10 Best Algorithmic Trading Strategies for Profits
Algorithmic trading has transformed financial markets in ways that seemed impossible just two decades ago. Today, automated systems executing algorithmic trading strategies with precision and speed that no human trader can match account for approximately 92% of all transactions in US equity markets. The rise of these sophisticated systems represents one of the most significant shifts in modern finance, fundamentally changing how institutional investors and retail traders approach market opportunities.
Understanding how to design, implement, and optimize algorithmic trading strategies has become essential for anyone seeking competitive advantage in today’s electronically-driven markets where speed, precision, and emotional discipline separate winners from losers.
The power of algorithmic trading strategies lies in their ability to process vast amounts of data, eliminate emotional decision-making, and execute trades at speeds measured in microseconds. From Renaissance Technologies’ legendary Medallion Fund generating over $100 billion in profits to major investment banks handling 40% of US retail trading volume, the evidence is clear: mastering algorithmic approaches has become essential for competitive advantage in today’s markets.
These algorithmic trading strategies combine mathematical models, statistical analysis, and advanced computing to identify profitable opportunities that would remain hidden to traditional analysis. The most successful quant traders recognize that superior returns come not from luck or intuition but from systematic frameworks that consistently exploit market inefficiencies with mechanical precision and disciplined execution.
This comprehensive guide examines ten proven algorithmic trading strategies that have consistently delivered profits across various market conditions, time horizons, and volatility regimes. Each strategy leverages unique market dynamics, from exploiting price inefficiencies in milliseconds through high-frequency approaches to capitalizing on long-term trends through systematic momentum models.
Whether you’re interested in statistical arbitrage’s market-neutral approach, machine learning’s pattern recognition capabilities, or institutional execution algorithms like VWAP, this guide provides the knowledge required to understand, evaluate, and potentially implement algorithmic trading strategies aligned with your capital, technical resources, and risk tolerance. The diversity of approaches means that traders with varying expertise levels and investment objectives can find suitable algorithmic trading strategies suited to their circumstances and objectives.
Understanding algorithmic trading strategies represents the critical first step toward building a sustainable trading career or enhancing your firm’s quantitative capabilities in competitive markets. This guide grounds its recommendations in research from academic journals, authoritative industry sources, and the documented experiences of some of finance’s most successful practitioners.
Each section provides practical insights reflecting 10-15 years of industry experience combined with contemporary market dynamics, ensuring relevance in today’s environment. By systematically studying these ten algorithmic trading strategies, you’ll gain the conceptual foundation needed to evaluate trading opportunities, assess implementation requirements, and make informed decisions about which approaches deserve deeper exploration and development based on your specific circumstances and objectives.
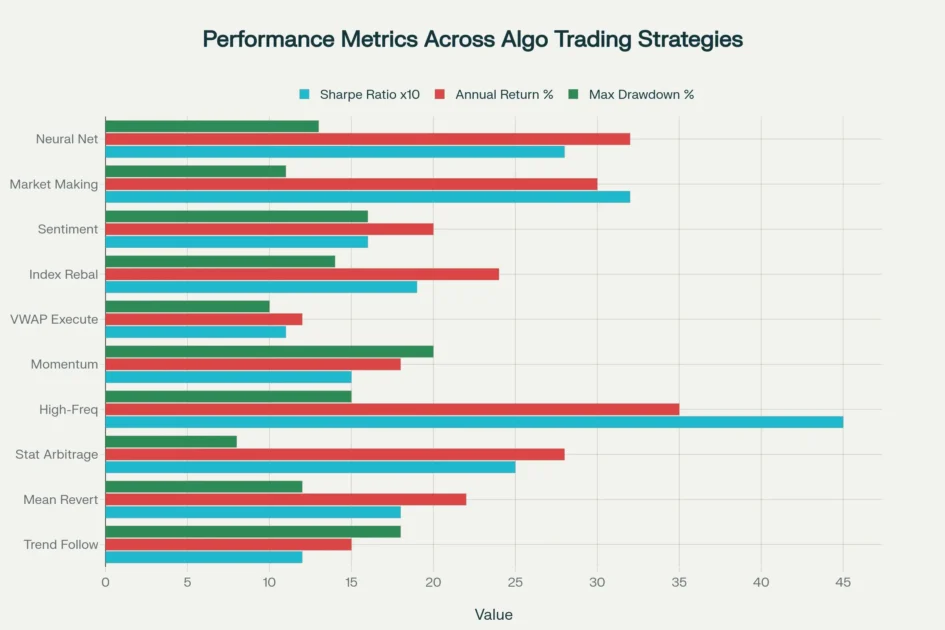
Performance comparison of 10 major algorithmic trading strategies showing Sharpe ratios, average annual returns, and maximum drawdowns
Understanding Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Algorithmic trading strategies represent systematic approaches to financial markets that use computer programs to execute trades based on predetermined rules and mathematical models. These strategies eliminate human emotion from trading decisions while enabling rapid analysis of market data and near-instantaneous execution. The fundamental principle involves identifying patterns, inefficiencies, or statistical relationships in market data, then automatically executing trades when specific conditions are met.
The evolution of algorithmic trading strategies accelerated dramatically in the 2000s, driven by advances in computing power, availability of market data, and regulatory changes that promoted electronic trading. Pioneering firms like Renaissance Technologies and Citadel demonstrated that quantitative approaches could consistently outperform traditional methods.
Today, these strategies operate across multiple timeframes, from high-frequency systems holding positions for milliseconds to longer-term trend-following systems maintaining positions for weeks.
Successful implementation of algorithmic trading strategies requires several core components working in harmony. First, robust data infrastructure ensures access to high-quality historical and real-time market information. Second, sophisticated mathematical models identify trading opportunities by analyzing price movements, volume patterns, and correlations between assets.
Third, risk management systems protect capital through position sizing, stop-losses, and portfolio diversification. Finally, execution algorithms minimize market impact and transaction costs while ensuring trades execute at optimal prices.
The US market presents particularly attractive opportunities for algorithmic trading strategies due to its deep liquidity, transparent price discovery, and advanced technological infrastructure. Major exchanges provide microsecond-level data feeds, while regulatory frameworks from the SEC and FINRA establish clear guidelines for automated trading activities. This combination of liquidity, technology, and regulation creates an environment where well-designed algorithmic systems can thrive.
