9 Critical Stock Market Crash Survival Strategies
The financial panorama shifts dramatically when markets enter freefall, and understanding how to protect wealth during these turbulent periods separates successful investors from those who suffer devastating losses.
Stock market crashes have historically wiped out trillions of dollars in value, yet those equipped with proven Stock Market Crash Survival strategies not only preserve capital but often emerge stronger when recovery begins. The 2008 financial crisis saw the S&P 500 plunge 57%, while the 2020 COVID-19 crash triggered a 34% decline in mere weeks. These events underscore the critical importance of preparation, strategic thinking, and disciplined execution when navigating market downturns.
Recent market conditions have heightened investor anxiety, with recession probabilities climbing and volatility indicators flashing warning signs. Americans face mounting financial pressure—one in three now have no emergency savings, with the median emergency fund shrinking to just $500. This financial fragility leaves millions vulnerable when markets crash, forcing panic selling that locks in losses and undermines long-term wealth accumulation. Understanding Stock Market Crash Survival tactics provides the foundation for weathering economic storms while positioning portfolios for eventual recovery.
This comprehensive guide examines nine critical strategies backed by decades of market data, academic research, and real-world performance during major downturns. From the Great Depression’s 25-year recovery period to the COVID-19 crash’s rapid six-month rebound, historical patterns reveal actionable insights for protecting capital.
These Stock Market Crash Survival strategies address both defensive positioning before crashes occur and opportunistic tactics during recovery phases. Whether managing retirement accounts or building long-term wealth, implementing these proven approaches can mean the difference between financial devastation and sustained prosperity through market cycles.
Mastering Stock Market Crash Survival requires comprehensive understanding of diversification principles, emergency fund adequacy, tactical rebalancing, and psychological resilience that prevents panic-driven decisions during maximum market stress.
The strategies detailed throughout this guide have proven their worth across multiple market crashes, from the 1929 Great Depression to modern algorithmic-driven flash crashes. Investors who embrace these Stock Market Crash Survival principles position themselves not merely to survive downturns but to capitalize on opportunities that emerge when fear reaches peak intensity.

Historical recovery times for major stock market crashes showing the difference between nominal and inflation-adjusted recovery periods
Build a Fortress: Portfolio Diversification as Your Primary Stock Market Crash Survival Defense
Portfolio diversification stands as the cornerstone of Stock Market Crash Survival, proven to reduce losses by 30-50% during severe market downturns. The 2008 financial crisis demonstrated this principle with remarkable clarity—investors holding 100% stock portfolios required 4.5 years to recover their losses, while those with 60% stocks and 40% bonds bounced back in just three years. More impressively, diversified multi-asset portfolios recovered in approximately 2.5 years while experiencing significantly smaller peak declines. This fundamental Stock Market Crash Survival strategy provides the first line of defense against catastrophic losses.
Asset class diversification works because different investments respond uniquely to economic conditions and market stress. During the 2008 crisis, while stocks plummeted 57%, high-quality bonds provided stability and even generated positive returns as investors fled to safety. This negative correlation between asset classes creates a buffer that absorbs market shocks and enhances Stock Market Crash Survival prospects. Geographic diversification adds another layer of protection, as international markets frequently move independently of U.S. equities. Real estate investment trusts, commodities, and alternative investments further enhance portfolio resilience by providing exposure to different economic drivers.
The mechanics of diversification extend beyond simple asset allocation to include sector, industry, and individual security selection. Research from the financial crisis period reveals that portfolios concentrated in cyclical sectors like financials and consumer discretionary suffered losses exceeding 70%, while those balanced across defensive sectors experienced far less damage. Technology stocks declined 35% during recessions on average, whereas consumer staples fell only 8% and utilities dropped just 10%. This sector-level diversification represents a critical component of comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival planning that many investors overlook until disaster strikes.
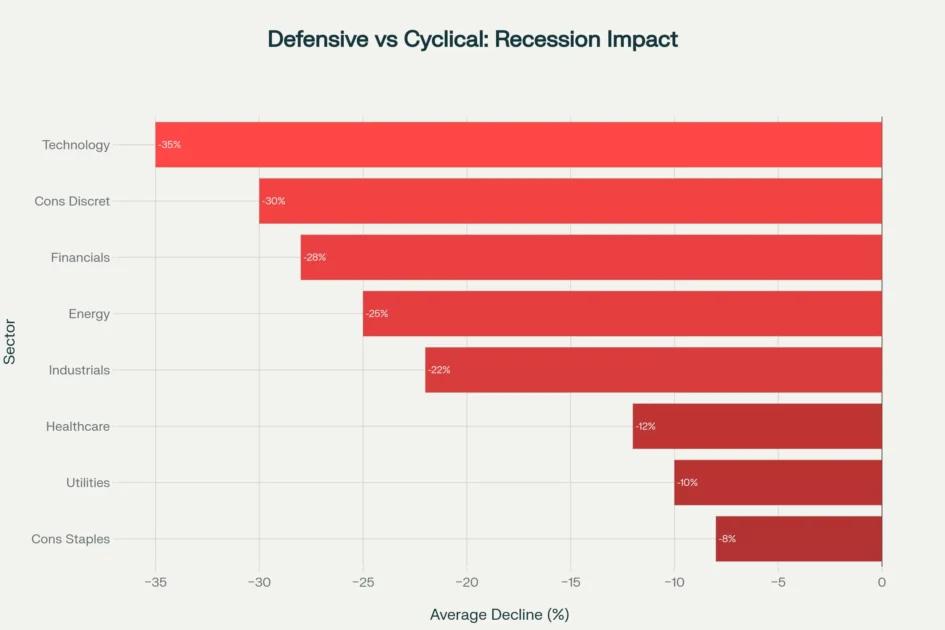
Sector performance comparison during economic recessions, highlighting defensive sectors’ resilience against market downturns
Target-date funds and balanced funds offer streamlined diversification for investors seeking simplified approaches to portfolio construction. These professionally managed vehicles automatically adjust asset allocation based on time horizons and risk tolerance, removing emotional decision-making from the equation. For hands-on investors, quarterly or semi-annual rebalancing maintains desired diversification levels, systematically selling overweighted assets and buying underweighted positions. This disciplined approach forces investors to sell high and buy low, counter to natural emotional tendencies that drive destructive behavior during crashes.
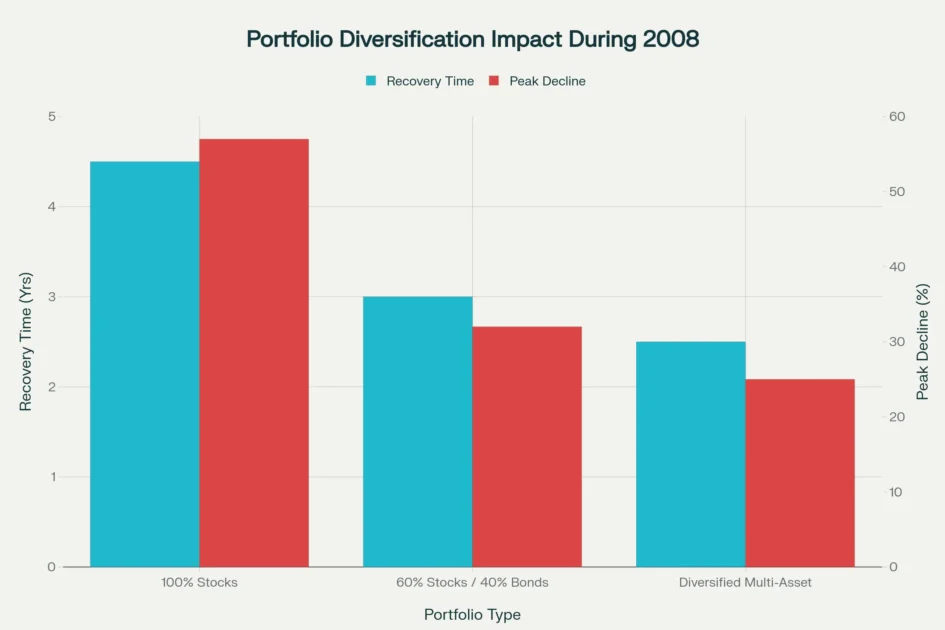
Comparison of recovery times and peak declines for different portfolio allocation strategies during the 2008 financial crisis
Establish Your Financial Moat: Emergency Fund Strategy for Stock Market Crash Survival
Emergency funds serve as the foundation of Stock Market Crash Survival, providing liquidity that prevents forced selling during market downturns. Financial advisors universally recommend maintaining three to six months of living expenses in readily accessible accounts, though many Americans fall dangerously short of this target. The median American emergency fund stands at just $500 in 2025, down from $600 the previous year—barely enough to cover a single unexpected car repair or medical bill. This financial fragility forces investors to liquidate investments at precisely the worst moments, locking in losses that might otherwise recover over time and undermining Stock Market Crash Survival efforts.
