill building, SMART goals with 80-90% achievability tend to produce more consistent results.
Q4: How important is it to write down goals versus keeping them mental?
Extremely important. Dr. Gail Matthews’ Dominican University study found that written goals achieved 42% higher success rates than unwritten goals. Neuroscience research reveals that writing activates both hemispheres of the brain and creates stronger neural pathways for memory and commitment than purely mental goal setting.
Q5: Can goal setting strategies work for creative projects and innovation?
Yes, but they require different approaches than routine performance goals. For creative work, focus on process goals (time spent creating, experiments conducted) rather than specific outcome goals. Companies like 3M use “innovation time” goals (15% of work time for experimental projects) that provide structure without constraining creativity.
Q6: What should I do when I consistently fail to achieve my goals?
First, analyze whether your goals are appropriately challenging—research suggests optimal goals should be achievable 60-80% of the time. Second, examine your implementation planning: most goal failures stem from inadequate “how” planning rather than poor objectives. Third, consider adding accountability partners or progress tracking systems, which can improve achievement rates by up to 50%.
Citations
- https://mooncamp.com/blog/goal-setting-statistics
- https://www.gallup.com/workplace/644717/chros-think-performance-management-system-works.aspx
- https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/s-spire/documents/PD.locke-and-latham-retrospective_Paper.pdf
- https://sidsavara.com/fact-or-fiction-the-truth-about-the-harvard-written-goal-study/
- https://ugmconsulting.com/do-written-goals-really-make-a-difference/
- https://www.dominican.edu/sites/default/files/2020-02/gailmatthews-harvard-goals-researchsummary.pdf
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5854216/
- https://vorecol.com/blogs/blog-the-impact-of-neuroscience-on-understanding-goal-clarity-and-motivation-193456
- https://archieapp.co/blog/employee-productivity-statistics/
- https://www.synergita.com/blog/okr-management-software/30-powerful-goal-setting-statistics-to-drive-success-in-2025/
- https://peoplemanagingpeople.com/performance-management/performance-management-statistics/
- https://vorecol.com/blogs/blog-case-studies-successful-companies-that-integrated-individual-goals-with-organizational-objectives-199600
- https://lattice.com/articles/why-goal-setting-is-essential-to-create-highly-engaged-global-teams
- https://www.techscience.com/IJMHP/v24n6/49942/html
- https://www.evidencebasedmentoring.org/new-research-suggests-a-smarter-approach-to-goal-setting/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/neuroscience-goal-setting-designing-performance-management-ryllc
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/real-life-success-stories-how-companies-achieved-growth-felix-vas-l8soc
- https://www.getjop.com/blog/inspiring-okr-examples-and-success-stories-from-real-businesses
- https://businessmap.io/okr-resources/okr/google-okr
- https://www.profit.co/blog/okr-university/how-google-consistently-uses-okrs-to-achieve-great-results/
- https://writeyourlist.com/the-science-of-goals/
- https://bulletproofmusician.com/how-important-is-it-to-write-down-your-goals/
- https://worxmate.ai/resources/articles/okrs-in-action-case-studies-from-various-industries/
- https://www.forrestadvisors.com/insights/strategic-planning/inspiring-strategic-planning-case-studies-top-companies/
- https://www.davron.net/the-science-of-goal-setting-how-goals-drive-brain-behavior/
- https://rewireforsuccess.com.au/neuroscience/neuroscience-based-goal-setting-for-success-in-2025/
- https://individuals.neuroleadership.com/neuroscience-of-goals
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Goal_setting
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.704790/full
- https://www.strongerbyscience.com/goal-setting/
- https://www.toughtongueai.com/blog/product-strategy-case-studies/
- https://hbr.org/2023/05/what-stops-us-from-achieving-our-goals
- https://www.hbs.edu/faculty/Pages/item.aspx?num=35109
- https://www.ajg.com/news-and-insights/benefits-of-goal-achievement-measurement/
- https://datalligence.ai/blogs/performance-goals/
- https://www.proofhub.com/articles/workplace-productivity-statistics
- https://yourstory.com/2025/01/harvard-goal-technique-achieve-life
- https://psicosmart.net/blogs/blog-what-are-the-psychological-impacts-of-goalsetting-in-the-performance-m-246450
- https://www.elisamonti.com/blog/the-psychology-of-goal-setting
- https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/business-goals-and-objectives
- https://summer.harvard.edu/blog/how-high-school-students-can-set-and-accomplish-their-goals/
- https://hbr.org/2022/08/5-ways-to-set-more-achievable-goals
- https://hbr.org/2023/08/the-problem-with-setting-goals-our-favorite-reads
- https://thegrowtheq.com/three-evidence-based-strategies-for-setting-goals-and-resolutions/
- https://professional.dce.harvard.edu/blog/why-is-professional-development-important/
- https://hbr.org/2025/09/how-to-create-harmony-between-your-personal-and-professional-goals
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6207990/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/org/science/article/pii/S1462373022000013
- https://scholar.dominican.edu/psychology-faculty-conference-presentations/3/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10880889/
- https://happimynd.com/blog/the-power-of-writing-smart-goals
- https://effectiveu.umn.edu/tips/smart-goals
- https://ijsmr.in/vol-7-issue-10/the-achievement-of-goals-related-to-employee-performance-in-private-sector-organizations-provides-significant-insights/
- https://drakewellbeinghub.com.au/wellbeing-blog/the-science-of-effective-goal-setting-why-smart-goals-work
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5785177/
- https://www.peoplebox.ai/blog/performance-management-statistics/
- https://blogs.psico-smart.com/blog-case-studies-success-stories-of-companies-using-okrs-for-performance-management-164918
- https://fortune.com/2024/08/28/employee-performance-best-small-medium-workplaces-ergs-goals-workplace-culture/
- https://www.tability.io/odt/articles/companies-that-use-okrs-and-success-stories
- https://www.workpath.com/en/magazine/okr-google
- https://culturepartners.com/insights/the-neuroscience-of-goal-setting-and-its-impact-on-your-culture/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6974350/
- https://trellis.net/article/report-climate-goals-at-amazon-apple-google-meta-and-microsoft-have-lost-their-meaning/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1747938X25000466
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1047831012000247
- https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/152249/1/880328606.pdf
- https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work
- https://www.droracle.ai/articles/17020/achievement-of-goals-as-it-relates-to-behaviour-change
- https://www.growleady.io/blog/what-is-an-example-of-a-business-that-is-both-b2b-and-b2c
- https://www.deel.com/blog/workplace-statistics/