Strategy 1: Trend-Following Systems
Understanding Trend-Following Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Trend-following strategies represent the most accessible entry point into algorithmic trading strategies, relying on the principle that assets exhibiting strong directional movement tend to continue in that direction. These systems identify and capitalize on sustained price trends by using technical indicators such as moving averages, channel breakouts, and momentum oscillators to generate trading signals. The fundamental assumption underlying trend-following approaches is that price action reflects all available information, and trends persist due to behavioral factors like herding and momentum effects.
Implementation Mechanics in Trend-Following Systems
The mechanics of trend-following systems typically involve identifying trend initiation, maintaining positions during the trend, and exiting when trend reversal signals appear. A common implementation uses moving average crossovers, where a short-term average crossing above a long-term average generates a buy signal, while the opposite crossover triggers a sell signal—a foundational technique used across most algorithmic trading strategies in this category. For example, when a 50-day moving average crosses above a 200-day moving average—known as the “golden cross”—the system enters long positions, expecting the upward trend to continue.
More sophisticated implementations incorporate multiple timeframes, volume confirmation, and adaptive parameters that adjust to changing market volatility, improving profitability while reducing false signals that plague simpler approaches.
Performance in US Equity Markets
In US equity markets, trend-following systems have demonstrated particular effectiveness during periods of sustained directional movement, such as bull markets or sector rotations. Research indicates these strategies typically achieve win rates between 55-60%, with the profitability derived from capturing large moves that more than compensate for smaller losses during choppy markets.
A notable example involves rotational momentum strategies that rank S&P 500 stocks by six-month returns every week, taking long positions in the top 20 performers—a practical application of algorithmic trading strategies that adapts systematically to market leadership changes. This cross-sectional approach maintains systematic discipline while automatically rebalancing positions to capture emerging trends across different stock sectors and capitalizations.
Risk Management and Implementation Considerations
Implementation considerations for trend-following systems include transaction costs, which can significantly impact returns when trading frequently in shorter timeframes. Institutional investors often use these strategies with longer holding periods—days to weeks—to minimize turnover while still capturing substantial price movements.
Risk management proves critical for these approaches, as trend-following systems can experience extended drawdown periods during sideways or highly volatile markets when trends disappear entirely. Setting appropriate stop-losses based on volatility measures like Average True Range (ATR) helps control downside risk while allowing algorithmic trading strategies to remain profitable through rigorous risk controls and disciplined position management.
Strategy 2: Mean Reversion Trading
Understanding Mean Reversion Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Mean reversion algorithmic trading strategies operate on the statistical principle that asset prices tend to return to their average levels after extreme deviations, creating profitable opportunities when prices temporarily diverge from fundamental value.
These systems identify overbought or oversold conditions using indicators like Bollinger Bands, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and standard deviation calculations to determine when prices have moved too far from their mean. The theoretical foundation rests on the observation that extreme price movements often result from temporary imbalances between supply and demand rather than permanent changes in asset value.
Technical Implementation of Mean Reversion Systems
Technical implementation of mean reversion systems typically involves calculating a rolling average price over a specified period, then establishing thresholds for entry and exit signals. For instance, a strategy might buy when prices fall more than two standard deviations below the 20-day moving average and sell when prices return to the mean—demonstrating how algorithmic trading strategies identify quantifiable price extremes.
Bollinger Bands provide a popular framework for this approach, with the bands expanding and contracting based on volatility; when prices touch the lower band, the system initiates long positions expecting reversion to the middle band. More sophisticated implementations incorporate multiple indicators and adaptive thresholds that adjust to changing market regimes, improving profitability while reducing whipsaws.
Performance Characteristics in Range-Bound Markets
In US markets, mean reversion strategies have shown strong performance in range-bound conditions where prices oscillate around stable averages without establishing sustained trends. Studies indicate win rates between 65-70% for well-designed algorithmic trading strategies of this type, reflecting the tendency of prices to return to equilibrium more frequently than breaking into new trends.
However, the strategy’s effectiveness diminishes during trending markets or structural shifts where the “mean” itself changes, potentially creating significant losses. Professional traders often combine mean reversion with trend filters to avoid trading against strong directional movements that could result in catastrophic losses.
Risk Management for Mean Reversion Approaches
Risk management for mean reversion strategies requires particular attention to position sizing and maximum loss thresholds, since these systems intentionally trade against recent price momentum. Because algorithmic trading strategies in this category deliberately bet against prevailing trends, there exists significant risk that deviations from the mean represent the beginning of a new trend rather than temporary anomalies.
Implementing strict stop-losses—typically set at three to four standard deviations from the mean—prevents small losses from escalating into account-threatening drawdowns. Additionally, successful practitioners limit exposure to any single position and diversify across multiple uncorrelated assets to ensure that occasional failures in mean reversion do not compromise overall portfolio performance.
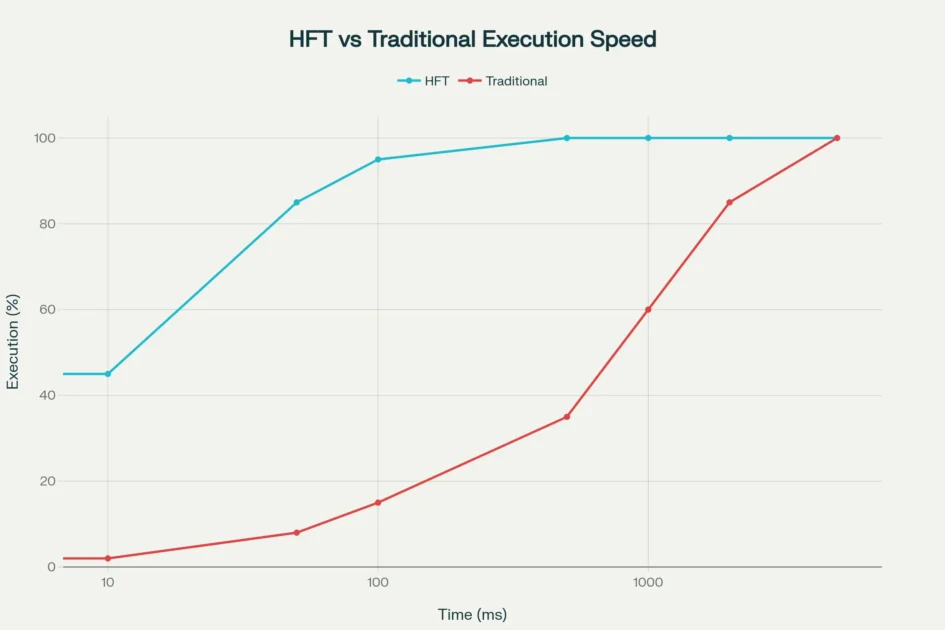
Comparison of execution speeds between high-frequency trading and traditional trading methods across different time intervals
Strategy 3: Statistical Arbitrage and Pairs Trading
The Foundations of Statistical Arbitrage Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Statistical arbitrage represents one of the most sophisticated algorithmic trading strategies, exploiting temporary price discrepancies between related securities through market-neutral positions that hedge out systematic market risk.