The mathematical impact of emergency fund availability becomes stark when examining three-year portfolio outcomes following market crashes. Investors without emergency reserves who face forced selling to cover living expenses see portfolio values remain 15% below starting levels after three years. In contrast, those with adequate cash reserves who maintain positions through downturns typically recover to 110% of initial values over the same period.
Most remarkably, investors combining emergency funds with disciplined dollar-cost averaging achieve 125% recovery rates while experiencing dramatically lower emotional stress throughout the crisis. These outcomes demonstrate why emergency reserves represent non-negotiable elements of effective Stock Market Crash Survival strategies.

Impact of emergency fund strategies on portfolio recovery and investor stress levels following a market crash
Optimal emergency fund construction employs a tiered approach that balances accessibility with modest returns. Tier one consists of one month’s expenses in high-yield savings accounts or money market accounts, providing immediate access within 24 hours. Tier two holds two to three months of expenses in money market mutual funds or short-term certificates of deposit, accessible within 2-3 business days.
Tier three comprises remaining emergency reserves in Treasury I Bonds or CD ladders with staggered maturities, offering inflation protection and higher yields for funds unlikely to be needed immediately. This structured approach maximizes Stock Market Crash Survival readiness while generating reasonable returns on cash reserves.
Retirees face unique emergency fund requirements due to sequence-of-returns risk—the danger that market crashes early in retirement permanently impair portfolio sustainability. Financial planners recommend retirees maintain two to four years of living expenses in cash and cash equivalents, far exceeding the standard three to six months advised for working professionals.
This extended runway allows retirees to draw from cash reserves rather than selling depressed stocks during prolonged bear markets. Historical data shows retirees forced to take large withdrawals during market crashes face dramatically increased longevity risk, potentially outliving their savings. Adequate emergency reserves represent the single most important Stock Market Crash Survival tool for those living on portfolio withdrawals.
Master the Art of Buying Low: Dollar-Cost Averaging for Stock Market Crash Survival
Dollar-cost averaging represents a powerful Stock Market Crash Survival technique that removes emotional decision-making while systematically building positions at lower prices. This strategy involves investing fixed dollar amounts at regular intervals regardless of market conditions, naturally purchasing more shares when prices fall and fewer when prices rise.
During the 2020 COVID-19 crash, investors employing dollar-cost averaging accumulated 26.2 shares over six months with $600 in capital, compared to just 24 shares purchased via lump-sum investment at the market peak. This resulted in an investment value of $560.16 versus $513 for lump-sum investors—a 9% advantage despite overall market decline.
The Great Recession provided even more dramatic evidence of dollar-cost averaging effectiveness as a Stock Market Crash Survival strategy during prolonged downturns. Investors who maintained monthly $1,000 investments in the S&P 500 from November 2007 through November 2008 experienced losses of $2,928. While substantial, this represented significantly less damage than the $4,017 loss suffered by those who invested $12,000 as a lump sum at the market peak.
The mathematical advantage stems from lower average cost basis—dollar-cost averaging investors continued accumulating shares at progressively lower prices as markets declined, positioning them for stronger recovery when markets eventually rebounded.
Historical analysis reveals dollar-cost averaging outperforms lump-sum investing primarily during periods of high market volatility and sustained downtrends. Vanguard research demonstrates that lump-sum investing produces superior returns approximately two-thirds of the time because markets generally trend upward over long periods. However, during the specific conditions of market crashes and bear markets—precisely when Stock Market Crash Survival strategies matter most—dollar-cost averaging provides both superior returns and psychological benefits that keep investors engaged rather than fleeing to cash.
The emotional advantage of dollar-cost averaging often exceeds its mathematical benefits during market turmoil. Behavioral finance research shows investors frequently make catastrophic decisions during crashes, panic-selling positions at market bottoms and missing subsequent recoveries. Dollar-cost averaging creates a disciplined framework that counters these destructive impulses, keeping investors systematically buying as others sell.
This emotional anchor proves invaluable for Stock Market Crash Survival during extreme volatility when fear reaches peak intensity. Many Americans already employ dollar-cost averaging through 401(k) contributions, automatically diverting portions of each paycheck into retirement accounts regardless of market conditions.
Rotate to Safety: Defensive Sector Strategy for Stock Market Crash Survival
Defensive sector rotation constitutes a critical Stock Market Crash Survival tactic that leverages fundamental differences in how industries perform during economic downturns. Historical data from multiple recessions reveals striking performance disparities—technology stocks decline an average 35% during economic contractions, while consumer staples fall only 8%, healthcare drops 12%, and utilities decline just 10%.
These defensive sectors maintain relative stability because they provide goods and services consumers require regardless of economic conditions, from groceries and medications to electricity and water. Understanding these patterns represents essential knowledge for effective Stock Market Crash Survival planning.
Consumer staples companies like Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, Walmart, and Costco exemplify defensive characteristics that protect portfolios during crashes. These businesses sell products people buy consistently—toilet paper, food, beverages, and household essentials—creating revenue streams far less vulnerable to economic cycles than discretionary spending categories.
The Consumer Staples Select Sector SPDR ETF (XLP) demonstrated this resilience during recent market turmoil, declining just 7% from 52-week highs while broader markets fell 18%. The sector’s 2.6% dividend yield provides additional downside protection and income stability when capital appreciation evaporates, enhancing overall Stock Market Crash Survival outcomes.
Utilities represent another cornerstone defensive sector, providing essential services that maintain consistent demand across economic conditions. Duke Energy, NextEra Energy, Southern Company, and American Water Works exemplify utility investments that combine stable cash flows with attractive dividend yields ranging from 1.76% to 3.80%.
The Utilities Select Sector SPDR ETF (XLU) declined only 11% from recent peaks compared to the S&P 500’s 18% drawdown, while offering a 3.06% dividend yield. Regulated utility monopolies enjoy pricing power and predictable revenue that insulate them from competitive pressures affecting other industries.
These characteristics make utilities essential components of comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival strategies. Healthcare sector positioning offers a third defensive pillar, as medical services, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology maintain demand through recessions. People continue requiring medications, medical procedures, and healthcare services regardless of economic stress, making this sector particularly resilient. During the 2008-2009 financial crisis, healthcare stocks declined just 31% compared to the S&P 500’s 50% plunge.
The sector includes both growth-oriented biotechnology companies developing breakthrough treatments and stable pharmaceutical giants providing consistent dividends. Strategic allocation to these defensive sectors before crashes materialize provides portfolio insurance that softens losses when markets eventually turn. This proactive positioning separates successful Stock Market Crash Survival practitioners from those who react after damage has occurred.
Shield Your Positions: Strategic Use of Stop-Loss Orders in Stock Market Crash Survival
Stop-loss orders provide mechanical protection against catastrophic losses by automatically triggering sales when securities fall to predetermined price levels. These risk management tools remove emotional decision-making during market panics, executing disciplined exit strategies that preserve capital for redeployment when conditions improve.
Research on optimal stop-loss placement suggests setting triggers 8-15% below purchase prices for most stocks, with wider stops for more volatile positions. William O’Neil, founder of Investor’s Business Daily, recommends an 8% stop-loss rule based on extensive historical analysis. This approach limits losses to manageable levels while providing sufficient buffer for normal market volatility, making it valuable for Stock Market Crash Survival planning.
Trailing stop-loss orders offer enhanced protection by automatically adjusting upward as stock prices rise, locking in gains while maintaining downside protection. These dynamic stops follow stock prices higher without requiring manual adjustments, allowing profits to run while automatically protecting against reversals. For example, an investor purchasing stock at $100 might set a 15% trailing stop-loss, initially triggering at $85. If the stock rises to $150, the stop automatically adjusts to $127.50, protecting a substantial portion of the gain while remaining positioned for further upside. During bear markets, trailing stops help investors exit deteriorating positions before losses become severe, supporting overall Stock Market Crash Survival objectives.
Critical implementation considerations determine whether stop-loss strategies enhance or undermine portfolio performance. Never enter stop-loss orders directly with brokers, as intraday volatility or flash crashes may trigger unnecessary executions despite closing prices remaining above stop levels.
Instead, calculate stop-loss levels manually using spreadsheets or employ automatic alert services that notify when stops are breached, allowing informed decisions about execution. Round-number stops attract algorithmic trading that deliberately pushes prices through popular stop levels before reversing. Placing stops at odd numbers—for example, $34.75 rather than $35—reduces vulnerability to this manipulation and improves Stock Market Crash Survival effectiveness.
The limitations of stop-loss strategies during extreme market dislocation require acknowledgment. Circuit breakers and trading halts during severe crashes can prevent stop-loss orders from executing, leaving investors exposed to gap-down openings when trading resumes. Additionally, stop-losses provide execution protection but not price protection—in fast-moving markets, actual sale prices may significantly undershoot stop levels.
These constraints make stop-losses most effective in gradually declining markets rather than sudden crashes. Combining stop-loss discipline with other Stock Market Crash Survival strategies creates more robust protection than relying on any single approach.
Harvest Tax Benefits from Market Pain: Tax-Loss Harvesting for Stock Market Crash Survival
Tax-loss harvesting transforms market losses into valuable tax benefits by strategically selling depreciated positions to offset capital gains and ordinary income. This sophisticated Stock Market Crash Survival technique allows investors to realize losses that reduce current tax burdens while immediately reinvesting proceeds in similar assets to maintain market exposure. When executed properly, tax-loss harvesting can generate tax savings of 15-35% on harvested losses, directly enhancing after-tax returns. Understanding this strategy represents advanced Stock Market Crash Survival knowledge that separates sophisticated investors from novices.
The mechanics of tax-loss harvesting involve selling investments trading below their cost basis and using those realized losses to offset realized capital gains dollar-for-dollar. After offsetting all gains, investors can apply up to $3,000 of additional losses against ordinary income annually. Any remaining losses carry forward indefinitely to offset future gains and income, creating a permanent tax asset.
For example, an investor realizing $30,000 in losses and $25,000 in gains pays zero capital gains taxes, uses $3,000 to reduce ordinary income, and carries forward $2,000 to future tax years. At a 15% long-term capital gains rate and 35% ordinary income rate, this scenario generates $4,800 in total tax savings—demonstrating the powerful financial benefits of incorporating tax-loss harvesting into Stock Market Crash Survival strategies.
Successful tax-loss harvesting requires careful attention to the IRS wash-sale rule, which prohibits claiming losses if substantially identical securities are repurchased within 30 days before or after the sale. To maintain market exposure while harvesting losses, investors can sell one security and immediately purchase a similar but not substantially identical replacement.
For instance, selling the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) at a loss and purchasing the iShares Core S&P Total U.S. Stock Market ETF (ITOT) satisfies wash-sale requirements while maintaining broad equity exposure. After 31 days, investors can swap back to the original holding if desired. This tactical maneuvering enhances Stock Market Crash Survival outcomes without triggering adverse tax consequences.
Optimal tax-loss harvesting occurs throughout the year rather than exclusively in December, as waiting until year-end risks missing opportunities when losses recover before execution. During volatile markets and extended downturns, multiple harvesting opportunities emerge as positions decline to successively lower levels. Investors can harvest losses on the same position multiple times by purchasing alternatives after each sale, progressively lowering their cost basis.
High-income earners benefit most from tax-loss harvesting due to higher marginal tax rates, though the strategy provides value across income levels. Automated tax-loss harvesting services from robo-advisors and wealth management platforms make this Stock Market Crash Survival strategy accessible to investors who lack expertise for manual implementation.
Buy the Rebound: Rebalancing for Faster Stock Market Crash Survival Recovery
Portfolio rebalancing during market crashes forces investors to systematically sell relatively strong assets and purchase temporarily depressed securities, positioning portfolios for enhanced recovery when markets stabilize. This disciplined Stock Market Crash Survival approach counters natural emotional tendencies that lead investors to add to winners and avoid losers, behavior that increases risk during bull markets and delays recovery during bear markets.
Academic research examining rebalancing strategies during major downturns reveals that portfolios rebalanced during crashes recover significantly faster than those left untouched. Understanding rebalancing mechanics represents essential knowledge for effective Stock Market Crash Survival implementation.
The 2008 financial crisis provided dramatic evidence of rebalancing benefits. A 50/50 stock-bond portfolio that underwent no rebalancing suffered a low point value of $82.32 and required substantial time to recover. The same portfolio rebalanced back to 50/50 after a 20% decline reached a low of $78.90—initially worse—but recovered materially faster once markets stabilized.
More aggressive rebalancing to a 60/40 allocation at the 40% decline point produced even stronger long-term results despite temporarily increasing equity exposure during maximum turmoil. These strategies worked because they forced systematic buying of stocks at historically low prices, maximizing eventual recovery gains and demonstrating advanced Stock Market Crash Survival techniques.
Rebalancing mechanics involve comparing current portfolio allocations to target percentages and executing trades to restore desired balances. Many investors rebalance on fixed schedules—quarterly, semi-annually, or annually—reviewing allocations and adjusting as needed. Others employ threshold-based rebalancing, triggering adjustments when allocations drift beyond predetermined bands, typically 5% from targets.
For example, a 60/40 stock-bond portfolio would trigger rebalancing if stocks rose to 65% or fell to 55% of total value. This approach ensures rebalancing occurs when meaningful allocation shifts have occurred rather than on arbitrary calendar dates. Both methods support comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival objectives when executed consistently.
The emotional challenge of rebalancing during crashes cannot be understated. Shifting from bonds that have held value relatively well into stocks that have plunged 30-50% requires psychological fortitude that many investors lack. Seeing portfolio values decline further after rebalancing—as often happens when stocks continue falling—tests investor discipline severely.
Academic research confirms that most investors struggle to execute aggressive rebalancing during maximum market stress. Automated rebalancing through target-date funds, balanced funds, or robo-advisors removes this emotional burden, executing necessary trades without requiring active decision-making when fear peaks. This automation enhances Stock Market Crash Survival prospects for investors who recognize their emotional limitations.
Build Income Streams: Quality Dividend Growth Investing for Stock Market Crash Survival
Quality dividend growth stocks provide critical stability during market crashes by generating consistent income that offsets capital losses and reduces portfolio volatility. During the 2008 financial crisis, S&P 500 stock prices plummeted 57%, yet dividends declined only 21%—demonstrating dramatically higher stability for income versus capital appreciation. Investors focused specifically on dividend growth stocks with 10+ years of consecutive annual increases experienced minimal or no dividend disruption throughout the crisis.
This income stability allows investors to maintain living expenses without selling depreciated positions, providing psychological comfort that prevents panic-driven decisions and supports Stock Market Crash Survival objectives. The mathematical impact of dividend stability extends beyond mere income preservation to encompass total return enhancement during recoveries. Reinvested dividends purchase additional shares at depressed prices during market crashes, accelerating portfolio recovery when prices eventually rebound.
Historical analysis shows dividends contributed 16% of total S&P 500 returns during the growth-focused 1990s but became far more important during the subsequent “lost decade” of 2000-2009. Companies maintaining and increasing dividends through recessions demonstrate financial strength, manageable debt levels, and sustainable business models—characteristics that correlate with superior long-term performance and improved Stock Market Crash Survival outcomes.