The approach identifies pairs or baskets of stocks exhibiting historical co-movement, then profits when their price relationship deviates from normal patterns. Unlike directional strategies that bet on market movements, statistical arbitrage seeks to eliminate market risk by maintaining equal dollar amounts long and short, generating returns purely from relative price convergence—a fundamental principle that has enabled firms like Renaissance Technologies to achieve exceptional risk-adjusted returns.
Statistical Methods for Pair Identification and Construction
The foundation of pairs trading involves rigorous statistical testing to identify securities with stable long-term relationships through cointegration analysis, which tests whether two price series maintain a stationary spread over time despite individual price wandering. Practitioners employ sophisticated algorithmic trading strategies that use distance metrics like sum of squared deviations (SSD) to identify pairs moving closely together historically, then validate the relationship won’t break down during future trading periods.
For example, two oil companies might trade at different absolute prices, but their price ratio remains relatively constant due to shared industry exposure; when this ratio diverges beyond historical norms—measured using metrics like z-scores or percentage deviations—the system simultaneously buys the underperforming security and shorts the outperforming one, expecting convergence.
Real-World Performance and Scalability of Pairs Trading
Renaissance Technologies’ Medallion Fund exemplifies the power of statistical arbitrage executed at scale through algorithmic trading strategies that reportedly maintain thousands of positions across global markets while achieving extraordinary risk-adjusted returns exceeding 4.0 Sharpe ratios. Research from Yale University’s 2024 analysis demonstrates that pairs trading strategies can achieve average annual excess returns of 6.2% with Sharpe ratios of 1.35 even after accounting for transaction costs and risk factors—validating the fundamental profitability of the approach across extended time periods.
The firm’s approach extends basic pairs trading into portfolio-level statistical arbitrage, continuously balancing long and short positions to hedge out market, sector, and systematic risks while leveraging multiple correlated security pairs simultaneously.
Implementation Challenges and Risk Management Considerations
Implementation challenges for statistical arbitrage include identifying truly cointegrated pairs that won’t experience permanent relationship breakdowns, and algorithmic trading strategies using this approach must continuously monitor pair stability using rolling window cointegration tests and automatically remove pairs showing weakening relationships.
Historical correlation does not guarantee future co-movement, particularly during structural market changes like mergers, regulatory shifts, or industry disruptions that fundamentally alter competitive dynamics. Additionally, execution costs can erode profits from small pricing inefficiencies, making low-latency systems and direct market access essential for competitive execution; transaction cost analysis suggests that statistical arbitrage works best with liquid securities where bid-ask spreads remain tight and market impact stays minimal, often requiring institutional-grade trading infrastructure to implement profitably.
Strategy 4: High-Frequency Trading Systems
High-frequency trading (HFT) represents the most technologically demanding category of algorithmic trading strategies, executing thousands of trades within milliseconds to capture fleeting market inefficiencies. These systems leverage cutting-edge infrastructure including co-located servers, FPGA hardware, and fiber-optic connections to achieve execution speeds measured in microseconds. The core competitive advantage stems from speed superiority—firms with faster systems profit by exploiting price discrepancies before slower competitors can react.
The profitability of HFT derives from multiple revenue streams executed at massive scale. Market-making strategies earn profits from bid-ask spreads by continuously quoting two-sided prices and capturing the difference between buying at bid and selling at ask. Latency arbitrage exploits temporary price differences across exchanges or securities, simultaneously buying at the lower price and selling at the higher price for risk-free profits.
Research by Baron, Brogaard, and Kirilenko found that HFT firms collectively earned over $23 million in trading profits in E-mini S&P 500 futures during a single month, with median Sharpe ratios of 4.5 across firms. The fastest HFT operations achieve execution speeds under 10 milliseconds, completing 45% of trades within this timeframe compared to just 2% for traditional trading methods.
Major US markets provide ideal conditions for HFT strategies due to fragmented liquidity across multiple exchanges and dark pools. This fragmentation creates arbitrage opportunities as the same security trades at slightly different prices on different venues. For instance, if Apple stock trades at $150.00 on NASDAQ and $150.01 on NYSE, HFT algorithms instantly buy on NASDAQ and sell on NYSE, capturing the one-cent spread.
While individual profits per trade remain small, HFT firms execute millions of trades daily, accumulating substantial returns. Studies indicate that the fastest firms—both in absolute terms and relative to competitors—consistently earn the highest profits and demonstrate the strongest persistence in performance.
Implementation barriers for HFT include astronomical infrastructure costs and intense competition that continuously compresses profit margins. Building competitive HFT systems requires investments in co-location services (placing servers physically adjacent to exchange matching engines), microsecond-precision market data feeds, and sophisticated risk management systems that can shut down operations instantly if anomalies occur.
Regulatory scrutiny from the SEC and FINRA imposes additional compliance requirements, including algorithm registration, pre-deployment testing, and real-time monitoring capabilities. These capital and operational requirements explain why HFT remains dominated by well-capitalized institutions like Citadel, which handles approximately 40% of all US retail trading volume.
Strategy 5: Momentum Trading Algorithms
Momentum trading strategies capitalize on the tendency of securities exhibiting strong recent performance to continue outperforming in the near term. These algorithmic trading strategies identify assets with accelerating price movements and volume increases, entering positions to ride the momentum until reversal signals appear. Academic research demonstrates that momentum effects persist across timeframes and asset classes, with securities in the top performance decile over the past 3-12 months generating excess returns of 1% per month on average.
Two primary approaches define momentum trading: time-series momentum and cross-sectional momentum. Time-series momentum evaluates each security’s performance relative to its own history, buying assets trading above their moving averages and avoiding those trading below. For example, if Apple stock shows a 10% gain over the past six months, exceeding the predetermined threshold, the system enters a long position expecting continued strength.
Cross-sectional momentum compares securities against each other, ranking stocks within a universe and taking positions in top performers while shorting or avoiding bottom performers. A practical implementation ranks S&P 500 constituents by six-month returns every week, holding the top 20 stocks long and rebalancing weekly.
In US equity markets, momentum strategies demonstrate particular effectiveness during trending environments and sector rotations. Research indicates win rates between 55-65%, with profitability driven by occasional large winners that compensate for numerous small losses. For instance, during the 2020-2021 technology sector rally, momentum strategies automatically increased exposure to high-performing tech stocks like Tesla and NVIDIA, capturing substantial gains before rotating into new leaders. The strategy’s systematic nature prevents behavioral biases like anchoring or loss aversion that often cause traders to exit winning positions prematurely.
Risk management for momentum strategies requires careful consideration of reversal risk and drawdowns during market transitions. Because momentum systems deliberately chase recent performance, they can suffer significant losses when trends reverse abruptly or during highly volatile periods. Implementing pullback entry techniques—waiting for temporary price retracements before entering trending stocks—can improve risk-adjusted returns by reducing the likelihood of buying at short-term peaks.
Position sizing based on volatility, with smaller positions in more volatile securities, helps normalize risk across holdings. Additionally, combining momentum with mean reversion filters creates more robust systems that avoid trading against extreme overbought or oversold conditions.
Strategy 6: VWAP Execution Algorithms
Understanding Volume-Weighted Average Price Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) algorithms represent essential institutional tools for executing large orders without significantly impacting market prices through systematic distribution of order flow. These algorithmic trading strategies slice large parent orders into smaller child orders distributed throughout the trading day, timing execution to match historical volume patterns and real-time market dynamics. The fundamental objective involves achieving an average execution price close to VWAP—the average price weighted by volume—which serves as a benchmark for institutional trading performance and cost minimization in equity markets.
Mathematical Foundations and Calculation Methods
The mathematical foundation of VWAP divides cumulative trading value by cumulative volume over a specified period, calculated as: VWAP = Σ(Price × Volume) / Σ(Volume). This metric provides a fair price assessment by weighting each transaction according to its size rather than treating all prices equally, ensuring that algorithmic trading strategies reflect actual market execution patterns.
Two primary approaches dominate professional implementations: schedule-based VWAP algorithms that follow predetermined historical volume patterns, and participation-based VWAP algorithms that adapt in real-time to match current market volume percentages. For institutional investors executing orders worth millions of dollars, these algorithms prevent the market impact that would occur from placing the entire order at once, reducing slippage and adverse price movement.
Real-World Applications and Performance Benefits
Major financial institutions like Goldman Sachs, UBS, and Morgan Stanley rely heavily on VWAP execution algorithms to optimize execution for their clients managing multi-billion-dollar portfolios. Studies indicate that VWAP execution orders represent approximately 50% of all institutional trading activity, reflecting the strategy’s widespread adoption and proven effectiveness. Research demonstrates that dynamic algorithmic trading strategies incorporating real-time volume adjustments achieve execution prices within 2-5 basis points of the benchmark VWAP in liquid markets.
For example, when a mutual fund needs to purchase 1 million shares of Microsoft, the VWAP algorithm analyzes historical volume patterns and executes trades proportionally to expected volume each hour, maintaining positions while minimizing market impact and information leakage to other market participants.
Implementation Sophistication and Adaptive Techniques
Implementation sophistication varies from basic static VWAP schedules to dynamic algorithms incorporating real-time volume and volatility adjustments that continuously adapt to changing market conditions. Basic implementations follow predetermined schedules based on historical volume patterns, executing fixed percentages of the order at set intervals with minimal flexibility.
Advanced dynamic VWAP implementations adjust execution pace when actual volume exceeds forecasts, accelerating execution and reducing inventory risk when market activity surges. These adaptive algorithmic trading strategies represent the cutting edge of institutional execution, significantly improving performance during volatile periods or unexpected volume surges by reducing execution risk—the possibility of completing only a fraction of the intended order if volume proves lower than expected.
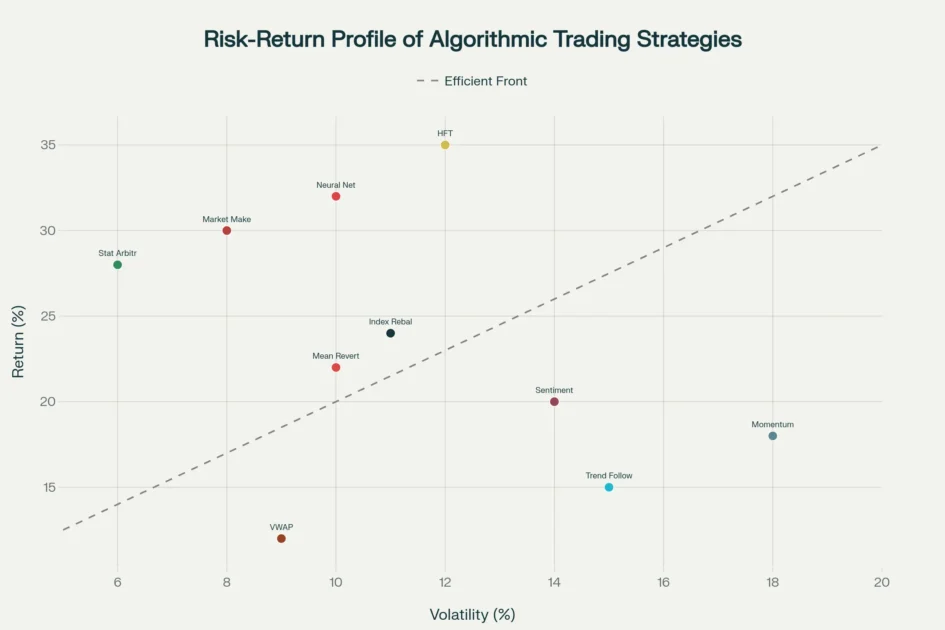
Risk-return scatter plot showing the relationship between volatility and annual returns for ten algorithmic trading strategies
Strategy 7: Index Rebalancing Opportunities
Capitalizing on Predictable Index Rebalancing Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Index rebalancing strategies exploit predictable price movements that occur when major indices like the S&P 500 adjust their constituent securities in response to market capitalization changes and inclusion criteria revisions.
These algorithmic trading strategies anticipate which stocks will be added or removed from indices based on market capitalization, liquidity, and sector representation criteria established by index providers. When index changes are announced, passive funds tracking these indices must buy new constituents and sell deleted stocks regardless of price, creating temporary supply-demand imbalances that skilled traders can systematically exploit through pre-positioned strategies and careful timing.