Identifying quality dividend growth stocks requires analysis of multiple financial metrics and historical performance. Strong candidates typically feature dividend payout ratios below 60%, leaving ample cash flow for dividend maintenance and growth during economic stress. Debt-to-equity ratios below industry averages indicate financial flexibility to weather downturns without cutting dividends. Ten-year histories of annual dividend increases demonstrate management commitment to shareholder income and business model resilience.
Companies that maintained or increased dividends through previous recessions provide strongest confidence for future crash survival. Sectors with natural defensive characteristics—consumer staples, utilities, healthcare—contain the highest concentration of reliable dividend growers that support Stock Market Crash Survival strategies.
The Dividend Aristocrats—S&P 500 companies with 25+ consecutive years of dividend increases—exemplify these quality characteristics. This elite group includes Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, and Walmart, among others. These companies combine mature business models generating consistent cash flows with moderate growth sufficient to support regular dividend increases.
During 2008’s market carnage, many Dividend Aristocrats not only maintained but actually increased dividends, providing rare positive news in an environment of relentless negative developments. Current dividend yields for these stocks range from 2-4%, providing meaningful income while awaiting market recovery. Incorporating these quality dividend payers represents intelligent Stock Market Crash Survival planning for income-focused investors.
Maintain Firepower: Cash Reserve Strategy for Opportunistic Stock Market Crash Survival
Maintaining substantial cash reserves during bull markets positions investors to capitalize on severely discounted prices when crashes materialize, embodying Warren Buffett’s famous dictum to “be greedy when others are fearful”. Buffett himself demonstrated this principle dramatically during recent years, accumulating a staggering $325 billion cash position throughout 2024 as markets reached all-time highs.
This contrarian stance allowed Buffett to deploy capital aggressively during previous crashes, including his September 2008 investment of $5 billion in Goldman Sachs at the depths of the financial crisis. These opportunistic investments generated enormous returns as markets recovered, validating the strategic value of cash reserves as a Stock Market Crash Survival tool during market euphoria.
Historical patterns reveal market crashes create once-in-a-generation buying opportunities for investors prepared with cash reserves. Following the ten worst trading days in U.S. stock market history between 1989 and 2020, five-year returns averaged over 100%, with some periods generating annual equivalent returns exceeding 15%. The most severe single-day decline—a 9% plunge on October 15, 2008—was followed by a five-year return of 109%, equivalent to 15.9% annually.
Even more remarkably, many of the best market days occur immediately following the worst days, meaning investors who sell during panics often miss dramatic rebounds. Cash-rich investors positioned to buy during maximum fear capture these gains while others flee to safety, demonstrating advanced Stock Market Crash Survival tactics.
The psychology of maintaining cash reserves challenges investors accustomed to remaining fully invested to maximize returns. During bull markets, cash appears to be “dead money” earning minimal returns while stocks soar, creating fear of missing out that drives most investors toward full equity exposure. Buffett’s willingness to hold massive cash positions during market peaks reflects his disciplined focus on valuation rather than short-term relative performance.
This approach recognizes that preserving capital during overvalued markets matters more than capturing the final months of bull market gains. The alternative—remaining fully invested into crashes—forces either riding out severe losses or selling at precisely the wrong time. Maintaining dry powder represents sophisticated Stock Market Crash Survival thinking that separates legendary investors from the crowd.
Optimal cash positioning for opportunistic buying typically ranges from 10-20% of portfolio value during extended bull markets, providing meaningful buying power without sacrificing excessive returns during continued market appreciation. This reserve should reside in high-yield savings accounts, money market funds, or short-term Treasury securities earning modest returns while remaining immediately accessible. As market valuations reach extreme levels—price-to-earnings ratios exceeding historical norms by wide margins—increasing cash to 20-30% provides greater ammunition for eventual crashes.
This disciplined approach requires patience and conviction, qualities that separate successful long-term investors from those who follow the crowd into disasters. Strategic cash management represents the final pillar of comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival preparation.
Learn from History: Case Studies in Stock Market Crash Survival
The 2020 COVID-19 Crash: Speed, Recovery, and Modern Stock Market Crash Survival Dynamics
The Fastest Bear Market in History
The COVID-19 crash of March 2020 offers the most recent and compelling case study in Stock Market Crash Survival, demonstrating both the speed of modern market declines and the power of aggressive policy responses. From February 20 to March 23, 2020, the S&P 500 plummeted 34% in just 33 days, marking the fastest bear market in recorded history. The Dow Jones experienced multiple trading halts due to circuit breakers triggered by 7-10% single-day declines, with March 12 witnessing a stunning 2,352-point drop following the WHO pandemic declaration.
The S&P 500 experienced its largest single-day decline since the 1987 crash, dropping 12% as panic engulfed global markets. Unemployment applications skyrocketed to unprecedented levels, with over three million Americans filing in a single week—ten times historical norms. These conditions tested every principle of Stock Market Crash Survival as investors confronted unprecedented uncertainty.
Unprecedented Policy Response and V-Shaped Recovery
The recovery from the COVID-19 crash proved equally remarkable, validating Stock Market Crash Survival strategies that emphasized staying invested and maintaining perspective. Massive fiscal stimulus including $2.3 trillion in government support combined with Federal Reserve interventions slashing interest rates to near-zero stabilized markets within weeks. By August 2020, the S&P 500 had recovered all losses and established new all-time highs, despite ongoing economic disruption and no available vaccines.
The full year 2020 closed with the S&P 500 up over 16%, rewarding investors who maintained positions through extreme volatility. This six-month nominal recovery period and approximately seven-month real recovery represented the fastest major crash rebound in modern history. The episode demonstrated that effective Stock Market Crash Survival requires faith in long-term market resilience even when short-term conditions appear catastrophic.
Behavioral Lessons: The Cost of Panic Selling
Behavioral analysis of investor responses during the COVID-19 crash reveals the critical importance of emotional discipline in Stock Market Crash Survival. Panic selling peaked in mid-March 2020 as lockdowns expanded and infection rates accelerated, with retail investors liquidating positions at precisely the worst moment.
Those who sold on March 23—the market bottom—missed the subsequent 70% rally over the following year. Research confirms that investors experience the pain of losing money far more intensely than the joy of gaining it, causing them to sell at the worst possible times.
In contrast, investors who maintained positions or employed dollar-cost averaging during the crash captured the full recovery and substantial additional gains. The episode reinforced that emotional decisions during maximum fear consistently undermine long-term wealth accumulation and effective Stock Market Crash Survival.
The 2008 Financial Crisis: Prolonged Pain and Systemic Stock Market Crash Survival Challenges
The Slow-Motion Train Wreck
The 2008 financial crisis provides contrasting lessons about prolonged market declines and the dangers of leverage and concentration in vulnerable sectors. Unlike the COVID-19 crash’s sharp V-shaped recovery, the 2008-2009 crisis featured a gradual 18-month decline from October 2007 peak to March 2009 trough, with multiple false recoveries that trapped optimistic investors.
The S&P 500 ultimately fell 57% peak-to-trough, requiring 5.5 years to recover nominal losses and 6 years for real inflation-adjusted recovery. Investors concentrated in financial stocks suffered catastrophic losses exceeding 70%, with major institutions including Lehman Brothers, Bear Stearns, and Washington Mutual failing entirely or requiring government rescue. This prolonged agony tested Stock Market Crash Survival skills far differently than rapid crashes that recover quickly.
The Critical Role of Diversification in Stock Market Crash Survival
This episode demonstrated the absolute necessity of diversification and the particular danger of leverage during systemic crises. Portfolio diversification proved essential—investors holding 100% stock portfolios required 4.5 years to recover, while those with 60/40 stock-bond allocations recovered in just three years.
Dividend stocks provided critical stability as S&P 500 prices plummeted 57% while dividends declined only 21%. Many quality dividend-paying companies including Procter & Gamble, Johnson & Johnson, and Walmart actually increased dividends throughout the crisis, providing rare positive news amid relentless negative developments. Government bonds served as safe havens, with high-quality bond yields falling from 4.59% to 2.94% as prices soared. These asset classes demonstrated their value in comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival portfolios.