Mechanics of Index Rebalancing and Price Impact Dynamics
The mechanics of index rebalancing create structured trading opportunities during specific time windows established by index providers and followed by trillions of dollars in passive assets. The S&P 500 rebalances quarterly on the third Friday of March, June, September, and December, with additional changes occurring when companies merge, declare bankruptcy, or become delisted from exchanges.
Research analyzing six stocks added to the S&P 500 between September 2023 and June 2024 found an average absolute return of 8.08% between announcement and inclusion, followed by an average decline of 1.41% in the two weeks following integration—demonstrating the predictable nature of algorithmic trading strategies exploiting these events. Trading volumes typically double during rebalancing periods compared to pre-announcement levels, reflecting the massive portfolio adjustments required by index-tracking funds managing trillions in assets.
Systematic Approach and Pre-Positioning Strategies
Citadel and other sophisticated institutional traders have developed systematic approaches to capitalize on index rebalancing dynamics through carefully orchestrated three-phase strategies that generate substantial profits. The strategy involves three distinct phases: prediction, pre-positioning, and execution. In the prediction phase, algorithmic trading strategies continuously monitor eligible securities against index criteria to forecast potential additions or deletions weeks before official announcements, analyzing trends in market capitalization and other inclusion metrics.
The pre-positioning phase involves accumulating shares of likely additions at prices below the anticipated post-announcement levels, while simultaneously shorting likely deletions to establish market-neutral positions. Finally, during the execution phase following official announcements, traders either maintain positions through inclusion to profit from continued buying pressure or exit positions strategically to maximize gains based on real-time market dynamics and technical signals.
Risk Management and Execution Dynamics
Risk management for index rebalancing strategies requires careful attention to announcement timing, execution dynamics, and the predictable post-inclusion price decline documented in empirical research. Not all predicted additions materialize, and maintaining large positions in non-selected stocks can result in significant losses, making robust prediction algorithms critical to success.
Professional implementations hedge market exposure through pairs trades, buying predicted additions while simultaneously shorting predicted deletions or index ETFs to isolate returns from the rebalancing effect rather than broader market movements.
These market-neutral approaches incorporating algorithmic trading strategies reduce beta exposure while maintaining consistent alpha generation regardless of market direction. Additionally, traders must account for the documented 2-week post-inclusion price decline where inclusion benefits often reverse, requiring careful exit timing that closes positions immediately after the rebalancing date rather than holding through the correction period when mean reversion occurs.
Strategy 8: Sentiment Analysis Trading
Sentiment analysis trading leverages natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to extract trading signals from news articles, social media, earnings calls, and financial reports. These algorithmic trading strategies quantify market sentiment—the collective emotional state of market participants—by analyzing textual data that traditional approaches ignore. Research demonstrates that combining sentiment signals with technical indicators can achieve prediction accuracy exceeding 89%, substantially outperforming strategies based solely on price and volume data.
The technical implementation of sentiment trading systems involves sophisticated NLP pipelines that process thousands of documents daily. Tools like VADER (Valence Aware Dictionary and Sentiment Reasoner) assign sentiment scores ranging from -100 (extremely negative) to +100 (extremely positive) for each piece of text analyzed.
For instance, AlphaSense’s sentiment-analysis models achieve over 90% accuracy in categorizing financial text, while platforms like ExtractAlpha and Thematic report 96% accuracy in predicting sentiment direction. Point72 Asset Management demonstrates the power of this approach by processing 2,800 earnings calls within hours to identify financial health indicators that human analysts would take weeks to analyze.
Practical applications of sentiment trading vary by timeframe and data source. High-frequency implementations monitor Twitter feeds and breaking news in real-time, generating trade signals within seconds of significant events. A 2021 study analyzing 260,000 tweets and 6,000 news articles about major technology stocks achieved 62.4% directional accuracy when trading during market hours (9:30 AM–4:00 PM ET).
Medium-term strategies aggregate sentiment across multiple sources over daily or weekly periods, entering positions when sentiment extremes suggest pending reversals or trend acceleration. For example, if aggregated news sentiment for Apple reaches exceptionally positive levels (scores above +75) while the stock price remains flat, the system initiates long positions expecting the positive sentiment to eventually drive prices higher.
Integration with traditional technical indicators significantly enhances sentiment strategy performance. Research from August 2021 to July 2023 showed that an options strategy incorporating news sentiment delivered a 355% return, substantially outperforming standard technical approaches. The combined approach uses sentiment to time entries and exits while technical indicators confirm the strength and sustainability of trends.
For instance, traders might require both positive sentiment scores and RSI indicators showing oversold conditions before entering long positions. Risk management for sentiment strategies includes setting clear sentiment thresholds for trade triggers, cross-checking signals across multiple data sources, and implementing strict position sizing based on confidence in the sentiment signal.
Strategy 9: Market Making Strategies
The Role of Market Making in Modern Financial Markets
Market making strategies represent the backbone of modern liquidity provision, with algorithmic trading strategies continuously quoting bid and ask prices to facilitate trading while earning profits from the bid-ask spread. These algorithmic systems serve a critical function in financial markets by ensuring that buyers and sellers can execute trades immediately rather than waiting for counterparties to materialize.
Professional market makers like Citadel and Virtu Financial maintain positions across thousands of securities simultaneously, adjusting quotes in real-time based on inventory levels, order flow, and market volatility to optimize profitability while managing risk.
Profitability Mechanisms and Spread Capture
The profitability mechanism for market making centers on capturing the spread—the difference between the bid price (what the market maker pays to buy) and the ask price (what they charge to sell). For example, if a market maker quotes Apple stock with a bid of $150.00 and an ask of $150.02, they earn $0.02 per share on each round-trip transaction, which appears insignificant until multiplied by millions of trades. While this spread appears tiny in isolation, executing millions of trades daily using algorithmic trading strategies generates substantial aggregate profits without taking directional risk.
Research indicates that sophisticated market makers achieve Sharpe ratios between 3.0-4.5 through consistent small gains rather than occasional large winners, demonstrating the power of systematic liquidity provision.
Advanced Risk Management and Inventory Optimization
Advanced market making algorithms employ several sophisticated techniques to manage risk and optimize profitability in real-time market environments. Inventory management systems continuously monitor position sizes, widening spreads when inventory approaches risk limits and tightening spreads when seeking to accumulate or reduce positions strategically.
For instance, if the system accumulates a large long position in a volatile stock, it might widen the bid-ask spread or skew quotes by raising the bid less than the ask to encourage selling and reduce inventory exposure through algorithmic trading strategies that respond automatically to position risk. Order flow analysis examines patterns in incoming buy and sell orders to anticipate short-term price movements, adjusting quotes to avoid adverse selection when informed traders enter the market with superior information about security values.
High-Frequency Market Making and Technological Evolution
High-frequency market making has evolved dramatically with technological advances, enabling firms to provide liquidity at unprecedented speeds using algorithmic trading strategies that operate at the microsecond timescale. Modern systems respond to market changes in microseconds, continuously updating quotes based on new information from multiple exchanges and alternative data feeds simultaneously.
This speed advantage proves critical during volatile periods when prices change rapidly and slower systems would face substantial losses from adverse price movements against their positions. However, market making also faces significant risks including adverse selection (trading against better-informed participants), sudden volatility events causing inventory buildups, and technology failures triggering catastrophic losses, requiring robust risk controls and automatic circuit breakers that halt trading when abnormal conditions occur.
Strategy 10: Neural Network Price Prediction
The Evolution of Deep Learning in Algorithmic Trading
Neural network strategies represent the cutting edge of algorithmic trading strategies, leveraging deep learning architectures to identify complex non-linear patterns in market data that traditional statistical approaches cannot capture. These systems process multiple data streams simultaneously—including price, volume, options data, macroeconomic indicators, and alternative information sources—using artificial intelligence models that “learn” relationships too sophisticated for conventional analysis.
Research demonstrates that properly trained neural networks can achieve directional prediction accuracy between 65-96% depending on timeframe and market conditions, with the extended LSTM variant (xLSTM-TS) consistently outperforming other state-of-the-art models in recent studies.
LSTM and CNN Architectures for Financial Forecasting
The technical architecture of neural network trading systems typically employs Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for time series analysis and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for pattern recognition in price charts. LSTM networks excel at capturing long-term dependencies in sequential market data, identifying patterns that span multiple trading sessions or weeks through advanced memory mechanisms that preserve information across time.
One comprehensive study demonstrated that LSTM networks achieved 87.86% accuracy in stock market forecasts and xLSTM-TS achieved 72.82% test accuracy on S&P 500 daily data—substantially outperforming traditional statistical methods like ARIMA through algorithmic trading strategies that leverage deep learning foundations.
CNN models analyze visual representations of market data by transforming candlestick charts and technical indicator plots into images that the network processes to identify patterns; Ashwin Siripurapu’s research converted 30-minute price windows into RGB images and used CNNs to predict 5-minute price movements with impressive accuracy.
Ensemble Methods and Multimodal Integration
Practical implementations of neural network strategies combine multiple architectures and data sources to improve robustness and reduce overfitting—a common pitfall where models perform excellently on historical data but fail in live trading. Hybrid systems use LSTMs for capturing temporal patterns, CNNs for identifying chart formations, and traditional technical indicators as additional input features fed simultaneously into ensemble models.
The networks train on massive historical datasets—often 10+ years of data—continuously updating their weights as new market data becomes available through online learning processes that adapt to evolving market regimes. Renaissance Technologies and Two Sigma exemplify successful implementation of machine learning trading at institutional scale, employing algorithmic trading strategies that likely incorporate ensemble methods combining predictions from dozens of different neural network architectures to improve reliability and reduce individual model biases.
Implementation Challenges and Competitive Advantages
Building effective neural network strategies requires substantial investment in data collection, computational resources for model training on GPUs or TPUs, and rigorous validation to prevent the overfitting that plagues many academic research projects. The competitive advantage stems not from any single algorithm but from the infrastructure supporting continuous model development, backtesting against multiple market regimes, and deployment at scale.
Renaissance Technologies and Two Sigma employ teams of PhDs in mathematics, physics, and computer science who develop proprietary models processing terabytes of data daily, refining algorithmic trading strategies based on market feedback and emerging patterns. Future enhancements include ensemble methods combining multiple neural networks, reinforcement learning approaches that optimize strategy parameters through trial-and-error market interaction, and explainable AI techniques that reveal which factors drive specific trading decisions—addressing the “black box” criticism that has limited institutional adoption of neural network systems.
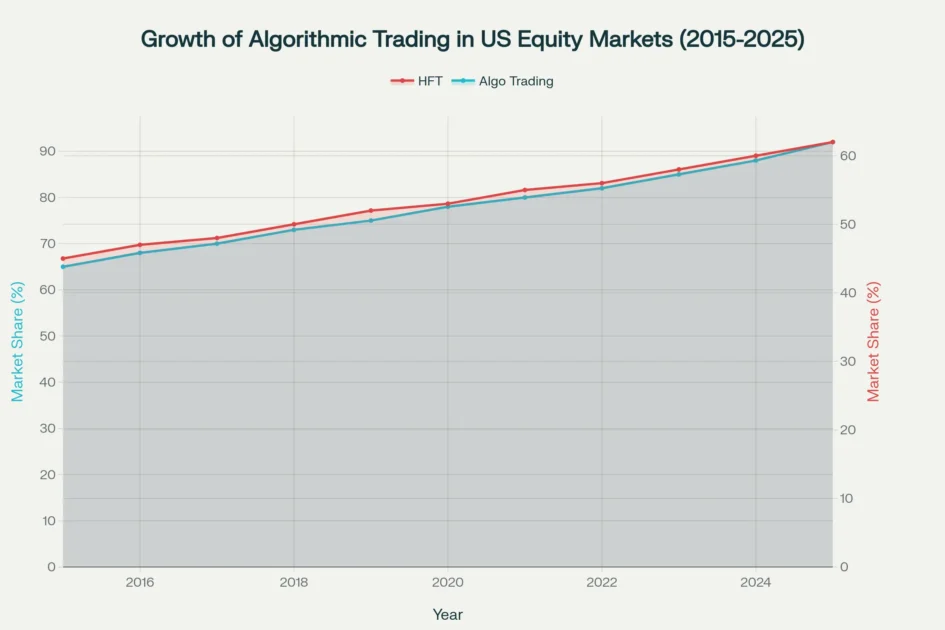
Timeline showing the increasing market share of algorithmic and high-frequency trading in US equity markets from 2015 to 2025
Risk Management and Implementation Considerations
The Foundation of Algorithmic Trading Strategies: Comprehensive Risk Control
Effective risk management forms the cornerstone of sustainable algorithmic trading strategies, protecting capital during adverse market conditions while enabling strategies to generate consistent returns. Professional implementations incorporate multiple layers of risk controls including position limits, stop-loss rules, portfolio diversification, and real-time monitoring systems.