Opportunity for Prepared Investors
The crisis created extraordinary opportunities for investors maintaining cash reserves and emotional discipline. Following the ten worst trading days between 1989 and 2020, five-year returns averaged over 100%. Warren Buffett deployed $5 billion into Goldman Sachs at the September 2008 depths, generating enormous returns as markets recovered. Mutual fund pioneer John Templeton’s Depression-era strategy of buying 104 companies for under $1 per share and selling for $40,000 near World War II’s end demonstrated the wealth-building potential of contrarian investing during maximum fear.
The lesson remains clear—prepared investors with capital and courage profit enormously from crashes while others panic. Opportunistic Stock Market Crash Survival requires both defensive preparation and offensive capability when conditions turn favorable.
The Dot-Com Bubble (2000-2002): Valuation Matters for Stock Market Crash Survival
The Rise and Fall of Irrational Exuberance
The dot-com bubble burst between 2000 and 2002 provides enduring lessons about speculation, valuation, and the dangers of herd behavior. The NASDAQ rose from under 1,000 in 1995 to over 5,000 by March 10, 2000—a 400% gain driven by internet euphoria. Companies with no revenue or profits traded at astronomical valuations as investors believed the internet guaranteed limitless growth. When the bubble burst, the NASDAQ plummeted 78% by October 2002, wiping out over $5 trillion in market value. Hundreds of companies including Pets.com and Webvan folded entirely, while survivors like Microsoft took 17 years to recover their 2000 peaks. This episode revealed that Stock Market Crash Survival requires fundamental analysis rather than momentum chasing.
Technical Warning Signs Investors Ignored
Technical indicators flashed clear warnings before the crash, yet most investors ignored them amid widespread euphoria. Markets showed extreme overbought conditions, with price charts going parabolic—a classic sign of unsustainable gains. Market breadth narrowed dramatically, meaning fewer stocks were driving gains while most lagged. Momentum indicators diverged as stocks kept rising but with progressively less strength. Sector concentration reached extremes with technology dominating indexes, while speculative feedback loops created buying frenzies disconnected from fundamentals. Federal Reserve rate hikes in 2000 ultimately pricked the bubble, triggering the collapse. Investors skilled in Stock Market Crash Survival recognize these warning signs and adjust positioning accordingly.
Survivors and Lessons for Modern Markets
Despite the devastation, quality companies with real business models survived and thrived. Amazon, eBay, Google, and Nvidia emerged stronger, refining strategies and dominating their fields. The infrastructure investments made during the bubble—data centers and fiber-optic networks—later supported cloud computing and mobile internet growth.
Venture capitalist Fred Wilson noted that “nothing important has ever been built without irrational exuberance,” acknowledging that while much capital was lost, the foundation for today’s digital economy was created. For investors, the dot-com bubble reinforced timeless lessons: fundamentals matter, valuation counts, and herd behavior during euphoria leads to devastating losses. Understanding these patterns enhances modern Stock Market Crash Survival capabilities.
The Great Depression (1929): The Ultimate Stock Market Crash Survival Test
The Crash That Changed Everything
The 1929 stock market crash and subsequent Great Depression represent the ultimate test of Stock Market Crash Survival, with recovery taking 25 years for nominal values and 29 years for inflation-adjusted returns. The crash began October 24, 1929—”Black Thursday”—as panicked selling overwhelmed exchanges. By late October, stocks had lost $30 billion in value, equivalent to more than $400 billion today.
The market ultimately fell 89% from peak to trough, with approximately 86,000 businesses failing by the Depression’s end. Buying stocks on margin with as little as 10% down amplified losses catastrophically—a 10% stock decline wiped out entire investments. This remains the most severe Stock Market Crash Survival challenge in American financial history.
Strategies That Worked in the Darkest Times
Despite the devastation, certain strategies enabled survival and even prosperity. Diversification proved essential—government bonds served as safe havens while stocks cratered, with bond returns averaging 6.04% during the 1930s versus catastrophic stock losses. Wall Street tycoons Alfred Loomis and Landon Thorne liquidated all stock holdings in early 1929 and moved into long-term Treasury bonds and cash, continuing to profit while peers faced ruin.
Cash reserves enabled opportunistic buying at Depression lows—John Templeton’s $10,000 investment in 104 companies trading under $1 grew to $40,000 by World War II’s end. These tactics represent timeless Stock Market Crash Survival principles applicable across all market eras.
Companies That Survived Through Adaptation
Some corporations survived by adapting operations to Depression realities. Sears faced millions in losses from home-building loan defaults but pivoted its department store business toward quality staple goods at cheaper prices rather than fashion merchandise. By doubling down on essentials like socks and underwear and maintaining affordable pricing, Sears doubled its store count by the Depression’s end.
The lessons remain relevant—companies providing essential goods and services at value prices survive downturns, while those dependent on discretionary spending face existential threats. For equity investors, selecting companies with these characteristics enhances Stock Market Crash Survival prospects.
The 2010 Flash Crash: Modern Technology and Stock Market Crash Survival Systemic Fragility
When Markets Lost Control
The May 6, 2010 Flash Crash demonstrated how modern technology and algorithmic trading can trigger devastating market disruptions in minutes. At 2:32 PM EDT, the Dow Jones plummeted over 1,000 points—more than 9%—in approximately 36 minutes, wiping out $1 trillion in market value. Individual stocks experienced extraordinary price volatility, with some blue-chip shares temporarily trading for pennies while others reached absurd highs. The VIX volatility index surged 22.5%, while Canadian markets lost over 5% as the crash rippled across North America. This event revealed new Stock Market Crash Survival challenges posed by computerized trading systems.
The Cascade of Algorithmic Selling
SEC and CFTC investigations revealed that a single large mutual fund selling 75,000 E-Mini S&P contracts worth $4.1 billion triggered the cascade. The fund’s algorithm targeted a 9% execution rate based on previous minute’s volume without regard to price or time. This enormous sell order exhausted available buyers, causing high-frequency trading algorithms to aggressively sell, accelerating price declines exponentially. Many high-frequency traders halted operations entirely, removing liquidity precisely when markets needed it most.
Trading pauses for E-Mini contracts eventually allowed stabilization, with markets recovering most losses within hours. Understanding these dynamics helps modern investors implement effective Stock Market Crash Survival strategies.
Lessons About Market Structure and Stop-Loss Risks
The Flash Crash exposed vulnerabilities in modern market structure and highlighted risks of automated trading strategies. Stop-loss orders proved particularly problematic as intraday volatility triggered unnecessary executions despite closing prices recovering. The episode led to new circuit breaker rules and trading protocols designed to prevent similar disruptions.
For individual investors, the Flash Crash reinforced the importance of avoiding market orders during extreme volatility and understanding that stop-loss orders provide execution but not price protection. These lessons inform modern Stock Market Crash Survival best practices for navigating technology-driven market disruptions.
Taking Action: Implementing Your Stock Market Crash Survival Plan
Phase 1: Comprehensive Portfolio Assessment and Risk Analysis for Stock Market Crash Survival
Conduct a Full Financial Inventory
Implementing comprehensive Stock Market Crash Survival strategies requires immediate action across multiple dimensions, beginning with honest portfolio assessment and risk evaluation. Start by documenting all assets including investment accounts, retirement funds, real estate, cash savings, and other holdings to establish a complete financial picture.
Calculate current asset allocation percentages across stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, and alternative investments, comparing these to target allocations appropriate for your time horizon and risk tolerance. Create a detailed spreadsheet listing each investment position, purchase price, current value, percentage of portfolio, and asset class to identify concentration risks. This foundational work represents the first step in developing effective Stock Market Crash Survival capabilities.