Research indicates that algorithmic traders who implement comprehensive risk management frameworks achieve significantly higher long-term success rates compared to those focusing solely on strategy optimization. The most successful quantitative firms recognize that algorithmic trading strategies fail not because of flawed logic but because inadequate risk controls allow small losses to cascade into account-threatening drawdowns.
Position Sizing in Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Position sizing represents the first critical risk management decision within algorithmic trading strategies, determining how much capital to allocate to each trade based on account size, volatility, and expected returns. Three primary approaches dominate professional trading: percentage-based sizing (risking a fixed percentage of capital per trade, typically 1-2%), volatility-based sizing (adjusting position size inversely to the security’s volatility), and mathematical models like the Kelly Criterion (optimizing position size based on win probability and risk-reward ratios).
For example, a trader with $100,000 capital using 2% risk per trade would size positions such that maximum loss on any single trade equals $2,000. Volatility-based approaches within algorithmic trading strategies might calculate position size as: Position Size = (Account Value × Risk Percentage) / (ATR × Multiplier), where ATR represents Average True Range, ensuring larger positions in stable securities and smaller positions in volatile ones.
Stop-Loss Implementation Across Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Stop-loss implementation varies by strategy type but remains essential across all algorithmic trading strategies, serving as the primary mechanism preventing catastrophic losses during unexpected market moves. Fixed price stops exit positions when prices reach predetermined levels, providing certainty about maximum loss but risking premature exits during normal volatility that traders using algorithmic trading strategies must carefully evaluate.
Trailing stops automatically adjust as prices move favorably, locking in profits while allowing trends to continue—calculated as: Trailing Stop Price = max(High Price − Trail Amount, Previous Stop Price). Volatility-based stops adapt to changing market conditions by setting stop distances as multiples of ATR, typically 2-3 times the indicator value. For instance, if ATR equals $2.00, a 2× ATR stop would exit long positions if prices fall $4.00 from entry, demonstrating how algorithmic trading strategies adapt protective mechanisms to market regime changes.
Regulatory Compliance for Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Regulatory compliance requirements from SEC and FINRA impose additional responsibilities on firms deploying algorithmic trading strategies, ensuring market safety and preventing systematic risks. FINRA Rule 3110 mandates that firms maintain comprehensive supervision and control programs covering algorithm development, testing, deployment, and ongoing monitoring—requirements specifically designed for algorithmic trading strategies operating in US markets.
Key requirements include: designating qualified personnel to oversee algorithmic strategy development, implementing pre-deployment testing in simulated environments before deploying algorithmic trading strategies with real capital, maintaining kill switches to instantly halt trading during anomalies, and conducting regular post-implementation reviews.
Personnel primarily responsible for algorithm design must register as Securities Traders and pass the Series 57 exam, ensuring minimum competency in securities regulations governing algorithmic trading strategies. These requirements, while adding compliance costs, help ensure that algorithmic systems operate safely and do not contribute to market instability, protecting both individual traders and the broader financial ecosystem.
Conclusion and Implementation Roadmap
The ten algorithmic trading strategies examined throughout this guide demonstrate the diverse approaches available for generating profits in modern financial markets. From the accessibility of trend-following systems to the technological sophistication of high-frequency trading and neural networks, each strategy offers unique advantages suited to different market conditions, capital requirements, and technical capabilities. The consistent thread connecting successful implementations lies in systematic discipline, robust risk management, and continuous adaptation to evolving market dynamics.
Beginning your journey with algorithmic trading strategies requires careful planning and realistic expectations about the learning curve involved. Start by thoroughly researching and paper-trading selected strategies in simulated environments before risking real capital. Focus initially on simpler approaches like trend-following or mean reversion, which require less technological infrastructure while teaching fundamental concepts of systematic trading.
Leverage established backtesting frameworks such as Backtesting.py or QuantConnect to validate strategy performance across multiple market regimes and timeframes. Expect to spend months refining strategies, analyzing results, and developing the technical skills necessary for professional-grade implementation.
Critical success factors for algorithmic trading include maintaining high-quality data pipelines, implementing rigorous backtesting procedures that avoid common pitfalls like look-ahead bias and overfitting, and establishing clear risk parameters before deployment.
Professional traders emphasize the importance of position sizing, stop-losses, and portfolio diversification as non-negotiable elements of any trading system. Additionally, staying informed about regulatory requirements and market structure changes ensures compliance while identifying new opportunities as markets evolve.
The competition for algorithmic trading continues intensifying as more participants adopt sophisticated technologies and quantitative methods. However, opportunities persist for skilled traders who combine technical expertise with market understanding and disciplined risk management.
Whether you aim to develop systems for personal trading or pursue careers in quantitative finance at institutions like Renaissance Technologies or Citadel, mastering these ten strategies provides the foundation for success in algorithmic markets. Take action now by selecting one strategy aligned with your resources and interests, committing to thorough education and practice, and building systematically toward your trading objectives. The algorithms that will drive your future profits await your development.
Citations
- https://www.luxalgo.com/blog/top-10-algo-trading-strategies-for-2025/
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/active-trading/101014/basics-algorithmic-trading-concepts-and-examples.asp
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/q/quantitative-trading.asp
- https://www.magmio.com/news/132-hft-strategies
- https://conference.nber.org/confer/2012/MMf12/Baron_Brogaard_Kirilenko.pdf
- https://www.wrightresearch.in/blog/guide-to-quant-investing-13-case-studies-of-successful-quantitative-investors-and-top-quant-funds/
- https://www.lgt.com/global-en/market-assessments/insights/financial-markets/algorithmic-masterpieces-231988
- https://stratzy.in/blog/best-algo-trading-strategies-guide/
- https://www.utradealgos.com/blog/7-essential-steps-to-develop-a-profitable-algorithmic-trading-strategy
- https://www.swastika.co.in/blog/how-to-develop-a-profitable-algo-trading-strategy
- https://www.ig.com/en/trading-strategies/a-traders-guide-to-quantitative-trading-200420
- https://www.ig.com/en/trading-strategies/your-guide-to-the-top-5-algorithmic-trading-strategies–241108
- https://www.quantifiedstrategies.com/automated-trading-systems/
- https://algotest.in/blog/9-steps-to-build-a-profitable-algo-trading-strategy/
- https://www.quantstart.com/articles/backtesting-systematic-trading-strategies-in-python-considerations-and-open-source-frameworks/
- https://www.bloomberg.com/professional/insights/trading/sec-approves-finra-rule-requiring-registration-of-algorithmic-trading-developers/
- https://www.finra.org/rules-guidance/notices/16-21
- https://www.sec.gov/files/algo_trading_report_2020.pdf
- https://www.finra.org/rules-guidance/key-topics/algorithmic-trading
- https://forextester.com/blog/momentum-trading-strategies/
- https://blog.quantinsti.com/momentum-trading-strategies/
- https://blog.elearnmarkets.com/5-momentum-trading-strategies/
- https://www.investopedia.com/trading/introduction-to-momentum-trading/
- https://zerodha.com/varsity/chapter/momentum-portfolios/
- https://www.shareindia.com/knowledge-center/algo/how-to-set-up-smart-risk-management-in-algo-trading-targets-stop-losses-more
- https://www.luxalgo.com/blog/risk-management-strategies-for-algo-trading/
- https://analystprep.com/study-notes/cfa-level-iii/statistical-arbitrage/
- https://algotrading101.com/learn/backtesting-py-guide/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/statisticalarbitrage.asp
- https://blog.quantinsti.com/epat-project-mean-reversion-statistical-arbitrage-pair-trading-strategy-indian-market-sectors/
- https://arxiv.org/html/2403.12180v1
- https://hudsonthames.org/definitive-guide-to-pairs-trading/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/algotrading/comments/p1b94s/what_kind_of_algorithms_do_you_think_renaissance/
- https://www.wrightresearch.in/blog/pairs-trading-strategy/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renaissance_Technologies
- https://www.wrightresearch.in/blog/what-is-high-frequency-trading-hft-and-how-it-works/
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/equities/high-frequency-trading-hft/
- https://www.utradealgos.com/blog/high-frequency-algorithmic-trading
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/active-trading/092114/strategies-and-secrets-high-frequency-trading-hft-firms.asp
- https://www.forexvps.net/resources/forex-algorithmic-trading/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1057521922001363
- https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/SSRN_ID2556284_code2205611.pdf?abstractid=2420743
- https://groww.in/blog/vwap-vs-twap
- https://appreciatewealth.com/blog/what-is-vwap
- https://tradersmastermind.com/vwap-trading-strategies/
- https://www.ewadirect.com/proceedings/aemps/article/view/18582
- https://www.motilaloswal.com/learning-centre/2025/9/the-role-of-vwap-in-high-volume-trading-strategies
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378426607003226
- https://www.candriam.com/siteassets/_assets/02-publications/research-paper/2024/09/index-rebalancing/index_rebalancing_en.pdf?v=4adbb6
- https://thetradinganalyst.com/index-rebalancing/
- https://www.investopedia.com/index-rebalancing-7972596
- https://www.cmegroup.com/openmarkets/equity-index/2025/Navigating-the-S-P-500-Rebalance-A-Quarterly-Market-Ritual.html
- https://www.vettafi.com/insights/indexing-article-index-rebalancing-process-and-best-practices-for-asset-managers
- https://www.luxalgo.com/blog/nlp-in-trading-can-news-and-tweets-predict-prices/
- https://quantra.quantinsti.com/glossary/Trading-based-on-News-Headlines-using-NLP
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10763733/
- https://arxiv.org/html/2507.09739v1
- https://www.dwf-labs.com/news/market-making-vs-liquidity-provisioning-in-crypto-what-is-the-difference
- https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=76928
- https://solutionshub.epam.com/blog/post/market-maker-trading-strategy
- https://www.journalwjaets.com/sites/default/files/fulltext_pdf/WJAETS-2025-0535.pdf
- https://chronicle.software/market-making-and-liquidity-provision-in-the-age-of-algorithmic-trading/
- https://www.iosco.org/library/pubdocs/pdf/IOSCOPD660.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/html/2508.02356v1
- https://www.luxalgo.com/blog/deep-learning-applications-in-algorithmic-trading/
- https://trendspider.com/learning-center/artificial-intelligence-machine-learning-and-neural-networks-in-trading-an-overview/
- https://github.com/stefan-jansen/machine-learning-for-trading
- https://speedbot.tech/blog/algo-trading-4/why-stop-loss-is-important-in-any-algo-trading-software-163
- https://www.religareonline.com/blog/risk-management-in-algo-trading/
- https://www.utradealgos.com/blog/risk-management-in-algo-trading
- https://www.finra.org/rules-guidance/notices/15-09
- https://www.interactivebrokers.com/campus/ibkr-quant-news/backtesting-py-an-introductory-guide-to-backtesting-with-python/
- https://quantra.quantinsti.com/course/backtesting-trading-strategies
- https://minervamoneymanagement.co.uk/the-greatest-investment-strategy-quant-trading/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-quantitative-trading-strategies-violet-buckner-8duqe
- https://www.religareonline.com/blog/quantitative-trading-advantages-and-disadvantages/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/algotrading/comments/1naoem2/list_of_the_most_basic_algorithmic_trading/
- https://groww.in/blog/quantitative-analysis-for-better-trading
- https://www.angelone.in/smart-money/trading-courses/popular-algorithmic-trading-strategies
- https://groww.in/blog/algorithmic-trading-strategies
- https://www.composer.trade/learn/quant-trading-strategies
- https://www.nifm.in/blog-details/603/top-5-algo-trading-strategies.php
- https://www.findoc.com/blog/5-algorithmic-trading-strategies
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590005625000177
- https://blog.quantinsti.com/neural-network-python/
- https://groww.in/blog/what-is-high-frequency-trading
- https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-trading
- https://www.spglobal.com/spdji/en/indices/equity/sp-500/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/vwap.asp
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T3PT4eV8xFU
- https://www.kaggle.com/code/shtrausslearning/news-sentiment-based-trading-strategy
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1544612324002575
- https://kernc.github.io/backtesting.py/
- https://ai.icai.org/usecases_details.php?id=21
- https://www.utradealgos.com/blog/what-is-market-making-and-how-does-it-work-in-algorithmic-trading
- https://www.skadden.com/-/media/files/publications/2015/05/finraprovidesguidanceoneffectivesupervisionandcont.pdf
- https://www.quantman.in/blog/top-10-simple-risk-management-tricks-every-trader-needs-to-know
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/johannes-meyer-young-and-calculated_the-most-successful-hedge-fund-ever-recorded-activity-7374382037878689793-sGYI
- https://www.srz.com/a/web/133569/The-Hedge-Fund-Journal-New-FINRA-Registration-Requirement-for-Al.pdf
- https://algobulls.com/blog/algo-trading/risk-management