Identify Vulnerabilities and Concentration Risks
Analyze your portfolio for dangerous concentration in individual securities, sectors, or geographic regions that could amplify losses during crashes. Examine sector weightings to determine overexposure to cyclical industries like technology, financials, and consumer discretionary that suffer disproportionately during recessions. Review individual position sizes—no single stock should exceed 5-10% of portfolio value to prevent catastrophic losses from company-specific disasters. Assess geographic diversification to ensure adequate international exposure that provides some insulation from U.S.-specific economic problems. Identifying these vulnerabilities enables targeted improvements that strengthen Stock Market Crash Survival readiness.
Perform Portfolio Stress Testing
Conduct formal stress tests to understand how your portfolio would perform under adverse market conditions. Use historical scenario analysis to calculate what losses you would have incurred during the 2008 financial crisis, 2020 COVID crash, or 2000 dot-com collapse with your current allocation. UBS and other firms offer bear market calculators that estimate portfolio values at market troughs and recovery timeframes based on worst historical circumstances.
Consider Monte Carlo simulations that run thousands of randomly generated market scenarios to assess probability of meeting retirement goals across various market conditions. These stress tests reveal whether current allocations can withstand severe downturns without forcing lifestyle changes or premature asset liquidation. Stress testing provides objective data about Stock Market Crash Survival preparedness that guides necessary adjustments.
Phase 2: Building Your Financial Foundation for Stock Market Crash Survival
Calculate and Fund Emergency Reserves
Most importantly, calculate required emergency fund levels based on monthly expenses and ensure adequate cash reserves exist in accessible accounts separate from investment portfolios. Working professionals should target three to six months of living expenses, while retirees require two to four years due to sequence-of-returns risk.
Bankrate’s 2025 research reveals that 27% of Americans have no emergency savings whatsoever, while the median emergency fund stands at just $500—dangerously inadequate for weathering market crashes. Begin systematic monthly transfers into high-yield savings accounts until reaching target emergency fund levels. Emergency reserves represent the absolute foundation of Stock Market Crash Survival that cannot be skipped or shortchanged.
Implement a Tiered Cash Management System
Structure emergency funds using a three-tier approach that balances accessibility with returns. Tier one holds one month’s expenses in high-yield savings accounts or money market accounts providing immediate 24-hour access. Tier two contains two to three months of expenses in money market mutual funds or short-term certificates of deposit accessible within 2-3 business days.
Tier three comprises remaining reserves in Treasury I Bonds or CD ladders with staggered maturities, offering inflation protection and higher yields for funds unlikely to be needed immediately. This structure ensures liquidity for emergencies while generating meaningful returns on cash reserves. Tiered cash management optimizes Stock Market Crash Survival preparedness without sacrificing all investment returns.
Eliminate High-Interest Debt
Before aggressive investing, eliminate high-interest debt that erodes wealth faster than investments can grow. Credit card debt charging 18-25% interest destroys more value than stock market gains create, making debt elimination the highest-return investment for most Americans. Create a systematic debt reduction plan focusing first on highest-interest obligations while maintaining minimum payments on others.
The psychological benefit of debt elimination reduces financial stress and increases ability to maintain investment discipline during market volatility. Debt freedom enhances Stock Market Crash Survival by eliminating forced liquidations to service high-interest obligations.
Phase 3: Strategic Portfolio Repositioning for Enhanced Stock Market Crash Survival
Gradual Reallocation to Target Diversification
For investors currently overexposed to equities or lacking adequate diversification, implement gradual reallocation over 3-6 months to prevent the risk of exiting markets just before rallies while reducing vulnerability to crashes. Establish target allocations for stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments based on age, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Rebalance systematically using new contributions rather than selling existing positions when possible to minimize tax consequences. Focus particularly on adding defensive sector exposure through consumer staples, utilities, and healthcare to reduce portfolio volatility. Gradual repositioning builds Stock Market Crash Survival capabilities without triggering unnecessary tax bills or market timing risks.
Implement Dollar-Cost Averaging for New Investments
Begin dollar-cost averaging additional savings into diversified index funds, defensive sector ETFs, or quality dividend growth stocks rather than attempting to time perfect entry points. Automate monthly contributions to investment accounts to remove emotional decision-making and ensure consistent execution regardless of market conditions.
Historical data confirms dollar-cost averaging outperforms lump-sum investing specifically during high volatility periods and sustained downtrends—precisely the conditions where Stock Market Crash Survival strategies matter most. Many Americans already employ this strategy through 401(k) contributions, automatically diverting portions of each paycheck into retirement accounts. Systematic investing removes emotion and improves Stock Market Crash Survival outcomes.
Establish Defensive Positions Before Crashes Occur
Proactively rotate a portion of the portfolio toward defensive sectors that outperform during recessions. Consumer staples stocks like Procter & Gamble, Walmart, and Coca-Cola decline an average of just 8% during recessions compared to 35% for technology stocks. Utilities including Duke Energy and NextEra Energy fall only 10% while providing 2-4% dividend yields that support total returns.
Healthcare companies maintain demand across economic conditions, declining just 12% on average during downturns. Build positions in these defensive sectors gradually during market strength to avoid chasing performance during crashes. Defensive positioning before crashes materialize represents proactive Stock Market Crash Survival rather than reactive panic selling.
Phase 4: Advanced Tactical Strategies for Stock Market Crash Survival
Configure Stop-Loss Protection Systems
Advanced strategies including tactical sector rotation, stop-loss implementation, and tax-loss harvesting require greater sophistication but provide meaningful benefits for committed investors. Establish watchlists of defensive sector ETFs and quality dividend stocks for rotation during market volatility. Calculate appropriate stop-loss levels for existing positions using the 8-15% rule advocated by William O’Neil and other risk management experts.
Set alerts rather than automatic orders to maintain flexibility during execution and avoid triggering stops during temporary intraday volatility. Stop-loss discipline enhances Stock Market Crash Survival by limiting losses to predetermined levels.
Prepare Tax-Loss Harvesting Opportunities
Identify positions with substantial unrealized losses suitable for tax-loss harvesting during market downturns. Research alternative investments that satisfy wash-sale rules while maintaining desired exposures—for example, swapping Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF for iShares Core S&P Total U.S. Stock Market ETF provides nearly identical exposure while avoiding wash-sale disqualification.
Document cost basis for all positions to enable rapid execution when tax-loss harvesting opportunities emerge. High-income earners benefit most from tax-loss harvesting due to higher marginal tax rates, though the strategy provides value across income levels. Tax-loss harvesting turns Stock Market Crash Survival losses into valuable tax assets.
Build Quality Dividend Growth Positions
Establish positions in quality dividend growth stocks with 10+ year histories of annual increases, demonstrating financial strength and management commitment to shareholder income. Focus on Dividend Aristocrats—S&P 500 companies with 25+ consecutive years of dividend increases—including Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, and Walmart.
These companies combine mature business models generating consistent cash flows with moderate growth sufficient to support regular dividend increases. Target payout ratios below 60% and debt-to-equity ratios below industry averages to ensure dividend sustainability during recessions. Quality dividend stocks enhance Stock Market Crash Survival through income stability and reduced volatility.
Phase 5: Psychological Preparation and Emotional Defense for Stock Market Crash Survival
Document Your Investment Policy Statement
The psychological dimension of Stock Market Crash Survival often determines success or failure regardless of technical preparation. Document current investment strategy, time horizon, and reasons for position selection in a written investment policy statement to reference during emotional market periods. Include specific circumstances under which portfolio changes are permitted and minimum waiting periods before executing emotionally-driven decisions.
Research confirms that investors with documented plans significantly outperform those without formal strategies. Written investment policies strengthen Stock Market Crash Survival by providing rational anchors during irrational markets.
Educate Yourself on Market History and Recovery Patterns
Review historical crash recovery data regularly to maintain perspective that downturns prove temporary while long-term market trends favor patient investors. Study the 2020 COVID crash’s six-month recovery, 2008 crisis’s 5.5-year recovery, and Great Depression’s 25-year recovery to understand the range of possible outcomes. Recognize that following the ten worst trading days between 1989 and 2020, five-year returns averaged over 100%—rewarding investors who maintained discipline during maximum fear.
Understanding that the best market days often immediately follow the worst days prevents panic selling that locks in losses and misses recoveries. Historical knowledge builds confidence essential for Stock Market Crash Survival.
Implement the 72-Hour Rule
Most critically, commit to avoiding panic decisions by instituting a mandatory 72-hour waiting period before executing any portfolio changes during market crises. Research on panic selling reveals that overconfident investors are paradoxically more likely to engage in panic selling during downturns, even when financial literacy should prevent such behavior.
Male investors demonstrate greater susceptibility to panic selling than females, while those with university degrees show less vulnerability. Age correlates negatively with panic selling—older investors make fewer emotional mistakes than younger counterparts. The 72-hour rule prevents catastrophic emotional decisions that destroy wealth during temporary market dislocations and supports effective Stock Market Crash Survival.
Consider Professional Advisory Support
Consider working with fee-only financial advisors who provide objective guidance and help maintain discipline when fear peaks. Professional advisors offer accountability that prevents panic decisions, running Monte Carlo simulations and stress tests that quantify the impact of staying invested versus selling. Their experience navigating previous crashes provides valuable perspective during current turmoil when emotions overwhelm rational thinking.
Fee-only compensation structures align advisor interests with client outcomes, unlike commission-based advisors who profit from excessive trading. Professional guidance enhances Stock Market Crash Survival for investors who recognize they need external discipline during extreme market stress.
Phase 6: Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment for Sustained Stock Market Crash Survival
Establish Regular Review Schedules
Portfolio management requires ongoing attention rather than one-time setup. Schedule quarterly reviews to assess allocation drift, rebalancing needs, and changing circumstances. Annual comprehensive reviews should examine goal progress, risk tolerance changes, tax-loss harvesting opportunities, and whether emergency funds remain adequate. Major life events including marriage, divorce, children, job changes, or retirement require immediate plan adjustments regardless of review schedules. Regular monitoring maintains Stock Market Crash Survival readiness as circumstances evolve.
Maintain Disciplined Rebalancing
Execute rebalancing when allocations drift 5% or more from targets, or on predetermined quarterly or semi-annual schedules. This disciplined approach forces selling assets that have appreciated and buying those that have declined—systematically implementing “buy low, sell high” that most investors fail to execute. During market crashes, rebalancing requires shifting from bonds that have held value relatively well into stocks that have plunged 30-50%—psychologically difficult but mathematically optimal for long-term returns.
Automated rebalancing through target-date funds, balanced funds, or robo-advisors removes this emotional burden, executing necessary trades without requiring active decision-making when fear peaks. Consistent rebalancing represents essential Stock Market Crash Survival discipline.
Continuously Refine Your Crash Survival Strategy
Warren Buffett’s wisdom echoes across decades of market cycles: “Be fearful when others are greedy, and be greedy when others are fearful”. This contrarian approach separates successful long-term investors from those who follow the crowd into disasters. Stock Market Crash Survival requires preparation before crashes occur, discipline during maximum turmoil, and opportunism when others despair. The strategies outlined in this guide—diversification, emergency reserves, dollar-cost averaging, defensive positioning, stop-losses, tax-loss harvesting, rebalancing, dividend focus, and cash reserves—provide a comprehensive framework for navigating inevitable future market crashes.
History demonstrates that well-prepared investors not only survive crashes but emerge stronger, wealthier, and better positioned for long-term prosperity than those who panic when markets decline. Continuous improvement of Stock Market Crash Survival capabilities ensures readiness for whatever market challenges lie ahead.
Conclusion
The path to Stock Market Crash Survival begins long before markets enter freefall, requiring disciplined preparation, strategic positioning, and unwavering commitment to proven principles that separate successful investors from those who suffer catastrophic losses. The nine critical strategies examined throughout this comprehensive guide—portfolio diversification, emergency fund establishment, dollar-cost averaging, defensive sector rotation, stop-loss protection, tax-loss harvesting, systematic rebalancing, quality dividend investing, and cash reserve maintenance—provide a battle-tested framework for navigating inevitable market turbulence.
Historical evidence spanning nearly a century of market crashes demonstrates that investors implementing these Stock Market Crash Survival tactics not only preserve capital during downturns but position themselves to capture disproportionate gains during subsequent recoveries. The 2020 COVID crash’s six-month recovery rewarded disciplined investors with 70% gains while panic sellers locked in devastating losses, reinforcing timeless lessons about emotional control and strategic preparation.
Understanding that Stock Market Crash Survival demands both defensive protection and opportunistic aggression represents a critical mindset shift for most investors conditioned to fear volatility rather than exploit it. Warren Buffett’s $325 billion cash position accumulated throughout 2024’s market euphoria exemplifies the patience required to maintain firepower when valuations reach extremes, positioning Berkshire Hathaway to deploy capital aggressively when inevitable corrections materialize. The mathematical reality remains undeniable—following the ten worst trading days between 1989 and 2020, five-year returns averaged over 100%, with some periods generating annual equivalent returns exceeding 15%.
Yet most investors flee to safety precisely when maximum opportunities emerge, victims of emotional responses that override rational analysis. Implementing the 72-hour rule before executing any portfolio changes during market panics provides essential protection against these destructive impulses that permanently impair long-term wealth accumulation and effective Stock Market Crash Survival.
The technical execution of Stock Market Crash Survival strategies requires systematic implementation across multiple dimensions, beginning with comprehensive portfolio assessment and continuing through ongoing monitoring and tactical adjustments. Stress testing current allocations against historical crash scenarios reveals vulnerabilities that demand immediate attention, while emergency fund adequacy determines whether market downturns force catastrophic selling or enable opportunistic buying.
Research confirms that investors without emergency reserves who face forced liquidation see portfolio values remain 15% below starting levels three years after crashes, while those with adequate cash reserves maintaining positions recover to 110% of initial values. The difference between financial devastation and sustained prosperity often hinges on these foundational preparations completed before market stress materializes. Mastering Stock Market Crash Survival technical elements provides competitive advantages that compound over multiple market cycles.
The ultimate measure of Stock Market Crash Survival success extends beyond mere capital preservation to encompass psychological resilience, strategic opportunism, and long-term wealth compounding that transforms temporary market dislocations into permanent financial advantages. History teaches that every major crash—from the Great Depression’s 89% decline requiring 25 years for recovery to the COVID crash’s 34% plunge recovering in six months—eventually gives way to new bull markets that reward patient, disciplined investors while punishing those who abandoned ship during maximum turbulence.
The strategies, case studies, and action plans detailed throughout this guide provide comprehensive preparation for navigating the next inevitable market crash with confidence rather than fear, discipline rather than panic, and opportunism rather than paralysis. Commit today to implementing these Stock Market Crash Survival principles, building the financial fortress and psychological resilience that separate those who merely survive market crashes from those who emerge stronger, wealthier, and better positioned for long-term prosperity through consistent application of proven Stock Market Crash Survival strategies.
Citations
- https://www.lynalden.com/stock-market-crash-bear-market/
- https://goldsilver.com/industry-news/article/heres-how-long-it-really-takes-to-recover-from-stock-market-crashes/
- https://www.investopedia.com/timeline-of-stock-market-crashes-5217820
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/5-tips-weathering-recession
- https://www.bankrate.com/banking/savings/emergency-savings-report/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2025/09/15/american-emergency-funds-shrinking.html
- https://www.empower.com/the-currency/money/safety-net-emergency-savings-research
- https://www.farther.com/resources/foundations/how-to-protect-401-k-from-stock-market-crash
- https://blog.en.erste-am.com/five-years-since-covid-hit-a-historic-crash-and-the-lessons-learned/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/lizfrazierpeck/2021/02/11/the-coronavirus-crash-of-2020-and-the-investing-lesson-it-taught-us/
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/financial-advisors/100615/how-protect-your-portfolio-market-crash.asp
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/warren-buffett-prepares-market-crashes-140107829.html
- https://www.edelmanfinancialengines.com/education/investment-management/how-to-rebalance-a-portfolio/
- https://www.bankrate.com/investing/warren-buffett-tips-for-bear-market/
- https://www.aarp.org/money/retirement/1929-stock-market-crash-takeaways/
- https://www.avatrade.com/blog/trading-history/the-flash-crash-of-2010
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2010_flash_crash
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/warren-buffett-says-invest-market-144332988.html
- https://www.cnbc.com/2025/04/22/warren-buffetts-simple-rule-to-build-wealth-when-the-market-falls.html
- https://www.pimco.com/us/en/resources/education/recessions-what-investors-need-to-know
- https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/investing/what-to-invest-in-during-recession
- https://scrab.com/blog/master-navigating-a-stock-market-crash-a-step-by-step-survival-guide-for-investors
- https://money.usnews.com/financial-advisors/articles/best-investments-during-a-recession
- https://bullishbears.com/what-are-defensive-stocks/
- https://www.entrepreneur.com/finance/2-defensive-sectors-to-protect-your-portfolio-during-a/489640
- https://www.pittsburgh.equitableadvisors.com/resource-center/investment/rebalancing-your-portfolio
- https://whzwealth.com/blog/leveraging-your-emergency-fund-to-help-fuel-your-goals-tips-for-2025
- https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2025/05/18/how-much-emergency-savings-for-recession/83643820007/
- https://www.premieramerica.com/learn/education/blog/january-2025/how-to-build-an-emergency-fund-in-2025
- https://www.thrivent.com/insights/budgeting-saving/best-places-to-keep-your-emergency-fund-in-2025
- https://www.investors.com/etfs-and-funds/personal-finance/stock-market-crash-how-retirees-can-endure/
- https://www.troweprice.com/financial-intermediary/us/en/insights/articles/2024/q3/how-to-help-protect-your-investment-portfolio-during-stock-market-volatility.html
- https://smartasset.com/financial-advisor/dollar-cost-averaging-how-it-works-and-when-it-pays-off-2020
- https://www.americancentury.com/insights/dollar-cost-averaging/
- https://www.fidelity.com/learning-center/personal-finance/bear-market-investing
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/dollarcostaveraging.asp
- https://marketinsights.citi.com/Financial-Education/Investing/Systematic-Investing-and-Dollar-Cost-Averaging.html
- https://www.theentrustgroup.com/blog/should-you-invest-during-recession
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/042115/whats-best-investing-strategy-have-during-recession.asp
- https://www.morningstar.com/stocks/best-consumer-defensive-stocks-buy
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/trading/09/buy-stop-sell-stop-limit.asp
- https://www.personalfinancelab.com/beginners/strategies-for-beginners/stock-exit-strategies/
- https://www.quant-investing.com/blog/market-crash-how-to-protect-your-portfolio
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/stocks/09/use-stop-loss.asp
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/help-protect-your-position-using-stop-orders
- https://stoplosstracker.com/using-trailing-stops-in-a-bear-market/
- https://www.bdo.com/getmedia/350a52a5-cc00-493b-9f8c-2c99641fdc8c/BDOWA_Tax-Losses-How-a-Market-Downturn-Can-Work-for-You_Insert.pdf?ext=.pdf
- https://investor.vanguard.com/investor-resources-education/taxes/offset-gains-loss-harvesting
- https://www.blackrock.com/us/financial-professionals/investments/products/managed-accounts/tax-loss-harvesting
- https://www.jhinvestments.com/viewpoints/investing-basics/Tax-loss-harvesting-in-bear-and-bull-markets
- https://www.reddit.com/r/investing/comments/1catmoi/when_to_tax_loss_harvest_when_markets_keep_going/
- https://www.ssga.com/us/en/intermediary/insights/tax-loss-harvesting-in-down-markets
- https://www.financialplanningassociation.org/sites/default/files/2020-05/8%20Analyzing%20the%20Effects%20of%20Aggressive%20Rebalancing%20During%20Bear%20Markets.pdf
- https://www.troweprice.com/personal-investing/resources/insights/whats-the-best-approach-for-portfolio-rebalancing.html
- https://seekingalpha.com/article/4826469-how-to-survive-a-30-percent-market-crash-in-retirement
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/why-2-recession-proof-dividend-081500365.html
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/markets/071616/history-sp-500-dividend-yield.asp
- https://www.true-shares.com/a-lost-decade/
- https://www.hartfordfunds.com/insights/market-perspectives/equity/the-power-of-dividends.html
- https://www.proshares.com/browse-all-insights/insights/why-dividend-growth-is-a-timeless-strategy
- https://www.simplysafedividends.com/world-of-dividends/posts/939-20-best-recession-proof-dividend-stocks-for-a-2025-downturn
- https://www.reddit.com/r/dividends/comments/1ggepnz/what_happened_to_dividend_stocks_in_2008/
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/p-500s-dividend-yield-lowest-103200861.html
- https://www.reddit.com/r/DigitalbanksPh/comments/1jsty4q/warren_buffetts_guide_to_surviving_market_drops/
- https://www.schroders.com/en-us/us/wealth-management/insights/coronavirus-how-stock-markets-perform-after-heavy-falls/
- https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/warren-buffett-says-investors-could-be-playing-fire-heres-best-way-protect-your-portfolio
- https://www.ithinkfi.org/blog/blog-detail/ithink-blog/2025/10/01/understanding-emergency-funds—savings-accounts-in-2025
- https://www.pvamu.edu/blog/opinion-the-u-s-stock-market-crash-of-march-2020-lessons-from-economic-history/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2020_stock_market_crash
- https://adrofx.com/blog/psychology-panic-selling-understanding-its-triggers-and-effects
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/panic-selling-understanding-emotional-trap-how-avoid-iux-official-uxvkf
- https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/great-recession-and-its-aftermath
- https://www.reddit.com/r/stocks/comments/w3vy4e/how_long_it_took_from_the_2000_and_2008_crash/
- https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/stock-market-crash-of-1929
- https://www.marketplace.org/story/2008/09/30/investing-during-great-depression
- https://traderlion.com/tl-studies/dot-com-bubble/
- https://www.trustnet.com/investing/13455812/the-dot-com-bubble-lessons-from-tech-euphoria
- https://www.businessinsider.com/tech-bubble-nasdaq-correction-ai-2000-dot-com-bubble-crash-2025-3
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/dotcom-bubble.asp
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot-com_bubble
- https://www.nutmeg.com/insights/25-years-since-the-dot-com-bubble-burst
- https://www.law.georgetown.edu/denny-center/blog/undeterred-through-depression/
- https://www.skilledsurvival.com/surviving-the-great-depression/
- https://www.cftc.gov/sites/default/files/idc/groups/public/@economicanalysis/documents/file/oce_flashcrash0314.pdf
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/equities/2010-flash-crash/
- https://www.henricodolfing.com/2019/06/project-failure-case-study-knight-capital.html
- https://www.ruleoneinvesting.com/blog/how-to-invest/investment-planning
- https://moneysmart.gov.au/how-to-invest/develop-an-investing-plan
- https://checklist.com/investment-checklist
- https://www.investor.gov/introduction-investing/general-resources/investor-preparedness-checklist
- https://www.template.net/business/checklist-templates/investment-checklist/
- https://www.phoenixstrategy.group/blog/5-scenarios-to-stress-test-portfolio-volatility
- https://www.hawkinsash.cpa/stress-testing-your-investment-portfolio/
- https://www.ubs.com/global/en/wealthmanagement/insights/2024/bear-market-guidebook.html
- https://www.morningstar.com/business/insights/blog/portfolio-construction/portfolio-stress-testing
- https://wealthtender.com/insights/investing/investment-portfolio-stress-test/
- https://acmwealth.com/article-video/stress-testing-your-portfolio/
- https://fortune.com/2025/09/17/emergency-savings-boomer-genz-debt-unemployment-inflation/
- https://www.grimesco.com/emergency-funds-made-easy-how-to-build-your-financial-safety-net/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/investing/comments/1o5tc58/how_can_we_prepare_for_a_1929_market_crash_real/
- https://www.schwab.com/learn/story/portfolio-management-checklist
- https://www.reddit.com/r/StockMarket/comments/1g78whw/using_a_stoploss_to_protect_against_unexpected/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11927890/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11428550/



